Lateral plantar nerve
| Lateral plantar nerve | |
|---|---|
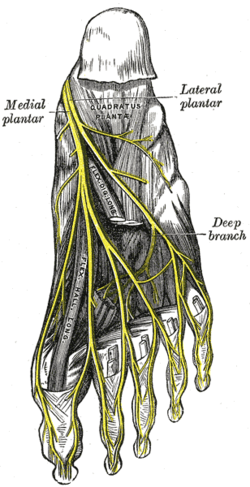 The plantar nerves. | |
 | |
| Details | |
| From | Tibial nerve |
| Innervates | Sole, abductor digiti minimi muscle (foot), flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle (foot), quadratus plantae, 3 lateral lumbricals of the foot, adductor hallucis muscle, plantar interossei muscles, dorsal interossei muscles |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus plantaris lateralis |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.069 |
| TA2 | 6593 |
| FMA | 44724 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The lateral plantar nerve (external plantar nerve) is a branch of the tibial nerve, in turn a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the skin of the fifth toe and lateral half of the fourth, as well as most of the deep muscles, its distribution being similar to that of the ulnar nerve in the hand.
It passes obliquely forward with the lateral plantar artery to the lateral side of the foot, lying between the flexor digitorum brevis and quadratus plantae and, in the interval between the flexor muscle and the abductor digiti minimi, divides into a superficial and a deep branch. Before its division, it supplies the quadratus plantae and abductor digiti minimi. It divides into deep and superficial branches.
Additional images
-
Nerves of the dorsum of the foot.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 963 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 963 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)


