Central Min
Appearance
| Central Min | |
|---|---|
| 闽中语 | |
| Min Zhong | |
| Native to | Southern China, United States (mainly California) |
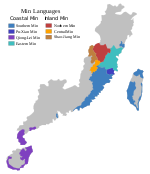
| Region | Yong'an, Sanming |
Native speakers | 700,000 (2004)[1] |
Sino-Tibetan
| |
Early forms | |
| Dialects | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | czo |
| Glottolog | minz1235 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-hb |
 Central Min | |
Central Min, or Min Zhong (simplified Chinese: 闽中语; traditional Chinese: 閩中語; pinyin: Mǐnzhōngyǔ), is a part of the Min group of varieties of Chinese. It is spoken in the valley of the Sha River in Sanming prefecture in the central mountain areas of Fujian, consisting of Yong'an, the urban area of Sanming (Sanyuan and Meilie districts) and Sha County.[5]
Dialects
Notes
References
- ^ Language Atlas of China (2nd ed.), City University of Hong Kong, 2012, p. 178, ISBN 978-7-10-007054-6.
- ^ Mei, Tsu-lin (1970), "Tones and prosody in Middle Chinese and the origin of the rising tone", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, 30: 86–110, doi:10.2307/2718766, JSTOR 2718766
- ^ Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1984), Middle Chinese: A study in Historical Phonology, Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, p. 3, ISBN 978-0-7748-0192-8
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2023-07-10). "Glottolog 4.8 - Min". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Archived from the original on 2023-10-13. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ^ Wurm, Stephen Adolphe; Li, Rong; Baumann, Theo; Lee, Mei W. (1987). Language Atlas of China. Longman. p. B-12. ISBN 978-962-359-085-3.
- Norman, Jerry (1974), "The initials of Proto-Min", Journal of Chinese Linguistics, 2 (1): 27–36, JSTOR 23749809. (includes a description of the phonology of the Yong'an dialect)