Lingaraja Temple
| Lingaraja Temple | |
|---|---|
 Shri Lingaraja Temple | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Hinduism |
| District | Khurda |
| Deity | Shiva As Lingaraja Parvati (consort) |
| Festivals | Shivaratri, Ashokastami |
| Location | |
| Location | Ekamra Kshetra, Old Town, Bhubaneshwar |
| State | Odisha |
| Country | India |
| Geographic coordinates | 20°14′18″N 85°50′01″E / 20.23833°N 85.83361°E |
| Architecture | |
| Type | Kalinga Architecture |
| Creator | Jajati Keshari[1] |
| Completed | 11th century CE |
| Part of a series on |
| Shaivism |
|---|
 |
|
|
Lingaraja Temple (Odia: [liŋɡɔraːd͡ʒɔ] ) is a Hindu temple dedicated to Shiva and is one of the oldest temples in Bhubaneswar, the capital of the Indian state of Odisha, India. The temple is the most prominent landmark of Bhubaneswar city and one of the major tourist attractions of the state.[2][3][4]
The Lingaraja temple is the largest temple in Bhubaneswar. The central tower of the temple is 180 ft (55 m) tall. The temple represents the quintessence of the Kalinga architecture and culminating the medieval stages of the architectural tradition at Bhubaneswar.[5] The temple is believed to be built by the kings from the Somavamsi dynasty, with later additions from the Ganga rulers. The temple is built in the Deula style that has four components namely, vimana (structure containing the sanctum), jagamohana (assembly hall), natamandira (festival hall) and bhoga-mandapa (hall of offerings), each increasing in the height to its predecessor. The temple complex has 108 other shrines and is enclosed by a large compound wall.
Bhubaneswar is called the Ekamra Kshetra as the deity of Lingaraja was originally under a mango tree (Ekamra) as noted in Ekamra Purana, a 13th-century Sanskrit treatise. The temple is active in worship practises, unlike most other temples in Bhubaneswar. The temple has images of Vishnu, possibly because of the rising prominence of Jagannath sect emanating from the Ganga rulers who built the Jagannath Temple in Puri in the 12th century. The central deity of the temple, Lingaraja, is worshipped as Shiva.
Lingaraja temple is maintained by the Temple Trust Board and the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). The temple has an average of 6,000 visitors per day and receives hundreds of thousands of visitors during festivals. Shivaratri festival is the major festival celebrated in the temple and event during 2012 witnessed 200,000 visitors. The temple compound is not open to non-Hindus, but there is a viewing platform beside the wall offering a good view of the main exteriors. This was originally erected for a visit by Lord Curzon when Viceroy.
History


The temple in its present form dates back to the last decade of the eleventh century. There is evidence that part of the temple was built during the sixth century CE as mentioned in some of the seventh century Sanskrit texts.[6] Fergusson believes that the temple might have been initiated by Lalat Indu Keshari who reigned from 615 to 657 CE. The Assembly hall (jagamohana), sanctum and temple tower were built during the eleventh century, while the Hall of offering (bhoga-mandapa) was built during the twelfth century. The natamandira was built by the wife of Salini between 1099 and 1104 CE.[7] By the time the Lingaraja temple was completely constructed, the Jagannath (form of Vishnu) sect had been growing in the region, which historians believe, is evidenced by the co-existence of Vishnu and Shiva worship at the temple. The kings of Ganga dynasty were ardent followers of Vaishnavism, [shaivism] and [shaktism] and built the Jagannath Temple at Puri in the 12th century.[1]
As per some accounts, the temple is believed to have been built by the Somavanshi king Yayati I (1025-1040), during the 11th century CE.[1] Jajati Keshari shifted his capital from Jajpur to Bhubaneswar which was referred to as Ekamra Kshetra in the Brahma Purana, an ancient scripture. One of the Somavamsi queens donated a village to the temple and the Brahmins attached to the temple received generous grants.[8] An inscription from the Saka year 1094 (1172 CE) indicates gifts of gold coins to the temple by Rajaraja II.[9] Another inscription of Narasimha I from the 11th century indicates offer of beetel leaves as tambula to the presiding deity.[10] Other stone inscriptions in the temple indicate royal grants from Chodaganga to the nearby village people.[11]
K.C. Panigrahi mentions that Yayti I had no time to build the temple and it should have been initiated by his sons Ananta Kesari and Udyota Kesari (believed to be other names of Yayati II as well). The argument provided against the view is that is his weak successors could not have constructed such a magnificent structure.[12]
Architecture
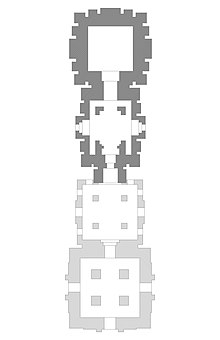

The Lingaraja temple is the largest temple in Bhubaneswar. James Fergusson (1808–86), a noted critic and historian rated the temple as "one of the finest examples of purely Hindu temple in India".[2] It is enshrined within a spacious compound wall of laterite measuring 520 ft (160 m) by 465 ft (142 m). The wall is 7.5 ft (2.3 m) thick and surmounted by a plain slant coping. Alongside the inner face of the boundary wall, there is a terrace to protect the compound wall against outside aggression.[5] The tower is 45.11 m (148.0 ft) high and the complex has 150 smaller shrines in its spacious courtyard. Each inch of the 55 m (180 ft) tall tower is sculpted.[2][12] The door in the gate of the entrance porch is made of sandalwood.[13]
The Lingaraja temple faces east and is built of sandstone and laterite. The main entrance is located in the east, while there are small entrances in the north and south. The temple is built in the Deula style that has four components namely, vimana (structure containing the sanctum), jagamohana (assembly hall), natamandira (festival hall) and bhoga-mandapa (hall of offerings), with all four in axial alignment with descending height.[12][14] The dance hall was associated with the raising prominence of the devadasi system that existed during the time.[6] The various units from the Hall of offering to the tower of the sanctum increase in height.
The bhogamandapa (Hall of offering) measures 42 ft (13 m) × 42 ft (13 m) from the inside, 56.25 ft (17.15 m) × 56.25 ft (17.15 m) from the outside and has four doors in each of the sides. The exterior walls of the hall has decorative sculptures of men and beast. The hall has a pyramidal roof made of up several horizontal layers arranged in sets of two with intervening platform. It bears an inverted bell and a kalasa in the top.[14][15][16] The natamandira (festival hall) measures 38 ft (12 m) × 38 ft (12 m) from the inside, 50 ft (15 m) × 50 ft (15 m) from the outside, has one main entrance and two side entrances. The side walls of the hall has decorative sculptures displaying women and couples. It has a flat roof sloping in stages. There are thick pylons inside the hall.[14][15][17]
The jagamohana (assembly hall) measures 35 ft (11 m) × 30 ft (9.1 m) from the inside, 55 ft (17 m) × 50 ft (15 m) from the outside, entrances from south and north and has a 30 metres (98 ft) tall roof. The hall has a pyramidal roof made of up several horizontal layers arranged in sets of two with intervening platform as in the Hall of offering. The facade to the entrances are decorated with perforated windows with lion sitting on hind legs. The inverted bell above second unit is adorned by kalasa and lions.[14][15] The rekha deula has a 60 m (200 ft) tall pyramidal tower over the sanctum and measures 22 ft (6.7 m) × 22 ft (6.7 m) from the inside, 52 ft (16 m) × 52 ft (16 m) from the outside over the sanctum. It is covered with decorative design and seated lion projecting from the walls. The sanctum is square in shape from the inside. The tower walls are sculpted with female figures in different poses.[14][15]
The temple has a vast courtyard mired with hundreds of small shrines.[12]
Religious significance

Bhubaneswar is called the Ekamra Kshetra as the deity of Lingaraja was originally under a mango tree (Ekamra). Ekamra Purana, a Sanskrit treatise of the 13th century mentions that the presiding deity was not seen as lingam (an aniconic form of Shiva) during the Satya and Treta yugas and only during the Dvapara and Kali yugas, it emerged as a lingam. The lingam in the temple is a natural unshaped stone that rests on a Sakti. Such a lingam is called Krutibasa or Swayambhu and is found in 64 places in different parts of India. With the advent of the Ganga dynasty in the early 12th century, during the period.[18]
It is attributed the raising prominence of Jagannath sect that became predominant during the construction of the temple. The Gangas remodelled the temple and introduced certain Vaishnavite elements like images of Vaishnava Dwarapalas namely Jaya and Prachanda, The flag of the temple was fixed to a Pinaka bow instead of trident usually found In Shiva temples[6][18]
Festivals and worship
As per Hindu legend, an underground river originating from the Lingaraja temple fills the Bindusagar Tank (meaning ocean drop) and the water is believed to heal physical and spiritual illness. The water from the tank is thus treated sacred and pilgrims take a holy dip during festive occasions.[16][19] The central deity of the temple, Lingaraja, is worshipped as Shiva.[6]

Shivaratri is the main festival celebrated annually in Phalgun month when thousands of devotees visit the temple.[20] Apart from a full day of fasting, bel leaves are offered to Lingaraja on this auspicious day. The main celebrations take place at night when devotees pray all night long. The devout usually break their fast after the Mahadipa (a huge lamp) is lit on the spire of the temple. This festival commemorates Lingaraja having slain a demon. Thousands of bol bom pilgrims carry water from river Mahanadi and walk all the way to the temple during the month of Shravana every year.[21] Sunian day is observed from royal times in the month of Bhandra, a day when temple servants, peasants and other holders of temple lands offer loyalty and tribute to Lingaraja.[22] Chandan Yatra (Sandalwood ceremony) is a 22-day festival celebrated in the temple when servants of the temple disport themselves in a specially made barge in Bindusagar tank. The deities and servants of the temples are anointed with sandalwood paste to protect from heat. Dances, communal feasts, and merrymaking are arranged by the people associated with the temple.[23]
Every year the chariot festival (Ratha-Yatra) of Lingaraja is celebrated on Ashokashtami. The deity is taken in a chariot to Rameshwar Deula temple. Thousands of devotees follow and pull brightly decorated chariots containing the idols of Lingaraj, Durga And Dolagovind. Maa Parvati visits Rameswar deula on Dasami but Lord Lingaraj refused her to stay there therefore Maa Parvati gets angry. After returning to temple promises Maa Parvati to take her during boat festival for 21 days. During GuruPanchami night Baba Lingaraj marries Maa Parvati in Kedar Gouri temple.Then in Sitalsasthi night returns to the temple with a grand procession.[24] The Lingaraja temple is active in worship practises, unlike the other ancient temples of Bhubaneshwar which are not active worship centres. Non Hindus are not allowed inside the temple, but it can be viewed from the viewing platform located outside the temple. The viewing platform and the back of the temple can be reached via a laneway located to the right of the main entrance of the temple.[2][6][16] Sanctity of the temple is maintained by disallowing dogs, unbathed visitors, menstruating women and families that encountered birth or death in the preceding 12 days.[25] In case of a foreign trespass, the temple follows a purification ritual and dumping of prasad (food offering) in a well.[26][27]
Staff and administration
King Jajati Keshari, believed to be the founder of the Lingaraja temple, deputed Brahmins who had migrated to south India as temple priests over the local Brahmins on account of their increased knowledge of Shaivism, due to increasing invasions from Muslim invaders. The focus was to enhance the temple practises from tribal rites to Sanskritic. While the exact number of castes involved in the nijogas (practises) is not known, Brahmins, tribal worshippers and inmates from Untouchable castes are believed to be part of the setup. Bose (1958) identified 41 services with the involvement of 22 separate castes and Mahaptra (1978) identified 30 services. It is understood from the records that kings and temple managers of different times introduced or discontinued certain services, fairs, offerings, and caste-centred core services during their regime.[22] As of 2012, the temple practised 36 different services (nijogas).[28]
In modern times, the Lingaraja temple priests are from three communities, namely Pujapanda Nijog, Brahman Nijog and Badu Nijog.[29] The Badu are non-Brahmin servant groups, whose origin is not ascertained due to unavailability of authentic records, while they are described as Vadu in chapter 62 of the Ekamrapurana. The caste group of Badu is called Niyoga, which elects the officers every year during the Sandalwood festival. Every Badu undergoes three distinct rites, namely, ear-piercing, marriage, and god-touching. Historically, the Badus performed five different temple duties - Paliabadu and Pharaka, which were considered important and Pochha, Pahada and Khataseja, which were considered inferior. From 1962, only Paliabadu and Pharaka practises are followed and the others are discontinued. The Badus also carry out ablution and dressing of the images of Siddhaganesh and Gopalini.[23] The temple is maintained by the Temple Trust Board and the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). The temple is guarded by security personnel deputed by the Police Commissioner of Bhubaneswar and security guards appointed by the temple administration.[26][27] The temple has an average of 6,000 visitors every day and receives lakhs of visitors during festivals.[3] The Shivaratri festival during 2012 witnessed 200,000 visitors.[30] As of 2011, the annual income of Lingaraja temple from hundis (donation boxes) is around ₹1.2 million per annum. Another ₹4 million is collected annually from other sources like rents from shops, cycle stands and agriculture lands. Starting 2011, the temple charges an amount for six types of religious worship (special pujas) carried out by the devotees.[31]
Gallery
-
A sculpted griffin or "udagajasingha" on the main temple spire.
-
Image of Bindusagar pond with Lingaraja temple in the background.
-
Varieties of Marigold for offering to Lingaraja during Shivaratri at Bhubaneswar.
-
Birds eye view of Lingaraj Temple during Deepa Dana February 2020.
-
Lingaraj Temple complex at dusk during Shivratri 2020.
-
Birds eye view of Bindu Sagar and Lingaraj Temple in MahaShibaratri, 2023
Notes
- ^ a b c Singh, Upinder (2008). A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th Century. New Delhi: Pearson Education India. p. 622. ISBN 978-813-17-1120-0.
- ^ a b c d "Bhubaneswar tourist attractions". Bhubaneswar Municipal Corporation. Archived from the original on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 12 September 2006.
- ^ a b "Cracks in Lingaraj on ASI team radar temple". The Times of India. 30 December 2012. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ Gopal, Madan (1990). K.S. Gautam (ed.). India through the ages. Publication Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India. p. 175.
- ^ a b Mohapatra, Ramesh Prasad (1986). Archaeology in Orissa. Vol. I. Delhi: B. R. Publishers. p. 69. ISBN 81-7018-346-4.
- ^ a b c d e "Bhubaneswar Lingaraj Temple". Tourism Development Corporation of Odisha. Archived from the original on 6 February 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2015.
- ^ Fergusson, James (1876). History of Indian and Eastern architecture, Volume 3. London: Harvard University. pp. 422–424.
- ^ Patnaik 1997, pp. 40–41.
- ^ Patnaik 1997, p. 57.
- ^ Patnaik 1997, p. 145.
- ^ Patnaik 1997, p. 59.
- ^ a b c d Parida 1999, pp. 105–8.
- ^ Patnaik 1997, p. 43.
- ^ a b c d e Jāvīd, ʻAlī; Javeed, Tabassum (2008). World Heritage Monuments. Algora Publishing. pp. 197–201. ISBN 9780875864846.
- ^ a b c d Goswami 1950, p. 73.
- ^ a b c Brockman, Norbert C. (2011). Encyclopedia of Sacred Places. California: ABC-CLIO, LLC. pp. 212–213. ISBN 978-1-59884-655-3.
- ^ Nayak, Smritilekha (2008). Dance and Architecture: Body, Form, Space and Transformation. p. 10. ISBN 9780549965183.
- ^ a b Panda, Dr.Saroj Kumar (April 2011). "Lingaraj Worship in Ekamra Kshetra" (PDF). The Orissa Review. LXVII (9). Government of Orissa: 61–62. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
- ^ Seymour, Susan C. (1999). Women, Family, and Child Care in India: A World in Transition. Cambridge University Press. p. 18. ISBN 0-521-59127-9.
- ^ "Thousands throng Lingaraj temple on Mahashivratri". Hindutan times, Delhi. 12 February 2010. Archived from the original on 10 June 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
- ^ "Thousands congregate at Lingaraj temple". The Hindu. 28 July 2008. Archived from the original on 14 October 2008. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ a b Misra & Preston 1978, pp. 12–13.
- ^ a b Ishwaran 1973, pp. 96–107.
- ^ "Hindus participate in Lingaraja's chariot procession in Bhubaneshwar". Hindustan Times, Delhi. 27 March 2007. Archived from the original on 10 June 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2012.
- ^ Kleinman, Arthur; Byron Good (1985). Culture and Depression: Studies in the Anthropology and Cross-Cultural Psychiatry of Affect and Disorder. London: University of California Press. p. 206. ISBN 0-520-05493-8.
- ^ a b "Russian enters Lingaraj temple". The Times of India. 24 January 2012. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ a b "Russian held for entering Lingaraj temple". The Daily Pioneer. 25 January 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ "Lingaraj servitors threaten strike". The Hindustan Times. 9 August 2010. Archived from the original on 1 December 2012. Retrieved 12 October 2012.
- ^ "Warring priests bring Lingaraj temple rituals to a halt". The Hindu. 9 August 2010. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ "Over two lakh devotees throng Lingaraj temple temple". The Hindu. 21 February 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ "Lingaraj to charge fee for spl pujas". The Times of India. 6 October 2011. Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
References
- Goswami, A. (1950). Designs from Orissan Temples (PDF). Calcutta and London: Thacker's Press and Directories, Limited. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2 March 2013.
- Ishwaran, K., ed. (1973). Contributions to Asian Studies. Vol. 3. Netherlands: Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 9789004035386.
- Misra, Bhabagrahi; Preston, James (1978). Community, Self and Identity. Great Britain: Mounton Publishers. ISBN 90-279-7650-3.
- Parida, A.N. (1999). Early Temples of Orissa (1st ed.). New Delhi: Commonwealth Publishers. ISBN 81-7169-519-1.
- Patnaik, Nihar Ranjan (1997). Economic History of Orissa. New Delhi: Indus Publishing Company. ISBN 81-7387-075-6.
External links
![]() Media related to Lingaraj Temple at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lingaraj Temple at Wikimedia Commons










