Portal:San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area Portal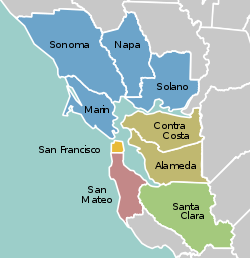  The San Francisco Bay Area (referred to locally as the Bay Area) is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco and San Pablo estuaries in Northern California. The region encompasses the major cities and metropolitan areas of San Jose, San Francisco, and Oakland, along with smaller urban and rural areas. The Bay Area's nine counties are Alameda, Contra Costa, Marin, Napa, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Clara, Solano, and Sonoma. Home to approximately 7.68 million people, the nine-county Bay Area contains many cities, towns, airports, and associated regional, state, and national parks, connected by a network of roads, highways, railroads, bridges, tunnels, and commuter rail. The combined statistical area of the region is the second-largest in California (after the Greater Los Angeles area), the fifth-largest in the United States, and the 43rd-largest urban area in the world with 8.80 million people. The Bay Area has the second-most Fortune 500 companies in the United States, after the New York metropolitan area, and is known for its natural beauty, liberal politics, entrepreneurship, and diversity. The area ranks second in highest density of college graduates, after the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area and performs above the state median household income in the 2010 census; it includes the five highest California counties by per capita income and two of the top 25 wealthiest counties in the United States. Based on a 2013 population report from the California Department of Finance, the Bay Area is the only region in California where the rate of people migrating in from other areas in the United States is greater than the rate of those leaving the region, led by Alameda and Contra Costa counties. (more...) Selected article In the late 1960s, few professional football games took longer than two and a half hours to play, and the Jets–Raiders three-hour television time slot was thought to be adequate. However, in this instance, a high-scoring contest between the two bitter American Football League rivals, together with a number of injuries and penalties, caused the game to run long. Although NBC executives had originally ordered that Heidi must begin on time, as 7 p.m. approached, and it became clear the exciting game would run long, they decided to postpone the start of the film and continue football coverage. However, when they tried to call the studio to implement their decision, they were unable to get through because so many members of the public were calling NBC to inquire, complain, or opine about the scheduled 7 p.m. cutoff that the NBC switchboards were jammed. As a result, the change could not be communicated, and Heidi began as scheduled, preempting the final moments of the game in the eastern part of the country—to the outrage of viewers there, who missed two Oakland touchdowns that turned the game around. The Heidi Game led to a change in the way professional football is shown on network television; ever since then, games have been shown to their conclusion before evening programming begins. The experience also led television networks to take steps to ensure that network personnel would be able to communicate with each other under similar circumstances in the future: special telephones (dubbed "Heidi phones") were installed that connected through a separate telephone exchange. In 1997, the Heidi Game was voted the most memorable regular season game in U.S. professional football history. (more...) Selected biography Edward Teller (Hungarian: Teller Ede; January 15, 1908 – September 9, 2003) was a Hungarian-born American theoretical physicist who, although he claimed he did not care for the title, is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb". He made numerous contributions to nuclear and molecular physics, spectroscopy (in particular, the Jahn–Teller and Renner–Teller effects) and surface physics. His extension of Enrico Fermi's theory of beta decay, in the form of the so-called Gamow–Teller transitions, provided an important stepping stone in its application, while the Jahn–Teller effect and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) theory have retained their original formulation and are still mainstays in physics and chemistry. Teller also made contributions to Thomas–Fermi theory, the precursor of density functional theory, a standard modern tool in the quantum mechanical treatment of complex molecules. In 1953, along with Nicholas Metropolis and Marshall Rosenbluth, Teller co-authored a paper which is a standard starting point for the applications of the Monte Carlo method to statistical mechanics. Teller emigrated to the United States in the 1930s, and was an early member of the Manhattan Project charged with developing the first atomic bombs. During this time he made a serious push to develop the first fusion-based weapons as well, but these were deferred until after World War II. After his controversial testimony in the security clearance hearing of his former Los Alamos colleague J. Robert Oppenheimer, Teller was ostracized by much of the scientific community. He continued to find support from the U.S. government and military research establishment, particularly for his advocacy for nuclear energy development, a strong nuclear arsenal, and a vigorous nuclear testing program. He was a co-founder of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), and was both its director and associate director for many years. (more...) Selected city In September 2010, Forbes magazine placed Atherton's zip code of 94027 at #2 on its annual list of America's most expensive zip codes. In October 2013, 94027 was placed at #1 on the list. In 1866, Atherton was known as Fair Oaks, and was a flag stop on the California Coast Line of the Southern Pacific Railroad between San Francisco and San Jose for the convenience of the owners of the large estates who lived north of Menlo Park. The entire area was called Menlo Park. It had been part of the Rancho de las Pulgas that had covered most of the area, which is now southern San Mateo County. There were several attempts to incorporate Fair Oaks, one in 1874 and another in 1911. (more...) Selected image
The Bay Area by year1956
 
Selected historical imageDid you know...
Previous Did you know... 
Selected periodic event The Big Game is the American college football rivalry game played by the California Golden Bears football team of the University of California, Berkeley and Stanford Cardinal football team of Stanford University. First played 132 years ago in 1892, it is the ninth most played college football rivalry game in the United States. "The Play", in their 1982 game, is considered one of the most memorable plays in American sports. (Cal linebacker Shea McIntyre, celebrating Berkeley reclaiming the Stanford Axe, pictured) Quote
Selected multimedia fileBay Area regions, geographic features and protected areasRelated PortalsWikiProject
Things you can do *Write an article on a Bay Area-related subject Selected panoramaSan Francisco Bay Area categoriesBay Area | San Francisco Bay | San Francisco | San Jose | Oakland | Cities | Census-designated places | Historic Places | National Landmarks | Counties: Alameda | Contra Costa | Marin | Napa | San Mateo | Santa Clara | Solano | Sonoma
Architecture | Attractions | Books | Culture | Economy | Education | Environment | Events & Festivals | Geography | Government | History | Landmarks | Law | Mass media | Military | Music | Organizations | Parks | People | Politics | Science | Sports | Transport
Full category tree
Select [►] to view the full category tree.
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |

















































