Democracy in Europe
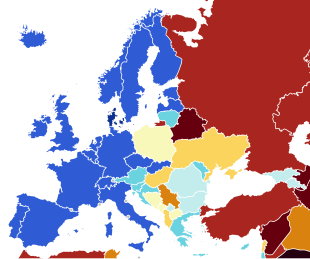
| 0.900–1.000 0.800–0.899 0.700–0.799 0.600–0.699 | 0.500–0.599 0.400–0.499 0.300–0.399 0.200–0.299 | 0.100–0.199 0.000–0.099 No data |
Democracy in Europe can be comparatively assessed[1] according to various definitions of democracy.[2] According to the V-Dem Democracy Indices, the European countries with the highest democracy scores in 2023 are Denmark, Norway and Sweden, meanwhile the European countries with lowest democracy scores in 2023 are Belarus, Russia and Turkey.[3]
Changes in democracy
After the fall of Communism most countries in Central and Eastern Europe either democratized or re-democratized.[4] Some democratic backsliding can be observed in parts of Europe, including Hungary and Poland.[5][6] The V-Dem Democracy Report identified for the year 2023 Montenegro and Kosovo as cases of stand-alone democratization and North Macedonia as a case of U-Turn democratization, while Poland as a small but statistically insignificant uptick in liberal democracy index.[7] Some view European democracies have become more consensual and less majoritarian over time.[8] Increased importance of constitutionalism has been claimed.[9]
Measures of democracy
The table below shows European countries scored on 2 high-level V-Dem Democracy indices and 4 mid-level Democracy Component indices evaluating the state of democracy in year 2023 which were published in 2024.[10][11][12]
| Country | Democracy Indices | Democracy Component Indices | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electoral | Liberal | Liberal | Egalitarian | Participatory | Deliberative | |
| 0.915 | 0.883 | 0.977 | 0.972 | 0.716 | 0.967 | |
| 0.896 | 0.831 | 0.933 | 0.875 | 0.634 | 0.905 | |
| 0.895 | 0.845 | 0.955 | 0.887 | 0.638 | 0.85 | |
| 0.895 | 0.814 | 0.909 | 0.931 | 0.648 | 0.91 | |
| 0.89 | 0.844 | 0.962 | 0.931 | 0.882 | 0.98 | |
| 0.886 | 0.836 | 0.955 | 0.961 | 0.655 | 0.988 | |
| 0.884 | 0.852 | 0.98 | 0.903 | 0.651 | 0.905 | |
| 0.878 | 0.798 | 0.91 | 0.939 | 0.578 | 0.975 | |
| 0.877 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 0.811 | 0.632 | 0.939 | |
| 0.871 | 0.805 | 0.933 | 0.913 | 0.585 | 0.88 | |
| 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.972 | 0.896 | 0.637 | 0.942 | |
| 0.856 | 0.812 | 0.967 | 0.941 | 0.662 | 0.976 | |
| 0.854 | 0.8 | 0.951 | 0.891 | 0.62 | 0.943 | |
| 0.852 | 0.772 | 0.914 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.843 | |
| 0.852 | 0.768 | 0.908 | 0.862 | 0.674 | 0.825 | |
| 0.845 | 0.751 | 0.887 | 0.795 | 0.611 | 0.872 | |
| 0.844 | 0.773 | 0.926 | 0.893 | 0.65 | 0.827 | |
| 0.843 | 0.757 | 0.902 | 0.841 | 0.645 | 0.828 | |
| 0.837 | 0.757 | 0.911 | 0.904 | 0.747 | 0.911 | |
| 0.834 | 0.744 | 0.896 | 0.87 | 0.659 | 0.845 | |
| 0.823 | 0.739 | 0.909 | 0.792 | 0.686 | 0.583 | |
| 0.798 | 0.735 | 0.938 | 0.868 | 0.692 | 0.822 | |
| 0.779 | 0.64 | 0.807 | 0.894 | 0.653 | 0.803 | |
| 0.774 | 0.636 | 0.817 | 0.869 | 0.574 | 0.837 | |
| 0.758 | 0.653 | 0.864 | 0.884 | 0.71 | 0.867 | |
| 0.751 | 0.582 | 0.752 | 0.835 | 0.641 | 0.868 | |
| 0.733 | 0.639 | 0.879 | 0.768 | 0.625 | 0.68 | |
| 0.713 | 0.608 | 0.86 | 0.8 | 0.665 | 0.93 | |
| 0.674 | 0.494 | 0.702 | 0.685 | 0.524 | 0.6 | |
| 0.669 | 0.501 | 0.72 | 0.674 | 0.657 | 0.35 | |
| 0.666 | 0.588 | 0.898 | 0.76 | 0.663 | 0.914 | |
| 0.634 | 0.422 | 0.611 | 0.811 | 0.442 | 0.69 | |
| 0.604 | 0.473 | 0.761 | 0.784 | 0.542 | 0.803 | |
| 0.588 | 0.444 | 0.729 | 0.877 | 0.555 | 0.719 | |
| 0.581 | 0.467 | 0.785 | 0.771 | 0.561 | 0.759 | |
| 0.56 | 0.359 | 0.584 | 0.598 | 0.61 | 0.64 | |
| 0.512 | 0.346 | 0.616 | 0.655 | 0.527 | 0.678 | |
| 0.51 | 0.402 | 0.75 | 0.706 | 0.555 | 0.444 | |
| 0.44 | 0.325 | 0.668 | 0.631 | 0.571 | 0.361 | |
| 0.415 | 0.249 | 0.5 | 0.654 | 0.58 | 0.761 | |
| 0.364 | 0.253 | 0.579 | 0.747 | 0.55 | 0.486 | |
| 0.287 | 0.113 | 0.245 | 0.53 | 0.416 | 0.195 | |
| 0.19 | 0.062 | 0.151 | 0.396 | 0.379 | 0.2 | |
| 0.157 | 0.036 | 0.082 | 0.734 | 0.161 | 0.044 | |
See also
- Act of Independence of Lithuania (1918)
- Athenian Revolution
- Age of Liberty (Sweden)
- Constitution of Norway (1814)
- Constitution of the Netherlands (1815)
- Constitution of Belgium (1831)
- Constitution of Denmark (1849)
- Czechoslovak declaration of independence (1918)
- Democracy in the Middle East and North Africa
- Democratic backsliding by country#Europe
- Democratization#Democratization by country
- Demokratizatsiya (Soviet Union)
- End of World War II in Europe
- Estonian Declaration of Independence (1918)
- French Revolution
- Glorious Revolution
- Magna Carta
- Greek transition to democracy (Metapolitefsi)
- Overthrow of the Roman monarchy
- People's Council of Latvia (1918)
- Politics of Europe
- Portuguese transition to democracy
- Representation of the People Act 1884
- Revolutions of 1848
- Revolutions of 1989
- Romanian revolution
- Rose Revolution
- Second Spanish Republic
- Second Polish Republic
- Singing Revolution
- Spanish transition to democracy
- Switzerland as a federal state
- Weimar Republic
- 1907 Finnish parliamentary election
- 1924 Greek republic referendum
- 1946 Italian institutional referendum
- 1989–1991 Ukrainian revolution
- 2018 Armenian Revolution
References
- ^ Geissel, Brigitte; Kneuer, Marianne; Lauth, Hans-Joachim (2016). "Measuring the quality of democracy: Introduction". International Political Science Review. 37 (5). Sage Publications: 571–579. doi:10.1177/0192512116669141. ISSN 0192-5121. JSTOR 26556872. S2CID 151808737. Retrieved 2023-04-03.
- ^ Greenwood, Shannon (2022-12-06). "Appendix A: Classifying democracies". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. Retrieved 2022-12-27.
- ^ Democracy Report 2023, Table 3, V-Dem Institute, 2023
- ^ Ágh, Attila (2020). "Rethinking the historical trajectory of ECE: From the "original sin" in democratization to redemocratization". Politics in Central Europe. 16 (2): 367–398. doi:10.2478/pce-2020-0017.
- ^ Sitter, Nick; Bakke, Elisabeth (2019). "Democratic Backsliding in the European Union". Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Politics. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780190228637.013.1476. ISBN 978-0-19-022863-7.
- ^ Cianetti, Licia, James Dawson, and Seán Hanley. "Rethinking “democratic backsliding” in Central and Eastern Europe–looking beyond Hungary and Poland." Rethinking'Democratic Backsliding'in Central and Eastern Europe. Routledge, 2020. 1-14.
- ^ Democracy Report 2024, Varieties of Democracy
- ^ The Future of Democracy in Europe Technology and the Evolution of Representation, 2020, Chapham House
- ^ Bickerton, Christopher (2018). "Beyond the European void? Reflections on Peter Mair's legacy". European Law Journal. 24 (4–5): 268–280. doi:10.1111/eulj.12287.
- ^ Democracy Report 2024, Varieties of Democracy
- ^ V-Dem Institute (2024). "The V-Dem Dataset". Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ Coppedge, Michael; Gerring, John; Glynn, Adam; Knutsen, Carl Henrik; Lindberg, Staffan I.; Pemstein, Daniel; Seim, Brigitte; Skaaning, Svend-Erik; Teorell, Jan (2020). Varieties of Democracy: Measuring Two Centuries of Political Change (1 ed.). Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108347860. ISBN 978-1-108-34786-0.
