United States District Court for the Northern District of West Virginia
| United States District Court for the Northern District of West Virginia | |
|---|---|
| (N.D. W. Va.) | |
 | |
| Location | Martinsburg |
| Appeals to | Fourth Circuit |
| Established | January 22, 1901 |
| Judges | 3 |
| Chief Judge | Tom Kleeh |
| Officers of the court | |
| U.S. Attorney | William J. Ihlenfeld II |
| U.S. Marshal | Terry Moore (acting) |
| www | |
The United States District Court for the Northern District of West Virginia (in case citations, N.D. W. Va.) is a federal court in the Fourth Circuit (except for patent claims and claims against the U.S. government under the Tucker Act, which are appealed to the Federal Circuit).
The District was established on June 22, 1901.[1]
As of October 12, 2021[update] the United States attorney is William J. Ihlenfeld II.[2]
Organization of the court
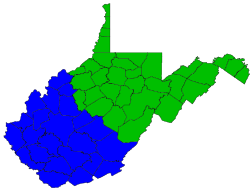
The United States District Court for the Northern District of West Virginia is one of two federal judicial districts in West Virginia.[3] Court for the Northern District is held at Clarksburg, Elkins, Martinsburg, and Wheeling.
Clarksburg Division comprises the following counties: Braxton, Calhoun, Doddridge, Gilmer, Harrison, Marion, Monongalia, Pleasants, Preston, Ritchie, and Taylor.
Elkins Division comprises the following counties: Barbour, Grant, Hardy, Lewis, Pendleton, Pocahontas, Randolph, Tucker, Upshur, and Webster.
Martinsburg Division comprises the following counties: Berkeley, Hampshire, Jefferson, Mineral, and Morgan.
Wheeling Division comprises the following counties: Brooke, Hancock, Marshall, Ohio, Tyler, and Wetzel.
Current judges
As of September 30, 2022[update]:
| # | Title | Judge | Duty station | Born | Term of service | Appointed by | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active | Chief | Senior | ||||||
| 16 | Chief Judge | Tom Kleeh | Clarksburg Elkins |
1974 | 2018–present | 2022–present | — | Trump |
| 14 | District Judge | John P. Bailey | Wheeling | 1951 | 2007–present | 2008–2015 | — | G.W. Bush |
| 15 | District Judge | Gina M. Groh | Martinsburg | 1964 | 2012–present | 2015–2022 | — | Obama |
| 11 | Senior Judge | Frederick Pfarr Stamp Jr. | inactive | 1934 | 1990–2006 | 1994–2001 | 2006–present | G.H.W. Bush |
| 12 | Senior Judge | Irene Patricia Murphy Keeley | inactive | 1944 | 1992–2017 | 2001–2008 | 2017–present | G.H.W. Bush |
Former judges
| # | Judge | State | Born–died | Active service | Chief Judge | Senior status | Appointed by | Reason for termination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Jay Jackson Jr. | WV | 1824–1907 | 1901–1905[Note 1] | — | — | Lincoln/Operation of law | retirement |
| 2 | Alston G. Dayton | WV | 1857–1920 | 1905–1920 | — | — | T. Roosevelt | death |
| 3 | William E. Baker | WV | 1873–1954 | 1921–1954 | 1948–1954 | 1954 | Harding | death |
| 4 | Harry Evans Watkins | WV | 1898–1963 | 1937–1963[Note 2] | 1954–1963 | — | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 5 | Herbert Stephenson Boreman | WV | 1897–1982 | 1954–1959 | — | — | Eisenhower | elevation to 4th Cir. |
| 6 | Charles Ferguson Paul | WV | 1902–1965 | 1960–1965 | 1963–1965 | — | Eisenhower | death |
| 7 | Sidney Lee Christie | WV | 1903–1974 | 1964–1974[Note 2] | — | — | L. Johnson | death |
| 8 | Robert Earl Maxwell | WV | 1924–2010 | 1965–1995 | 1965–1994 | 1995–2010 | L. Johnson | death |
| 9 | Charles Harold Haden II | WV | 1937–2004 | 1975–1983[Note 2] | — | — | Ford | seat abolished |
| 10 | William Matthew Kidd | WV | 1918–1998 | 1983–1990[Note 3] | — | 1990–1998 | Carter/Operation of law | death |
| 13 | W. Craig Broadwater | WV | 1950–2006 | 1996–2006 | — | — | Clinton | death |
- ^ Early in the course of the American Civil War, the western portion of Virginia rejected Virginia's secession from the United States, and itself seceded from Virginia. This area largely coincided with the existing Western District of Virginia. The portion of Virginia remaining loyal to the Union became the state of West Virginia, which was admitted as a state on June 20, 1863. On June 11, 1864, by 13 Stat. 124, the United States District Court for the Western District of Virginia became the United States District Court for the District of West Virginia, and those parts of the Western District that were not part of West Virginia were combined with what had previously been the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia to again form a single United States District Court for the District of Virginia. John Jay Jackson, who had been appointed to the Western District of Virginia, was reassigned by operation of law to the newly formed District of West Virginia. At the same time, John Curtiss Underwood, who had been appointed to the Eastern District of Virginia, was reassigned by operation of law to the newly formed District of Virginia. On February 3, 1871, the District of Virginia was again subdivided into Eastern and Western Districts, and Underwood was reassigned to the Eastern District, until his death. On July 1, 1901, the District of West Virginia was subdivided into the United States District Court for the Northern District of West Virginia and the United States District Court for the Southern District of West Virginia; Jackson was reassigned to the Northern District, until his retirement.
- ^ a b c Jointly appointed to the Northern and Southern Districts of West Virginia
- ^ Reassigned from the Southern District of West Virginia.
Chief judges
Chief judges have administrative responsibilities with respect to their district court. Unlike the Supreme Court, where one justice is specifically nominated to be chief, the office of chief judge rotates among the district court judges. To be chief, a judge must have been in active service on the court for at least one year, be under the age of 65, and have not previously served as chief judge.
A vacancy is filled by the judge highest in seniority among the group of qualified judges. The chief judge serves for a term of seven years, or until age 70, whichever occurs first. The age restrictions are waived if no members of the court would otherwise be qualified for the position.
When the office was created in 1948, the chief judge was the longest-serving judge who had not elected to retire, on what has since 1958 been known as senior status, or declined to serve as chief judge. After August 6, 1959, judges could not become or remain chief after turning 70 years old. The current rules have been in operation since October 1, 1982.
Succession of seats
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Courts of West Virginia
- List of current United States district judges
- List of United States federal courthouses in West Virginia
References
- ^ https://www.fjc.gov/history/courts/u.s.-district-courts-districts-west-virginia-legislative-history U.S. District Courts of West Virginia, Legislative history, Federal Judicial Center
- ^ "William J. Ihlenfeld, II sworn in as United States Attorney for the Northern District of West Virginia" (Press release). Wheeling, West Virginia: U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of West Virginia. October 12, 2021. Retrieved October 12, 2021.
- ^ 28 U.S.C. § 129

