Aroma compound

An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently volatile for transmission via the air to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose. As examples, various fragrant fruits have diverse aroma compounds,[1] particularly strawberries which are commercially cultivated to have appealing aromas, and contain several hundred aroma compounds.[1][2]
Generally, molecules meeting this specification have molecular weights of less than 310.[3] Flavors affect both the sense of taste and smell, whereas fragrances affect only smell. Flavors tend to be naturally occurring, and the term fragrances may also apply to synthetic compounds, such as those used in cosmetics.[4]
Aroma compounds can naturally be found in various foods, such as fruits and their peels, wine, spices, floral scent, perfumes, fragrance oils, and essential oils. For example, many form biochemically during the ripening of fruits and other crops.[1][5] Wines have more than 100 aromas that form as byproducts of fermentation.[6] Also, many of the aroma compounds play a significant role in the production of compounds used in the food service industry to flavor, improve, and generally increase the appeal of their products.[1]
An odorizer may add a detectable odor to a dangerous odorless substance, like propane, natural gas, or hydrogen, as a safety measure.
Aroma compounds classified by structure
Esters
| Compound name | Fragrance | Natural occurrence | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geranyl acetate | Fruity, Floral |
Rose | |
| Methyl formate | Ethereal | ||
| Methyl acetate | Sweet, nail polish Solvent |
||
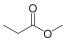
| Methyl propionate Methyl propanoate |
Sweet, fruity, rum-like | ||
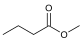
| Methyl butyrate Methyl butanoate |
Fruity | Apple Pineapple |
|
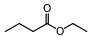
| Ethyl acetate | Sweet, solvent | Wine | |
| Ethyl butyrate Ethyl butanoate |
Fruity | Orange, Pineapple | |
| Isoamyl acetate | Fruity, Banana, Pear |
Banana plant | |
| Pentyl butyrate Pentyl butanoate |
Fruity | Pear Apricot |
|
| Pentyl pentanoate | Fruity | Apple | |
| Octyl acetate | Fruity | Orange | |
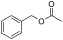
| Benzyl acetate | Fruity, Strawberry | Strawberries | |
| Methyl anthranilate | Fruity | Grape |  |
| Methyl salicylate | Minty, root beer | Wintergreen |  |
| Hexyl acetate | Floral, Fruity | Apple, Plum | 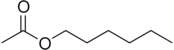 |
Linear terpenes
| Compound name | Fragrance | Natural occurrence | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
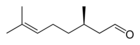
| Myrcene | Woody, complex | Verbena, Bay leaf | |
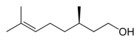
| Geraniol | Rose, flowery | Geranium, Lemon | |
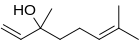
| Nerol | Sweet rose, flowery | Neroli, Lemongrass |  |
| Citral, lemonal Geranial, neral |
Lemon | Lemon myrtle, Lemongrass | |
| Citronellal | Lemon | Lemongrass | |
| Citronellol | Lemon | Lemongrass, rose Pelargonium |
|
| Linalool | Floral, sweet Woody |
Coriander, Sweet basil, Lavender, Honeysuckle | |
| Nerolidol | Woody, fresh bark | Neroli, ginger Jasmine |
|
| Ocimene | Fruity, Floral | Mango, Curcuma amada |
Cyclic terpenes
| Compound name | Fragrance | Natural occurrence | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Limonene | Orange | Orange, lemon | |
| Camphor | Camphor | Camphor laurel | |
| Menthol | Menthol | Mentha | |
| Carvone1 | Caraway or Spearmint | Caraway, dill, spearmint |
 |
| Terpineol | Lilac | Lilac, cajuput | |
| alpha-Ionone | Violet, woody | Violet |  |
| Thujone | Minty | Wormwood, lilac, juniper |
 |
| Eucalyptol | Eucalyptus | Eucalyptus | 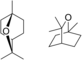 |
| Jasmone | spicy, fruity, floral in dilution | Jasmine, Honeysuckle | 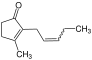 |
Note: Carvone, depending on its chirality, offers two different smells.
Aromatic
| Compound name | Fragrance | Natural occurrence | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzaldehyde | Almond | Bitter almond | |
| Eugenol | Clove | Clove |  |
| Cinnamaldehyde | Cinnamon | Cassia Cinnamon |
 |
| Ethyl maltol | Cooked fruit Caramelized sugar |
 | |
| Vanillin | Vanilla | Vanilla |  |
| Anisole | Anise | Anise | |
| Anethole | Anise | Anise Sweet basil |
 |
| Estragole | Tarragon | Tarragon |  |
| Thymol | Thyme | Thyme |
Amines
| Compound name | Fragrance | Natural occurrence | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|---|
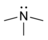
| Trimethylamine | Fishy Ammonia |
||
| Putrescine Diaminobutane |
Rotting flesh | Rotting flesh | |
| Cadaverine | Rotting flesh | Rotting flesh | |
| Pyridine | Fishy | Belladonna | |
| Indole | Fecal Flowery |
Feces Jasmine |
 |
| Skatole | Fecal Flowery |
Feces (diluted) Orange Blossoms |
 |
Other aroma compounds
Alcohols
- Furaneol (strawberry)
- 1-Hexanol (herbaceous, woody)
- cis-3-Hexen-1-ol (fresh cut grass)
- Menthol (peppermint)
Aldehydes
High concentrations of aldehydes tend to be very pungent and overwhelming, but low concentrations can evoke a wide range of aromas.
- Acetaldehyde (ethereal)
- Hexanal (green, grassy)
- cis-3-Hexenal (green tomatoes)
- Furfural (burnt oats)
- Hexyl cinnamaldehyde
- Isovaleraldehyde – nutty, fruity, cocoa-like
- Anisic aldehyde – floral, sweet, hawthorn. It is a crucial component of chocolate, vanilla, strawberry, raspberry, apricot, and others.
- Cuminaldehyde (4-propan-2-ylbenzaldehyde) – Spicy, cumin-like, green
Esters
- Fructone (fruity, apple-like)
- Ethyl methylphenylglycidate (Strawberry)
- alpha-Methylbenzyl acetate (Gardenia)
Ketones
- Cyclopentadecanone (musk-ketone)[7]
- Dihydrojasmone (fruity woody floral)
- Oct-1-en-3-one (blood, metallic, mushroom-like)[8]
- 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline (fresh bread, jasmine rice)
- 6-Acetyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine (fresh bread, tortillas, popcorn)
Lactones
- gamma-Decalactone intense peach flavor
- gamma-Nonalactone coconut odor, popular in suntan lotions
- delta-Octalactone creamy note
- Jasmine lactone powerful fatty-fruity peach and apricot
- Massoia lactone powerful creamy coconut
- Wine lactone sweet coconut odor
- Sotolon (maple syrup, curry, fenugreek)
Thiols
- Thioacetone (2-propanethione) A lightly studied organosulfur. Its smell is so potent it can be detected several hundred meters downwind mere seconds after a container is opened.
- Allyl thiol (2-propenethiol; allyl mercaptan; CH2=CHCH2SH) (garlic volatiles and garlic breath)[9]
- (Methylthio)methanethiol (CH3SCH2SH), the "mouse thiol", found in mouse urine and functions as a semiochemical for female mice[10]
- Ethanethiol, commonly called ethyl mercaptan (added to propane or other liquefied-petroleum gases used as fuel gases)
- 2-Methyl-2-propanethiol, commonly called tert-butyl mercaptan, is added as a blend of other components to natural gas used as fuel gas.
- Butane-1-thiol, commonly called butyl mercaptan, is a chemical intermediate.
- Grapefruit mercaptan (grapefruit)
- Methanethiol, commonly called methyl mercaptan (after eating Asparagus)
- Furan-2-ylmethanethiol, also called furfuryl mercaptan (roasted coffee)
- Benzyl mercaptan (leek or garlic-like)
Miscellaneous compounds
- Methylphosphine and dimethylphosphine (garlic-metallic, two of the most potent odorants known)[8]
- Phosphine (zinc phosphide poisoned bait)
- Diacetyl (butter flavor)
- Acetoin (butter flavor)
- Nerolin (orange flowers)
- Tetrahydrothiophene (added to natural gas)
- 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole (cork taint)
- Substituted pyrazines
Aroma-compound receptors
Animals that are capable of smell detect aroma compounds with their olfactory receptors. Olfactory receptors are cell-membrane receptors on the surface of sensory neurons in the olfactory system that detect airborne aroma compounds. Aroma compounds can then be identified by gas chromatography-olfactometry, which involves a human operator sniffing the GC effluent.[11]
In mammals, olfactory receptors are expressed on the surface of the olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity.[5]
Safety and regulation
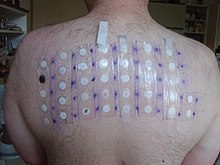
In 2005–06, fragrance mix was the third-most-prevalent allergen in patch tests (11.5%).[12] 'Fragrance' was voted Allergen of the Year in 2007 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society. An academic study in the United States published in 2016 has shown that "34.7 % of the population reported health problems, such as migraine headaches and respiratory difficulties, when exposed to fragranced products".[13]
The composition of fragrances is usually not disclosed in the label of the products, hiding the actual chemicals of the formula, which raises concerns among some consumers.[14] In the United States, this is because the law regulating cosmetics protects trade secrets.[15]
In the United States, fragrances are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration if present in cosmetics or drugs, by the Consumer Products Safety Commission if present in consumer products.[15] No pre-market approval is required, except for drugs. Fragrances are also generally regulated by the Toxic Substances Control Act of 1976 that "grandfathered" existing chemicals without further review or testing and put the burden of proof that a new substance is not safe on the EPA. The EPA, however, does not conduct independent safety testing but relies on data provided by the manufacturer.[16]
A 2019 study of the top-selling skin moisturizers found 45% of those marketed as "fragrance-free" contained fragrance.[17]
List of chemicals used as fragrances
In 2010, the International Fragrance Association published a list of 3,059 chemicals used in 2011 based on a voluntary survey of its members, identifying about 90% of the world's production volume of fragrances.[18]
See also
- Aroma of wine
- Eau de toilette
- Flavour and Fragrance Journal
- Fragrances of the World
- Foodpairing
- Odor
- Odor detection threshold
- Odorizer, a device for adding an odorant to gas flowing through a pipe
- Olfaction
- Olfactory receptor
- Olfactory system
- Pheromone
- vabbing
References
- ^ a b c d El Hadi, Muna; Zhang, Feng-Jie; Wu, Fei-Fei; Zhou, Chun-Hua; Tao, Jun (July 11, 2013). "Advances in fruit aroma volatile research". Molecules. 18 (7): 8200–8229. doi:10.3390/molecules18078200. ISSN 1420-3049. PMC 6270112. PMID 23852166.
- ^ Ulrich, Detlef; Kecke, Steffen; Olbricht, Klaus (March 13, 2018). "What do we know about the chemistry of strawberry aroma?". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 66 (13): 3291–3301. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01115. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 29533612.
- ^ Rothe, M; Specht, M (1976). "[Notes about molecular weights of aroma compounds]". Nahrung. 20 (3): 281–6. doi:10.1002/food.19760200308. PMID 958345. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ Fahlbusch, Karl-Georg; Hammerschmidt, Franz-Josef; Panten, Johannes; Pickenhagen, Wilhelm; Schatkowski, Dietmar; Bauer, Kurt; Garbe, Dorothea; Surburg, Horst. "Flavors and fragrances". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ a b Haugeneder, Annika; Trinkl, Johanna; Härtl, Katja; Hoffmann, Thomas; Allwood, James William; Schwab, Wilfried (October 26, 2018). "Answering biological questions by analysis of the strawberry metabolome". Metabolomics. 14 (11): 145. doi:10.1007/s11306-018-1441-x. ISSN 1573-3882. PMC 6394451. PMID 30830391.
- ^ Ilc, Tina; Werck-Reichhart, Danièle; Navrot, Nicolas (September 30, 2016). "Meta-analysis of the core aroma components of grape and wine aroma". Frontiers in Plant Science. 7: 1472. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.01472. ISSN 1664-462X. PMC 5042961. PMID 27746799.
- ^ Gane, S; Georganakis, D; Maniati, K; Vamvakias, M; Ragoussis, N; Skoulakis, EMC; Turin, L (2013). "Molecular-vibration-sensing component in human olfaction". PLOS ONE. 8 (1): e55780. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...855780G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055780. PMC 3555824. PMID 23372854.
- ^ a b Glindemann, D.; Dietrich, A.; Staerk, H.; Kuschk, P. (2005). "The Two Odors of Iron when Touched or Pickled: (Skin) Carbonyl Compounds and Organophosphines". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (42): 7006–7009. doi:10.1002/anie.200602100. PMID 17009284.
- ^ Block, E. (2010). Garlic and Other Alliums: The Lore and the Science. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-85404-190-9.
- ^ Lin, D.Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Block, E.; Katz, L.C. (2005). "Encoding social signals in the mouse main olfactory bulb". Nature. 434 (7032): 470–477. Bibcode:2005Natur.434..470L. doi:10.1038/nature03414. PMID 15724148. S2CID 162036.
- ^ Brattoli, M; Cisternino, E; Dambruoso, PR; de Gennaro, G; Giungato, P; Mazzone, A; Palmisani, J; Tutino, M (December 5, 2013). "Gas chromatography analysis with olfactometric detection (GC-O) as a useful methodology for chemical characterization of odorous compounds". Sensors (Basel, Switzerland). 13 (12): 16759–800. Bibcode:2013Senso..1316759B. doi:10.3390/s131216759. PMC 3892869. PMID 24316571.
- ^ Zug, Kathryn A.; Warshaw, Erin M.; Fowler, Joseph F.; Maibach, Howard I.; Belsito, Donald L.; Pratt, Melanie D.; Sasseville, Denis; Storrs, Frances J.; Taylor, James S.; Mathias, C. G. Toby; Deleo, Vincent A.; Rietschel, Robert L.; Marks, James (2009). "Patch-test results of the North American Contact Dermatitis Group 2005-2006". Dermatitis: Contact, Atopic, Occupational, Drug. 20 (3): 149–160. ISSN 2162-5220. PMID 19470301.
- ^ Anne Steinemann, "Fragranced consumer products: exposures and effects from emissions", Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, December 2016, Volume 9, Issue 8, pp 861–866.
- ^ Anne C. Steinemann et al., "Fragranced Consumer Products: Chemicals Emitted, Ingredients Unlisted", Environmental Impact Assessment Review, Vol. 31, Issue 3, April 2011, pp. 328-333.
- ^ a b Fragrances in Cosmetics
- ^ Randall Fitzgerald (2006). The Hundred Year Lie. Dutton, 2006. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-525-94951-0.
- ^ Patti Neighmond (October 2, 2017). "'Hypoallergenic' And 'Fragrance-Free' Moisturizer Claims Are Often False". NPR.
- ^ "IFRA Survey:Transparency List". IFRA. Retrieved December 3, 2014.