Demographic history of Palestine (region)
It has been suggested that this article be merged with Arab migrations to the Levant. (Discuss) Proposed since September 2024. |
| Year | Jews | Christians | Muslims | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st c. | Majority | – | – | ~1,250 | ||
| 4th c. | Majority | Minority | – | >1st c.[1][2] | ||
| 5th c. | Minority | Majority | – | >1st c. | ||
| End 12th c. | Minority | Minority | Majority | >225 | ||
| 14th c. | Minority | Minority | Majority | 150 | ||
| 1533–1539 | 5 | 6 | 145 | 156 | ||
| 1553–1554 | 7 | 9 | 188 | 205 | ||
| 1690–1691 | 2 | 11 | 219 | 232 | ||
| 1800 | 7 | 22 | 246 | 275 | ||
| 1890 | 43 | 57 | 432 | 532 | ||
| 1914 | 94 | 70 | 525 | 689 | ||
| 1922 | 84 | 71 | 589 | 752 | ||
| 1931 | 175 | 89 | 760 | 1,033 | ||
| 1947 | 630 | 143 | 1,181 | 1,970 | ||
| Estimates by Sergio DellaPergola (2001), drawing on the work of Bachi (1975). Figures in thousands.[3] | ||||||
The population of the region of Palestine, which approximately corresponds to modern Israel and the Palestinian territories, has varied in both size and ethnic composition throughout the history of Palestine.
Studies of Palestine's demographic changes over the millennia have shown that a Jewish majority in the first century AD had changed to a Christian majority by the 3rd century AD,[4] and later to a Muslim majority, which is thought to have existed in Mandatory Palestine (1920-1948) since at least the 12th century AD, during which the total shift to Arabic language was completed.[5]
Iron Age
During the seventh century BC, no fewer than eight nations were settled in Palestine. These included the Arameans of the kingdom of Geshur; the Samaritans who replaced the Israelite kingdom in Samaria; the Phoenicians in the northern cities and parts of Galilee; the Philistines in the Philistine pentapolis; the three kingdoms of the Transjordan– Ammon, Moab and Edom; and the Judaeans of Kingdom of Judah.[6]
According to Finkelstein and Broshi, the population of Palestine at the end of the eighth century BC was around 400,000. In the area of Judah in the central hills, Benjamin and Jerusalem, the population was approximately 110,000. By the early sixth century, Ofer's survey results suggest that around 100,000 lived in the kingdom of Judah, with the population in the central hills, Benjamin and Jerusalem about 69,000.[7]
A study by Yigal Shiloh of The Hebrew University suggests that the population of Palestine in the Iron Age could have never exceeded one million. He writes: "... the population of the country in the Roman-Byzantine period greatly exceeded that in the Iron Age..." Shiloh accepted Israeli archaeologist Magen Broshi's estimates of Palestine's population at 1,000,000–1,250,000 and noted that Iron Age Israel's population must have been less considering population growth. "...If we accept Broshi's population estimates, which appear to be confirmed by the results of recent research, it follows that the estimates for the population during the Iron Age must be set at a lower figure."[8] One study of population growth from 1000 BC to 750 BC estimated the population of Palestine (Judah and Israel) had an average natural growth of 0.4 per cent per annum.[9]
Persian period
| Territory | Carter | Lipschits | Finkelstein |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benjamin | 7625 | 12,500 | - |
| Jerusalem (and environs) | 1500 | 2750 | 400[fn 1] |
| Northern Judean Hills | 8850 | 9750 | - |
| Southern Judean Hills | 2150 | - | - |
| Shephelah | - | 4875 | - |
| Judean Desert/Eastern Strip | 525 | 250 | - |
| Total | 20,650 | 30,125 | 12,000 |
| Lipshits' data from The Fall and Rise of Jerusalem: Judah under Babylonian Rule, Carter's data from The Emergence of Yehud in the Persian Period, Finkelstein's data from The Territorial Extent and Demography of Yehud/Judea | |||
After the Babylonian conquest of Judah and exile, the population and settlement density of Jerusalem, the Shephelah and the Naqab desert dropped significantly.[10] The Persian province of Yehud Medinata was sparsely-populated and predominantly rural, with around half of the settlements of late Iron age Judah and a population of around 30,000 in the 5th to 4th centuries BC.[11][12] On the other hand, settlement continuity is discerned in the northern parts of the Judean mountains and the Benjamin area. Cities such as Tell en-Nasbeh, Gibeon and Bethel managed to escape destruction and remained continuously inhabited until the early Achaemenid rule.[10]
As early as the 7th century BC, Edomites had lived in the Naqab desert and southern Judah, and by the time Judah fell in 586 BC there was already a substantial Edomite population in southern Judah. When the kingdom of Edom itself succumbed, those people continued its traditions in the south, which the Arabic-speaking Qedarites controlled.[13][14][10][15] This area, which became known as Idumaea, was inhabited by a diverse population of Edomites, Judahites, Phoenicians, Qedarites and other Arabs.[16] Based on analysis of epigraphic material and ostraca from the region, around 32% of recorded names were Arabic, 27% were Edomite, 25% were Northwest Semitic, 10% were Judahite (Hebrew) and 5% were Phoenician.[17] A few names were also classified Egyptian and Old Iranian.[14]
The exilic returnees resettled during the time of Cyrus the Great, perhaps with a heightened sense of their ethnic identity.[10] Along the coast of western Palestine, the Phoenicians expanded their presence, while Moabites and Ammonites took refuge in the Cisjordan after the destruction of their kingdoms in 582 BC.[10]
Hellenistic and Hasmonean period
Following the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire and the subsequent Wars of the Diadochi, Palestine came under Hellenistic rule and was contested by the Seleucids and Ptolemaics.[18]
Between 167 and 160 BC, the Jewish rebel faction of the Maccabees revolted against Seleucid rule, ultimately leading to the independence of the Hasmonean dynasty. Under John Hyrcanus, the Hasmoneans expanded their territories beyond the traditional confines of Judea and incorporated non-Jewish areas in the process.[19][20][21][22] 1 Maccabees relates that the non-Jewish inhabitants of Gezer and Joppa were expelled by Simon Thassi, who settled Jews in their place.[23] Coinciding with the account of Josephus, archaeological evidence attests to significant destruction in the urban and rural settlements in Idumaea, Samaria and the coastal cities from the Hasmonean conquests, followed by the resettlement of Jews in the newly conquered territories.[24] Nevertheless, there's evidence that some of the non-Jewish inhabitants stayed in all of the newly conquered areas.[19]
Many sites in Idumaea experienced destruction, including Maresha, Khirbet el-Rasm, Tel Arad, Khirbet 'Uza and possibly Lachish. The lower city of Maresha and Tel Beersheba were soon abandoned, and evidence for an increased Idumaean presence in Egypt suggests some immigrated there. Idumaeans were eventually forcibly proselytized and co-opted into the Jewish nation by John Hyrcanus.[19] Further north, the Galilee received significant Jewish migration from Judea after its conquest, contributing to a 50% increase in settlements, while the pagan population was greatly reduced. By the end of Alexander Jannaeus' reign, the Galilee was also predominantly Jewish.[25] However, unlike John Hyrcanus, Alexander Jannaeus did not compel the non-Jews to assimilate to the Jewish ethnos and permitted minority ethnē to exist within Hasmonean borders, with the exception of Phoenician coastal cities in the north whom Josephus claims he enslaved.
Roman period
The Roman conquest of Judea led by Pompey took place in 63 BC. The Roman occupation encompassed the end of Jewish independence in Judea, the last years of the Hasmonean kingdom, the Herodian age and the rise of Christianity, the First Jewish–Roman War, and the fall of Jerusalem and the destruction of the Second Temple.[26] The total population of Pharisees, the forerunners of modern Rabbinic Judaism, was around 6,000 ("exakischilioi"), according to Josephus.[27] Local population displacements occurred with the expulsion of the Jews from Jerusalem[28] – "In the earlier revolt in the previous century, 66–73 CE, Rome destroyed the Temple and forbade Jews to live in the remaining parts of Jerusalem; for this reason, the Rabbis gathered instead on the Mediterranean coast in Yavneh near Jaffa". Dispersal to other parts of the Roman Empire occurred, but some earlier settlements were also established as early as 4 BC.[29]
Modern estimates vary: Applebaum argues that in the Herodian kingdom, there were 1.5 million Jews, a figure Ben David says covers the numbers in Judea alone. Salo Wittmayer Baron estimated the population at 2.3 million at the time of Roman emperor Claudius (reigned 41–54). According to Israeli archeologist Magen Broshi, west of the Jordan River the population certainly did not exceed 1 million:[30]
"... the population of Palestine in antiquity did not exceed a million persons. It can also be shown, moreover, that this was more or less the size of the population in the peak period – the late Byzantine period, around AD 600"[31]
Broshi made calculations based on the grain-producing capacity of Palestine and on its role in the indigenous diet, assuming an average annual per-capita consumption of 200 kg. (with a maximum of 250 kg.), which would work out to the limit of a sustainable population of 1,000,000 people, a figure which, Broshi states, remained roughly constant down to the end of the Byzantine period (600 CE).[32] The proportion of Jews to gentiles is also unknown.[30]
The Bar Kokhba revolt in the 2nd century saw a major shift in the population of Palestine. The sheer scale and scope of the overall destruction, according to a late epitome of Dio Cassius's Roman History, where he states that Roman war operations in the country had left some 580,000 Jews dead, with many more dying of hunger and disease, while 50 of their most important outposts and 985 of their most famous villages were razed to the ground. "Thus," writes Dio Cassius, "nearly the whole of Judaea was made desolate."[33][34] Goodblatt contends that while Bar Kokhba rendered much of the Judaean Mountains and the Hebron Hills desolate, Jewish communities continued to thrive in other parts of Judea and Palestine as a whole.
"The destruction of the Jewish metropolis of Jerusalem and its environs and the ventual refoundation of the city as the Roman colony of Aelia Capitolina had lasting repercussions. However, in other parts of Palestine the Jewish population remained strong. Literary and archaeological evidence indicates that in the Late Roman-early Byzantine era Jewish commuinities thrived along the eastern, southern and western edges of Judah, in the Galilee, Golan and the Beit Shean region. And a strong Jewish presence continued throughout this period in many poleis, including Caesarea Maritima and Scythopolis."[35]
When exactly Jews became a minority is disputed.[30][35] Eschel argues that a combination of three events: the rise of Christianity, the Jewish-Roman wars and Jewish Diaspora made Jews in the minority.[36] David Goodblatt contends that Jews suffered a setback following the Bar Kokhba revolt (132–136), noting that Jews were still in the majority until the 3rd century and even beyond, when Christianity became the empire's official religion, and continued to thrive in different parts of Palestine.[35] According to Doron Bar, archaeological evidence of synagogue remains demonstrate a central Jewish presence throughout Palestine during the entire Byzantine period.[37]
The 'ascension' of Constantine the Great in 312 and Christianity becoming the official state religion of Rome in 391, consequently brought to an end Jewish dominance in Palestine.[38] Already by the mid-3rd century the Jewish majority had been reported to have been lost, while others conclude that a Jewish majority lasted much longer – "What does seem clear is a different kind of change – immigration of Christians and the conversion of pagans, Samaritans, and Jews eventually produced a Christian majority".[4] After the Bar Kokhba revolt of 132–136 CE the make-up of the population of Palestine remains in doubt due to the sparsity of data in the historical record. Figures vary considerably as to the demographics of Palestine in the Christian era.[39]
No reliable data exist on the population of Palestine in the pre-Muslim period, either in absolute terms or in terms of shares of total population. Although many Jews were killed, expelled or sold off into slavery after the AD 66–70 and the 123–125 rebellions, the degree to which these transfers affected the Jewish dominance in Palestine is rarely addressed. What is certain is that Palestine did not lose its Jewish component. Goldblatt[4] concludes that the Jews may have remained a majority into the 3rd century AD and even beyond. He notes that 'Jewish followers of Jesus' (Jewish Christians) would not have taken part in the rebellions. Moreover, non-Christian conversions from Judaism after the Bar Kochba revolt were not given much attention.
"Indeed, many must have reacted to the catastrophe with despair and total abandonment of Judaism. Apostates from Judaism (aside from converts to Christianity) received little notice in antiquity from either Jewish or non-Jewish writers, but ambitious individuals are known to have turned pagan before the war, and it stands to reason that many more did so after its disastrous conclusion. It is impossible to determine the number who joined the budding Christian movement and the number who disappeared into the polytheist majority."[40]
Byzantine period
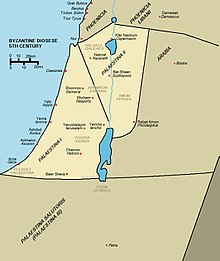
The administrative reorganization of the region in 284–305 AD by the Eastern Romans produced three Palestinian provinces of "Greater Palestine" which lasted from the 4th to the early 7th centuries: Palaestina Prima, which included the historic regions of Philistia, Judea and Samaria with the capital in Caesarea Maritima; Palaestina Secunda, which included the Galilee, the Golan Heights, as well as parts of Perea (western Transjordan) and the Decapolis, with its capital being Scythopolis; and Palaestina Salutaris which included Idumaea, the Naqab desert, Arabia Petraea, parts of Sinai, and Transjordan south of the Dead Sea, with its capital in Petra.[41][5]
Under the Byzantines, the religious landscape of Palestine underwent a significant transformation, propelled by the widescale Christianization of the local Jewish, pagan and Samaritan communities, as well as immigration of Christian pilgrims and monks into the Holy land.[42][43][44][45] After the failure of Bar Kokhba revolt in 135, Jews were barred from living in a large part of former Judaea.[46] During this period, Jews were concentrated in the Galilee, the Golan and marginal areas of the Judaean hills,[47] between Eleutheropolis and Hebron in the Daromas,[46] with significant Jewish settlement in the strip between Ein Gedi and Ascalon.[43] Jews also lived in the southern Jordan Valley near Jericho, where they were employed in date and Balsam plantations; around Narbata, in Samaria and in the Jezreel Valley. However, the main centres of Jewish life and culture during this period were the cosmopolitan cities of the coastal plains, particularly Lydda, Jamnia, Azotus and Caesarea Maritima.[46] Samaritans, originally concentrated in communities around Mount Gerizim, had spread beyond Samaria proper in the second century and established communities in the coastal plains, Judea and the Galilee, with some Samaritan villages located as far as Golan.[43] However, the Samaritan revolts against the Byzantines in 484–573 and their forced conversion to Christianity under Maurice (582–602) and Heraclius (610–641) significantly diminished their numbers.[45][44][48][49][50][51]
Pagan tradition flourished in the period before Constantine,[46] and pagans were a majority in the coastal plains,[47] Judea, Samaria, the Naqab and much of the urban centers.[43][52] Although proscribed in the Bible, pagan cults had thrived in Palestine throughout the First and Second Temple period, and many Jews did not escape it.[53][46][54][55][56] According to E. Friedheim, many Jews in Palestine also embraced paganism and pagan cults again following the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 AD.[57] Talmudic tradition forbid customs relating to 'the Amorite ways', showing a persistence of ancient Canaanite customs among the non-Jewish population and their inconsistent penetration into Jewish circles.[55]
Christian presence at the start of this period was mainly evidenced in Hellenistic cities and some of the villages in southern Judea.[43] However, Christianity's early influence in either the Jewish, Samaritan or pagan rural areas was minor and came at a much later stage around the sixth century, when many of the community churches in Judea, western Galilee, the Naqab and other places were built.[58][59][37][60] By the fifth century, many pagan temples in Palestine including those in Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Mamre, Tel Qadesh and Tel Dan, had been demolished, and churches were erected in their place.[42][58][61][59] In the rural sector, vast areas of Palestine, such as Galilee and Samaria, had Jewish and Samaritan majorities, and Christianity spread in these areas far more gradually and at a slower pace, achieving real momentum only during the second half of the Byzantine period.[37][62][35] Christianity had also spread in the Nabataean cities, towns and villages in southern Palestine, where a mixed Christian and pagan population lived, with elaborate churches built in Abdah, Mampsis and Subeita.[63]
Palestine reached its peak population of around 1 to 1.5 million during this period. However, estimates of the relative proportions of Jews, Samaritans and pagans vary widely and are speculative. By counting settlements, Avi-Yonah estimated that Jews comprised half the population of the Galilee at the end of the 3rd century, and a quarter in the other parts of the country, but had declined to 10–15% of the total by 614.[4] On the other hand, by counting churches and synagogues, Tsafrir estimated the Jewish proportion to be 25% in the Byzantine period.[4] Stemberger, however, considers that Jews were the largest population group at the beginning of the 4th century, closely followed by the pagans.[64] According to Schiffman, DellaPergola and Bar, Christians only became the majority of the country's population at the beginning of the fifth century,[65][66][58]
Islamic Period

Prior to the Muslim conquest of Palestine (635–640), Palaestina Prima had a population of 700,000, of which around 100,000 were Jews and 30-80,000 were Samaritans,[67] with the remainder being Chalcedonian and Miaphysite Christians.[5][68][69]
The pace of conversion to Islam among the Christian, Jewish, and Samaritan communities in Palestine varied during the early period (638–1098),[70] and opinions vary regarding the extent of Islamization during the early Islamic period.[71] While some argue Palestine was already majority Muslim by the time of arrival of the First Crusade, others contend that Christians were still in the majority and the process of mass adoption of Islam took place only from the 13th century onwards, during the Mamluk period.[71] Archaeologist Gideon Avni argues that archaeological surveys show that most Christian settlements and sites preserved their identity up to the crusader period, supplemented by the numerosity of churches and monasteries all over Palestine.[72] The early Muslim population, on the other hand, was confined to the Umayyad palaces in the Jordan Valley and around the Sea of Galilee, the ribat fortresses along the coast and the farms of the Naqab desert. Thus, conversion to Islam only gained real momentum in Palestine after Saladin's conquest of Jerusalem in 1187 and the expulsion of Franks.[72] Michael Ehrlich, on the other hand, believes conversion was rather quick and finalized by the time the crusades arrived in 1099.[70]
Urban centers continued to flourish after the Islamic conquest, but changes took place in the 9th and 10th centuries.[63][72] According to Ellenblum, climate disasters and earthquakes in the late 10th & 11th centuries created internal chaos and famines throughout the Middle East, as well as population decline.[73] Ehrlich argues the decline in urban centers likely caused local ecclesiastical administrations to weaken or disappear altogether, leaving Christians most susceptible to conversion. When certain urban centers collapsed, surrounding communities would have converted to Islam.[70] Per Ellenblum, the eastern Galilee and central Samaria, where Jews and Samaritans were concentrated respectively, were converted rather quickly and had a Muslim or Jewish-Muslim majority by the crusader period.[70][74] In Samaria, the sedentarization of nomadic tribes that penetrated Samaria was complemented by the mass conversion of the Samaritan population starting from the Tulunid period (884–905).[75] By the 12th century, central Samaria was the only fully Islamized region in Palestine, while Christians predominated in southern Samaria, the Sinjil-Jerusalem area, the western Galilee and the Hebron Hills, which only converted in later periods.[74] The introduction of Islam in the Hebron hills is archaeologically attested in Jewish villages but not Christian ones, mainly in Susya and Eshtemoa, where the local synagogues were repurposed as mosques.[72]
Coastal cities such as Ramla and Ascalon thrived under the Fatimids (969–1099), where many Shiite scholars sought refuge and Shiite shrines were built,[76] and the hinterland of Ramla was predominantly Muslim when the crusaders conquered it.[70] On the other hand, Sufis played an important role in the Islamization of the hinterland of Jerusalem, where they built many religious buildings during the Mamluk period, transforming the cultural landscape. According to Nimrod Luz, when a Sufi settled in a Christian village, the local population often converted to Islam.[77][78][79] According to Reuven Atimal, conversion to Islam appears to have halted and apparently even been reversed under the Kingdom of Jerusalem (1099–1291). With the advent of the Ayyubids (1187–1260) and then the consequent Mamluk takeover (1260–1517), it appears that the process of religious conversion to Islam was accelerated. By the start of the Ottoman period in 1516, it is commonly thought that the Muslim majority in the country was more-or-less like that of the mid-19th century.[80] Conversion among the Samaritan families of Nablus to Islam continued well into the 19th century.[81][82]
Ottoman period
| Year | Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ottoman | Muslims | Jews | Christians | Total | |
| 1850–1851 | 1267 | 300,000 | 13,000 | 27,000 | 340,000 |
| 1860–1861 | 1277 | 325,000 | 13,000 | 31,000 | 369,000 |
| 1877–1878 | 1295 | 386,320 | 13,942 | 40,588 | 440,850 |
| 1878–1879 | 1296 | 390,597 | 14,197 | 41,331 | 446,125 |
| 1879–1880 | 1297 | 394,935 | 14,460 | 42,089 | 451,484 |
| 1880–1881 | 1298 | 399,334 | 14,731 | 42,864 | 456,929 |
| 1881–1882 | 1299 | 403,795 | 15,011 | 43,659 | 462,465 |
| 1882–1883 | 1300 | 408,318 | 15,300 | 44,471 | 468,089 |
| 1883–1884 | 1301 | 412,906 | 15,599 | 45,302 | 473,807 |
| 1884–1885 | 1302 | 417,560 | 15,908 | 46,152 | 479,620 |
| 1885–1886 | 1303 | 422,280 | 16,228 | 47,022 | 485,530 |
| 1886–1887 | 1304 | 427,068 | 16,556 | 47,912 | 491,536 |
| 1887–1888 | 1305 | 431,925 | 16,897 | 48,823 | 497,645 |
| 1888–1889 | 1306 | 436,854 | 17,249 | 49,756 | 503,859 |
| 1889–1890 | 1307 | 441,267 | 17,614 | 51,065 | 509,946 |
| 1890–1891 | 1308 | 445,728 | 17,991 | 52,412 | 516,131 |
| 1891–1892 | 1309 | 450,239 | 18,380 | 53,792 | 522,411 |
| 1892–1893 | 1310 | 454,799 | 18,782 | 55,212 | 528,793 |
| 1893–1894 | 1311 | 459,410 | 19,198 | 56,670 | 535,278 |
| 1894–1895 | 1312 | 464,550 | 19,649 | 57,815 | 542,014 |
| 1895–1896 | 1313 | 469,750 | 20,117 | 58,987 | 548,854 |
| 1896–1897 | 1314 | 475,261 | 20,780 | 59,903 | 555,944 |
| 1897–1898 | 1315 | 480,843 | 21,466 | 60,834 | 563,143 |
| 1898–1899 | 1316 | 486,850 | 22,173 | 61,810 | 570,833 |
| 1899–1900 | 1317 | 492,940 | 22,905 | 62,801 | 578,646 |
| 1900–1901 | 1318 | 499,110 | 23,662 | 63,809 | 586,581 |
| 1901–1902 | 1319 | 505,364 | 24,446 | 64,832 | 594,642 |
| 1902–1903 | 1320 | 511,702 | 25,257 | 65,872 | 602,831 |
| 1903–1904 | 1321 | 518,126 | 26,096 | 66,928 | 611,150 |
| 1904–1905 | 1322 | 524,637 | 26,965 | 68,002 | 619,604 |
| 1905–1906 | 1323 | 531,236 | 27,862 | 69,092 | 628,190 |
| 1906–1907 | 1324 | 537,925 | 28,791 | 70,201 | 636,917 |
| 1907–1908 | 1325 | 544,704 | 29,753 | 71,327 | 645,784 |
| 1908–1909 | 1326 | 551,576 | 30,749 | 72,471 | 654,796 |
| 1909–1910 | 1327 | 558,541 | 31,778 | 73,633 | 663,952 |
| 1910–1911 | 1328 | 565,601 | 32,843 | 74,815 | 673,259 |
| 1910–1911 | 1329 | 572,758 | 33,946 | 76,015 | 682,719 |
| 1911–1912 | 1330 | 580,012 | 35,087 | 77,235 | 692,334 |
| 1912–1913 | 1331 | 587,366 | 36,267 | 78,474 | 702,107 |
| 1913–1914 | 1332 | 594,820 | 37,489 | 79,734 | 712,043 |
| 1914–1915 | 1333 | 602,377 | 38,754 | 81,012 | 722,143 |
| Figures from McCarthy, 1990, p. 10. | |||||
Early Ottoman period
During the first century of the Ottoman rule, i.e., 1550, Bernard Lewis in a study of Ottoman registers of the early Ottoman Rule of Palestine reports a population of around 300,000:[83][84]
From the mass of detail in the registers, it is possible to extract something like a general picture of the economic life of the country in that period. Out of a total population of about 300,000 souls, between a fifth and a quarter lived in the six towns of Jerusalem, Gaza, Safed, Nablus, Ramle, and Hebron. The remainder consisted mainly of peasants (fellahin), living in villages of varying size, and engaged in agriculture. Their main food-crops were wheat and barley in that order, supplemented by leguminous pulses, olives, fruit, and vegetables. In and around most of the towns there was a considerable number of vineyards, orchards, and vegetable gardens.
According to Justin McCarthy, the population of Palestine throughout the 17th and 18th centuries (1601–1801) was likely not much smaller than when it in 1850 (~340,000), after which it started to increase.[85][page needed]
Late Ottoman period
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, there were several migration waves of Egyptians to Palestine. One notable influx occurred in the 1780s due to a severe famine in Egypt. The main migration wave happened between 1829 and 1841, when Muhammad Ali and Ibrahim Pasha invaded Palestine, some Egyptian settlers and army dropouts stayed in Palestine after Egyptian retreat. These migrants primarily settled in the low country: in the Beisan area, Wadi Araba, the Jezreel valley, the Shephelah, the coastal plain and the Negev desert.[86][87] In total some 20,000 Egyptians had settled in Palestine by 1850.[86] Algerian refugees ("Maghrebis") also arrived in Palestine in the 1850s following Abdelkader's rebellion.[88][89] Many settled in abandoned villages in Galilee, and in Safed.[88]
| Ottoman population in 1850 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qaza (region) | Number of towns and villages |
Number of households
| ||||
| Muslims | Christians | Jews | Total | |||
| 1 | Jerusalem | |||||
| Jerusalem | 1 | 1,025 | 738 | 630 | 2,393 | |
| Countryside | 116 | 6,118 | 1,202 | - |
7,320 | |
| 2 | Hebron | |||||
| Hebron | 1 | 2,800 | - |
200 | 3,000 | |
| Countryside | 52 | 2,820 | - |
- |
2,820 | |
| 3 | Gaza | |||||
| Gaza | 1 | 2,690 | 65 | - |
2,755 | |
| Countryside | 55 | 6,417 | - |
- |
6,417 | |
| 3 | Jaffa | |||||
| Jaffa | 3 | 865 | 266 | - |
1,131 | |
| Ludd | . | 700 | 207 | - |
907 | |
| Ramla | . | 675 | 250 | - |
925 | |
| Countryside | 61 | 3,439 | - |
- |
3,439 | |
| 4 | Nablus | |||||
| Nablus | 1 | 1,356 | 108 | 14 | 1,478 | |
| Countryside | 176 | 13,022 | 202 | - |
13,224 | |
| 5 | Jinin | |||||
| Jinin | 1 | 656 | 16 | - |
672 | |
| Countryside | 39 | 2,120 | 17 | - |
2,137 | |
| 6 | Akka | |||||
| Akka | 1 | 547 | 210 | 6 | 763 | |
| Countryside | 34 | 1,768 | 1,021 | - |
2,789 | |
| 7 | Haifa | |||||
| Haifa | 1 | 224 | 228 | 8 | 460 | |
| Countryside | 41 | 2,011 | 161 | - |
2,171 | |
| 8 | Nazareth | |||||
| Nazareth | 1 | 275 | 1,073 | - |
1,348 | |
| Countryside | 38 | 1,606 | 544 | - |
2,150 | |
| 9 | Tiberias | |||||
| Tiberias | 1 | 159 | 66 | 400 | 625 | |
| Countryside | 7 | 507 | - |
- |
507 | |
| 10 | Safad | |||||
| Safad | 1 | 1,295 | 3 | 1,197 | 2,495 | |
| Countryside | 38 | 1,117 | 616 | - |
1,733 | |
| Figures from Ben-Arieh, in Scholch 1985, p. 388. | ||||||
In the late nineteenth century, prior to the rise of Zionism, Jews are thought to have comprised between 2% and 5% of the population of Palestine, although the precise population is not known.[90] Jewish immigration had begun following the 1839 Tanzimat reforms; between 1840 and 1880, the Jewish population of Palestine rose from 9,000 to 23,000.[91]
According to Alexander Scholch, Palestine in 1850 had about 350,000 inhabitants, 30% of whom lived in 13 towns; roughly 85% were Muslims, 11% were Christians and 4% Jews.[92]
The Ottoman census of 1878 indicated the following demographics for the three districts that best approximated what later became Mandatory Palestine; that is, the Mutasarrifate of Jerusalem, the Nablus Sanjak, and the Acre Sanjak.[90] In addition, some scholars estimate approximately 5,000-10,000 additional foreign-born Jews at this time:[93]
| Group | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Muslim citizens | 403,795 | 86–87% |
| Christian citizens | 43,659 | 9% |
| Jewish citizens | 15,011 | 3% |
| Jewish (foreign-born) | Est. 5–10,000 | 1–2% |
| Total | Up to 472,465 | 100.0% |
According to Ottoman statistics studied by Justin McCarthy,[94] the population of Palestine in the early 19th century was 350,000, in 1860 it was 411,000 and in 1900 about 600,000 of which 94% were Arabs.
The estimated 24,000 Jews in Palestine in 1882 represented just 0.3% of the world's Jewish population.[95]
1914 Ottoman census listed the following population figures:[96]
| Muslims | Greek Orthodox | Greek Catholics | Jews | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beirut vilayet | Acre Sanjak | Akka | 31,610 | 3,923 | 4,311 | 106 | 40,665 |
| Hayfa | 23,338 | 881 | 2,553 | 1,099 | 28,802 | ||
| Taberiye | 8,328 | 150 | 244 | 3,060 | 13,054 | ||
| Safed | 22,356 | 324 | 2044 | 4,126 | 31,322 | ||
| Nasıra | 11,527 | 2371 | 1588 | 19,912 | |||
| Total | 97,159 | 9,503 | 10,740 | 8,351 | 133,755 | ||
| Nablus Sanjak | Nablus | 74,500 | 1030 | 29 | 76,428 | ||
| Benissaab | 35,787 | 18 | 35,809 | ||||
| Cenin | 40,589 | 755 | 41,657 | ||||
| Total | 150,876 | 1803 | 29 | 153,854 | |||
| Jerusalem Sanjak | Kudüs-i Şerif | 70,270 | 19,717 | 533 | 18,190 | 120,921 | |
| Yafa | 62,758 | 5,312 | 553 | 2,105 | 72,206 | ||
| Gazze | 77,296 | 1006 | 243 | 78,597 | |||
| Halil'ül-Rahman | 55,720 | 721 | 56,444 | ||||
| Total | 266,044 | 26,035 | 1,086 | 21,259 | 328,168 | ||
| Total for the three sanjaks | 514,079 | 36,741 | 11,826 | 29,639 | 615,777 | ||
Per McCarthy's estimate, in 1914 Palestine had a population of 657,000 Muslim Arabs, 81,000 Christian Arabs, and 59,000 Jews.[85] McCarthy estimates the non-Jewish population of Palestine at 452,789 in 1882, 737,389 in 1914, 725,507 in 1922, 880,746 in 1931 and 1,339,763 in 1946.[97]
Based on the work of Roberto Bachi, Sergio Della Pergola estimated that Palestine's population in 1914 was 689,000, comprising 525,000 Muslims, 94,000 Jews, and 70,000 Christians.[3]
According to another estimate, the Jewish population in 1914 was 85,000 and subsequently fell to 56,000 in 1916–1919[98] as a result of World War I. During the war, the Ottoman authorities deported many Jews with foreign citizenship, while others left after they were presented with a choice of taking Ottoman citizenship or leaving Palestine. By December 1915 about 14% of the Jewish population had left, mainly for Egypt, where they awaited the war's end so they could return to Palestine.[99]
According to Dr. Mutaz M. Qafisheh, the number of people who held Ottoman citizenship prior to the British Mandate in 1922 was just over 729,873, of which 7,143 were Jews.[100] Qafisheh calculated this using population and immigration statistics from the 1946 Survey of Palestine, as well as the fact that 37,997 people acquired provisional Palestinian naturalization certificates in September 1922 for the purpose of voting in the legislative election,[101] of which all but 100 were Jews.[102] The 1922 census of Palestine lists 3,210 Christians as members of Armenian churches, 271 being Armenian Catholic (176 in Jerusalem-Jaffa, 10 in Samaria, and 85 in Northern) and 2,939 being Armenian Apostolic (11 in Southern, 2,800 in Jerusalem-Jaffa, eight in Samaria, and 120 in Northern) along with 2,970 Armenian speakers, including 2,906 in municipal areas (2,442 in Jerusalem, 216 in Jaffa, 101 in Haifa, four in Gaza, 13 in Nablus, one in Safad, 20 in Nazareth, 13 in Ramleh, one in Tiberias, 37 in Bethlehem, 25 in Acre, four in Tulkarem, 21 in Ramallah, six in Jenin, one in Beersheba, and one in Baisan).[103]
British Mandate era
Official reports
In 1920, the British Government's Interim Report on the Civil Administration of Palestine stated that there were hardly 700,000 people living in Palestine:
There are now in the whole of Palestine hardly 700,000 people, a population much less than that of the province of Gallilee alone in the time of Christ. Of these 235,000 live in the larger towns, 465,000 in the smaller towns and villages. Four-fifths of the whole population are Moslems. A small proportion of these are Bedouin Arabs; the remainder, although they speak Arabic and are termed Arabs, are largely of mixed race. Some 77,000 of the population are Christians, in large majority belonging to the Orthodox Church, and speaking Arabic. The minority are members of the Latin or of the Uniate Greek Catholic Church, or—a small number—are Protestants. The Jewish element of the population numbers 76,000. Almost all have entered Palestine during the last 40 years. Prior to 1850 there were in the country only a handful of Jews. In the following 30 years a few hundreds came to Palestine. Most of them were animated by religious motives; they came to pray and to die in the Holy Land, and to be buried in its soil. After the persecutions in Russia forty years ago, the movement of the Jews to Palestine assumed larger proportions. Jewish agricultural colonies were founded. They developed the culture of oranges and gave importance to the Jaffa orange trade. They cultivated the vine, and manufactured and exported wine. They drained swamps. They planted eucalyptus trees. They practised, with modern methods, all the processes of agriculture. There are at the present time 64 of these settlements, large and small, with a population of some 15,000.[104]
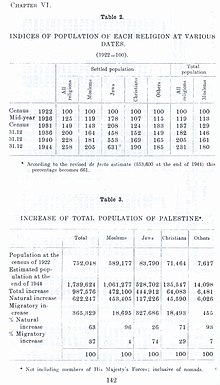
By 1948, the population had risen to 1,900,000, of whom 68% were Arabs, and 32% were Jews (UNSCOP report, including Bedouin).
| Year | Muslims | Christians | Jews | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1922 | 589,177 | 73,024 | 83,790 | 757,182 |
| 1931 | 759,717 | 91,398 | 174,610 | 1,035,821 |
| 1945 | 1,061,270 | 135,550 | 553,600 | 1,764,520 |
Report and general abstract of the Jewish agriculture was taken by the Palestine Zionist Executive in April 1927.
Object of the Census:
(p 85) Demography: to enumerate all Jewish inhabitants living in the agricultural and semi-agricultural communities.
(p 86) Number of Settlements: 130 places have been enumerated. If we consider the large settlements and the adjacent territories as one geographical unit, then we may group these places into 101 agricultural settlements, 3 semi-agricultural places (Affule, Shekhunath Borukhov and Neve Yaaqov) and 12 farms scattered throughout the country. In addition, there were a few places which, owing to technical difficulties, were not enumerated in the month of April. (Peqiin, Meiron, Mizpa and Zikhron David, numbering in the aggregate 100 persons).
Of these agricultural settlements, 32 are located in Judea, 12 in the Plain of Sharon, 32 are located in the Plain of Jesreel, 16 in Lower Galilee, and 9 in Upper Galilee. Most of them have a very small population – about one half being inhabited by less than 100 persons each. In 42 settlements there are from 100 to 500 persons, and in only five does the population exceed 1.000. viz.
Settlements Persons Pethah Tiqva 6,631 Rishon le-Ziyon 2,143 Rehovoth 1,689 Hadera 1,378 Zihron Yaaqov 1,260 (p 86) Number of Inhabitants: The aggregate population living in the agricultural and semi-agricultural places were 30.500.
Male Female 1 day – 10 years 3,298 3,188 11 years – 20 years 3,059 2,597 21 years – 30 years 5,743 4,100 31 years – 40 years 1,821 1,411 41 years – 50 years 1,011 0,922 Over 50 years and unknown 1,763 1,587 Total 16,695 13,805
- Length of Residence in Palestine
(p 87 & p 98) The pre-war population accounts for 9,473 persons, which is slightly less than one-third of the present population, whereas the rest are post-war immigrants. Some 10.000 persons settled since 1924, since the so-called middle-class immigration.
Length of residence in Years Men Women Children Total % 1 1504 1118 1746 4368 14.2 2 2406 2020 1575 6001 19.6 3 1311 913 1133 3357 11.5 4 695 556 720 1971 6.4 5 682 454 513 1649 5.4 6 856 403 390 1649 5.4 7 682 277 379 1358 4.3 8 139 45 261 445 1.5 9 39 10 200 249 0.8 10–13 237 218 893 1348 4.4 14–20 1882 1630 216 3728 12.1 21–29 864 800 - 1664 5.4 Over 30 836 930 - 1766 5.8 Unspecified 336 281 350 967 3.2 Total 12,469 9,655 8,376 30,500 100%
Late Arab and Muslim immigration to Palestine

Ottoman period, 1800–1918
At the end of the 18th century, there was a bi-directional movement between Egypt and Palestine. Between 1829 and 1841, thousands of Egyptian fellahin (peasants) arrived in Palestine fleeing Muhammad Ali Pasha's conscription, which he reasoned as the casus belli to invade Palestine in October 1831, ostensibly to repatriate the Egyptian fugitives.[106][107][108] Egyptian forced labourers, mostly from the Nile Delta, were brought in by Muhammad Ali and settled in sakināt (neighborhoods) along the coast for agriculture, which set off bad blood with the indigenous fellahin, who resented Muhammad Ali's plans and interference, prompting the wide-scale Peasants' revolt in Palestine in 1834.[106][109][110] After Egyptian defeat and retreat in 1841, many laborers and deserters stayed in Palestine.[107] Most of these settled and were quickly assimilated in the cities of Jaffa and Gaza, the Coastal plains and Wadi Ara.[107] Estimates of Egyptian migrants during this period generally place them at 15,000–30,000.[107] At the time, the sedentary population of Palestine fluctuated around 350,000.[107] Palestine experienced a few waves of immigration of Muslims from the lands lost by the Ottoman Empire in the 19th century. Algerians, Circassians and Bosniaks were mostly settled on vacant land and unlike the Egyptians they did not alter the geography of settlement significantly.[107]: 73
The Naqab desert further south preserved its Bedouin population, who had reportedly lived in the area since the 7th century. Many Bedouin tribes moved from the Hejaz and Transjordan in the 14th and 15th centuries. According to the 1922 census of Palestine, "The Ottoman authorities in 1914 placed the tribal population of Beersheba at 55,000, and since that date there has been a migration of tribes from the Hejaz and Southern Transjordan into the Beersheba area mainly as a result of succession of adequate rainfalls and of pressure exerted by other tribes east of the River Jordan." For 1922, the census gives a figure of 74,910 including 72,998 in the tribal areas.[111]
Demographer Uziel Schmelz, in his analysis of Ottoman registration data for 1905 populations of Jerusalem and Hebron kazas, found that most Ottoman citizens living in these areas, comprising about one quarter of the population of Palestine, were living at the place where they were born. Specifically, of Muslims, 93.1% were born in their current locality of residence, 5.2% were born elsewhere in Palestine, and 1.6% were born outside Palestine. Of Christians, 93.4% were born in their current locality, 3.0% were born elsewhere in Palestine, and 3.6% were born outside Palestine. Of Jews (excluding the large fraction who were not Ottoman citizens), 59.0% were born in their current locality, 1.9% were born elsewhere in Palestine, and 39.0% were born outside Palestine.[112]
British Mandate period, 1919–1948
This article contains too many or overly lengthy quotations. (June 2024) |

According to Roberto Bachi, head of the Israeli Institute of Statistics from 1949 onwards, between 1922 and 1945 there was a net Arab migration into Palestine of between 40,000 and 42,000, excluding 9,700 people who were incorporated after territorial adjustments were made to the borders in the 1920s. Based on these figures, and including those netted by the border alterations, Joseph Melzer calculates an upper boundary of 8.5% for Arab growth in the two decades, and interprets it to mean the local Palestinian community's growth was generated primarily by natural increase in birth rates, for both Muslims and Christians.[113]
| Year | Muslims | Christians | Jews | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1922 | 589,177 | 73,024 | 83,790 | 757,182 |
| 1931 | 759,717 | 174,610 | 91,398 | 1,035,821 |
| 1945 | 1,061,270 | 135,550 | 553,600 | 1,764,520 |
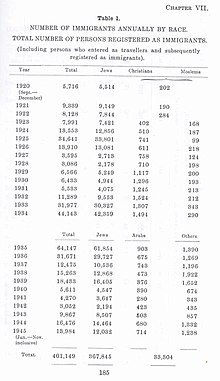
According to a Jewish Agency survey, 77% of Palestinian population growth in Palestine between 1914 and 1938, during which the Palestinian population doubled, was due to natural increase, while 23% was due to immigration. Arab immigration was primarily from Lebanon, Syria, Transjordan, and Egypt (all countries that bordered Palestine).[114]
The overall assessment of several British reports was that the increase in the Arab population was primarily due to natural increase.[115][116] These included the Hope Simpson Enquiry (1930),[117] the Passfield White Paper (1930),[118] the Peel Commission report (1937),[119] and the Survey of Palestine (1945).[120] However, the Hope Simpson Enquiry did note that there was significant illegal immigration from the surrounding Arab territories,[117] while the Peel Commission and Survey of Palestine claimed that immigration played only a minor role in the growth of the Arab population. The 1931 census of Palestine considered the question of illegal immigration since the previous census in 1922.[121] It estimated that unrecorded immigration during that period may have amounted to 9,000 Jews and 4,000 Arabs.[121] It also gave the proportion of persons living in Palestine in 1931 who were born outside Palestine: Muslims, 2%; Christians, 20%; Jews, 58%.[121] The statistical information for Arab immigration (and expulsions when the clandestine migrants were caught), with a contrast to the figures for Jewish immigration over the same period of 1936–1939, is given by Henry Laurens in the following terms[122]
-
- Palestinian immigration, 1936–1939
Jews Arabs 69,716 2,267
- Expulsions of illegals, 1937–1938
Jews Arabs (et al.). 125 1,704
According to Mark Tessler, at least some of the Arab population growth was the result of immigration, mostly from the Sinai, Lebanon, Syria, and Transjordan, stimulated by the relatively favorable economic conditions in Palestine, but he noted differing opinions among scholars over how substantial it was. He cited one study as putting the Arab population growth attributable to immigration between 1922 and 1931 at 7%, meaning that 4% of the Arab population in 1931 was foreign-born, while noting another estimate[123] put the growth in the Arab population attributable to immigration at 38.7%, which would mean that 11.8% of the Arab population in 1931 was foreign-born. Tessler wrote that "Israeli as well as Palestinian scholars have disputed this assertion, however, concluding that it is at best a theory and in all probability a myth."[124]
In a 1974 study, demographer Roberto Bachi estimated that about 900 Muslims per year were detected as illegal immigrants but not deported.[125] He noted the impossibility of estimating illegal immigration that was undetected, or the fraction of those persons who eventually departed.[125] He did note that there was an unexplained increase in the Muslim population between 1922 and 1931, and he did suggest, though qualifying it as a "mere guess", that this was due to a combination of unrecorded immigration (using the 1931 census report estimate) and undercounting in the 1922 census.[125]
While noting the uncertainty of earlier data, Bachi also observed that the Muslim population growth in the 19th century appeared to be high by world standards:
"[B]etween 1800 and 1914, the Muslim population had a yearly average increase of an order of magnitude of roughly 6–7 per thousand. This can be compared to the very crude estimate of about 4 per thousand for the "less developed countries" of the world (in Asia, Africa, and Latin America) between 1800 and 1910. It is possible that some part of the growth of the Muslim population was due to immigration. However, it seems likely that the dominant determinant of this modest growth was the beginning of some natural increase."[126]
According to Justin McCarthy, "... evidence for Muslim immigration into Palestine is minimal. Because no Ottoman records of that immigration have yet been discovered, one is thrown back on demographic analysis to evaluate Muslim migration."[127] McCarthy argues that there is no significant Arab immigration into mandatory Palestine:
From analyses of rates of increase of the Muslim population of the three Palestinian sanjaks, one can say with certainty that Muslim immigration after the 1870s was small. Had there been a large group of Muslim immigrants their numbers would have caused an unusual increase in the population and this would have appeared in the calculated rate of increase from one registration list to another... Such an increase would have been easily noticed; it was not there.[128]
The argument that Arab immigration somehow made up a large part of the Palestinian Arab population is thus statistically untenable. The vast majority of the Palestinian Arabs resident in 1947 were the sons and daughters of Arabs who were living in Palestine before modern Jewish immigration began. There is no reason to believe that they were not the sons and daughters of Arabs who had been in Palestine for many centuries.[129]
McCarthy also concludes that there was no significant internal migration to Jewish areas attributable to better economic conditions:
Some areas of Palestine did experience greater population growth than others, but the explanation for this is simple. Radical economic change was occurring all over the Mediterranean Basin at the time. Improved transportation, greater mercantile activity, and greater industry had increased the chances for employment in cities, especially coastal cities... Differential population increase was occurring all over the Eastern Mediterranean, not just in Palestine... The increase in Muslim population had little or nothing to do with Jewish immigration. In fact the province that experienced the greatest Jewish population growth (by .035 annually), Jerusalem Sanjak, was the province with the lowest rate of growth of Muslim population (.009).[130]
Fred M. Gottheil has questioned McCarthy's estimates of immigration. Gottheil says that McCarthy didn't give proper weight to the importance of economic incentives at the time, and that McCarthy cites Roberto Bachi's estimates as conclusive numbers, rather than lower bounds based on detected illegal immigration.[123][131]
Gad Gilbar has also concluded that the prosperity of Palestine in the 45–50 years before World War I was a result of the modernization and growth of the economy owing to its integration with the world economy and especially with the economies of Europe. Although the reasons for growth were exogenous to Palestine the bearers were not waves of Jewish immigration, foreign intervention nor Ottoman reforms but "primarily local Arab Muslims and Christians."[132] However, Gilbar did attribute the rapid growth of Jaffa and Haifa in the final three decades of Ottoman rule in part to migration, writing that "both attracted population from the rural and urban surroundings and immigrants from outside Palestine."[133]
Yehoshua Porath believes that the notion of "large-scale immigration of Arabs from the neighboring countries" is a myth "proposed by Zionist writers". He writes:
As all the research by historian Fares Abdul Rahim and geographers of modern Palestine shows, the Arab population began to grow again in the middle of the nineteenth century. That growth resulted from a new factor: the demographic revolution. Until the 1850s there was no "natural" increase of the population, but this began to change when modern medical treatment was introduced and modern hospitals were established, both by the Ottoman authorities and by the foreign Christian missionaries. The number of births remained steady but infant mortality decreased. This was the main reason for Arab population growth. ... No one would doubt that some migrant workers came to Palestine from Syria and Trans-Jordan and remained there. But one has to add to this that there were migrations in the opposite direction as well. For example, a tradition developed in Hebron to go to study and work in Cairo, with the result that a permanent community of Hebronites had been living in Cairo since the fifteenth century. Trans-Jordan exported unskilled casual labor to Palestine; but before 1948 its civil service attracted a good many educated Palestinian Arabs who did not find work in Palestine itself. Demographically speaking, however, neither movement of population was significant in comparison to the decisive factor of natural increase.[134]
Modern era
As of 2014[update], Israeli and Palestinian statistics for the overall numbers of Jews and Arabs in the area west of the Jordan, inclusive of Israel and the Palestinian territories, are similar and suggest a rough parity in the two populations. Palestinian statistics estimate 6.1 million Palestinians for that area, while Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics estimates 6.2 million Jews living in sovereign Israel. Gaza is estimated by the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) to have 1.7 million, and the West Bank 2.8 million Palestinians, while Israel proper has 1.7 million Arab citizens.[135] According to Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics, as of May 2006, of Israel's 7 million people, 77% were Jews, 18.5% Arabs, and 4.3% "others".[136] Among Jews, 68% were Sabras (Israeli-born), mostly second- or third-generation Israelis, and the rest are olim – 22% from Europe and the Americas, and 10% from Asia and Africa, including the Arab countries.[137]
According to these Israeli and Palestinian estimates, the population in Israel and the Palestinian territories stands at from 6.1 to 6.2 million Palestinians and 6.1 million Jews.[135][failed verification] According to Sergio DellaPergola, if foreign workers and non-Jewish Russian immigrants in Israel are subtracted, Jews are already a minority in the land between the river and the sea.[135] DellaPergola calculates that Palestinians as of January 2014 number 5.7 million as opposed to a "core Jewish population" of 6.1 million.[135]
The Palestinian statistics are contested by some right-wing Israeli think-tanks and non-demographers such as Yoram Ettinger, who claim they overestimate Palestinian numbers by double-counting and counting Palestinians who live abroad. The double-counting argument is dismissed by both Arnon Soffer, Ian Lustick[138] and DellaPergola, the latter dismissing Ettinger's calculations as 'delusional' or manipulated for ignoring the birth-rate differentials between the two populations (3 children per Jewish mother vs 3.4 for Palestinians generally, and 4.1 in the Gaza Strip). DellaPergola allows, however, for an inflation in the Palestinian statistics due to the counting of Palestinians who are abroad, a discrepancy of some 380,000 individuals.[135]
Demographics of the State of Israel
The latest Israeli census was conducted by Israel Central Bureau of Statistics in 2019. Israeli census excludes the Gaza Strip. It also excludes all West Bank Palestinian localities, including those in Area C, while it includes the annexed East Jerusalem. It also includes all Israeli settlements in the West Bank. The census also includes the occupied Syrian territory of Golan Heights.
As per this census, the total population in 2019 was 9,140,473.[139] Israeli population consists of 7,221,442 "Jews and others", and 1,919,031 Arabs, almost all of which Palestinians, with 26,261 in Golan Subdistrict, being Syrian, mostly Druze, and a small number Alawite. The population includes the Druze community of Israel (i.e. not Syrian Druze) as well, who generally self-identify as Israeli, and are the only Arab-speaking community that has mandatory military service in the IDF.
Demographics of the State of Palestine
The latest Palestinian Census was conducted by Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics in 2017.[140] The Palestinian census covers the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, including East Jerusalem. The Palestinian census does not cover Israeli settlements in the West Bank including those in East Jerusalem. The census does not provide any ethnic or religious distinction. However, it is reasonable to assume that almost everyone counted is Palestinian Arab.
As per this census, the total population of the Palestinian territories was 4,780,978.[140] The West Bank had a population of 2,881,687, whereas the Gaza Strip had a population of 1,899,291.
Combined demographics
This page or section uses colour as the only way to convey important information. (February 2024) |
| counted by Palestinian Authority | counted by Israel | ||
| Israel counts Palestinians only in East Jerusalem + all Israelis; Palestinian Authority counts all residents | counted by both |
| Region & Status |
By nationality | Total Population |
Year Source |
By ethnoreligious group | Area (km2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Israelis | Year Source |
Palestinian Non-Israeli Citizens |
Year Source |
Jewish | Arab | Other | ||||
| West Bank Areas A & B (Occupied, partial Palestinian control) | 0 | 1,828,115 | 2023 [141] |
1,828,115 | 2023 [141] |
0 | 1,828,115 | 0 | ||
| West Bank Area C (Occupied, full Israeli control) including Seam Zone[142] | 517,407 | 1/2024 [143][144] |
300,000 | 2019 [145][146] |
817,407 | 2019/ /-24[147] |
517,407 | 300,000 | not specified separately | |
| East Jerusalem (Occupied/Annexed)[148][149][150] | 240,832 incl. Israeli Arab ~18,982 |
2021 [151] |
370,552 | 2021 [151] |
611,384 | 2021 [151] |
221,850 | 389,534 incl. Israeli Arab ~18,982 |
not specified separately | |
| Total West Bank incl. East Jerusalem | 758,239 | 2,498,667 | 3,256,906 | [152] | 739,257 | 2,517,649 | not specified separately | 5,880 [153] | ||
| Gaza Strip | 0 | 2,226,544 | 2023 [141] |
2,226,544 | 2023 [141] |
0 | 2,226,544 | 0 | 365 | |
| Total Area of the Region of Palestine outside the Green Line | 7,087 | |||||||||
| Green Line | 8,289,657 | 2019/ -21/-3 [155] |
0 | 8,289,657 | 2019/ -21/-3 [154] |
6,787,743 74% |
1,299,484 20% |
554,000 6% |
20,582 [154] | |
| Golan Heights (Occupied/Annexed) [148][149][150][156] |
53,000 |
2021 |
0 |
2021 |
53,000 |
2021 |
27,000 | 26,000 | 0 | 1,154 |
| Total Area of the State of Israel as defined by the Israeli CBS | 22,072 | |||||||||
| CBS Total Population of Israel | 9,471,448 | 370,552
(i.e. East Jerusalem Palestinians) |
9,842,000 |
Dec. 2023 |
7,554,000 | Israeli cit. 1,734,000 Non-Israeli ~370,552 |
554,000 | |||
| Total Israel + Palestine combined | 9,471,448 | derived | 4,725,211 | derived | 14,833,110 | Sum | 7,554,000 (50.7%) | 6,778,193 (45.5%) Israeli 1,734,000 (11.6%), Non-Israeli 5,044,193 (33.9%) |
554,000 (3.7%) | 25,650 |
Note: Israeli definitions
The Israel Central Bureau of Statistics ("CBS") definition of the Area of the State of Israel:[159]
- includes East Jerusalem since 1967, which Israel unilaterally annexed
- includes the Golan Heights since 1982, which Israel unilaterally annexed
- excludes the West Bank other than East Jerusalem
The CBS' definition of the Population of Israel, however:[160]
- includes non-Israeli Palestinians (as well as Israeli Arabs/Palestinians) in East Jerusalem who have permission to live there
- includes Israeli settlers and others with Israeli residency permits living in the Area C of West Bank
- excludes Palestinian/Arab/other residents of Area C and East Jerusalem who do not have Israeli citizenship or residence
- excludes persons who are not registered (from 2008 on) and/or entered illegally, and foreign workers
See also
- History of Palestine
- Demographic history of Jerusalem
- Demographics of Israel
- Demographics of the Palestinian territories
- Muslim history in Palestine
- History of the Jewish community in Palestine
- History of Christianity in Palestine
- Genetic history of the Middle East
- Travelogues of Ottoman Palestine – for early travellers commenting on demographics
- Timeline of the Palestine region
- Time periods in the Palestine region
Notes
- ^ Excluding environs.
References
- ^ An Introduction to Jewish-Christian Relations by Edward Kessler P72
- ^ The Cambridge History of Judaism: Volume 4, The Late Roman-Rabbinic Period By William David Davies, Louis Finkelstein, P:409
- ^ a b Pergola, Sergio della (2001). "Demography in Israel/Palestine: Trends, Prospects, Policy Implications" (PDF). Semantic Scholar. S2CID 45782452. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 August 2018.
- ^ a b c d e David Goodblatt (2006). "The political and social history of the Jewish community in the Land of Israel, c. 235–638". In Steven Katz (ed.). The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. IV. Cambridge University Press. pp. 404–430. ISBN 978-0-521-77248-8.
- ^ a b c Estakhri quoted by Le Strange, G. (1890). Palestine Under the Moslems: A Description of Syria and the Holy Land from A.D. 650 to 1500. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund. pp. 25–30. OCLC 1004386.
- ^ Stern, Ephraim. "The Religious Revolution in Persian-Period Judah". Judah and the Judeans in the Persian Period, edited by Oded Lipschits and Manfred Oeming, University Park, USA: Penn State University Press, 2006, pp. 199-206. https://doi.org/10.1515/9781575065618-011
- ^ Carter, Charles E. (1999). The Emergence of Yehud in the Persian Period: A Social and Demographic Study. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9780567250889.
- ^ Yigal Shiloh, The Population of Iron Age Palestine in the Light of a Sample Analysis of Urban Plans, Areas, and Population Density, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, No. 239, p.33, 1980.
- ^ Pastor, Jack (2013). Land and Economy in Ancient Palestine. Routledge. p. 7. ISBN 9781134722648.
- ^ a b c d e Katherine ER. Southward, Ethnicity and the Mixed Marriage Crisis in Ezra, 9–10: An Anthropological Approach, Oxford University Press 2012 pp.103–203, esp. p.193.
- ^ Finkelstein, Israel; Silberman, Neil Asher (2001). The Bible Unearthed: Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Sacred Texts. The Free Press. ISBN 978-0-7432-2338-6.
- ^ Lipschits, Oded; Tal, Oren (2007). "The Settlement Archaeology of the Province of Judah: A Case Study". In Lipschits, Oded; Knoppers, Gary N.; Albertz, Rainer (eds.). Judah and the Judeans in the Fourth Century B.C.E. Penn State University Press. pp. 33–37. ISBN 978-1-57506-580-9.
- ^ Yigal Levin, The_Religion_of_Idumea_and_Its_Relationship_to_Early_Judaism 'The Religion of Idumea and Its Relationship to Early Judaism,' MDPI Religions 2020, 11, 487 pp.1–27 pp.2,4–5
- ^ a b Yigal Levin, 'Judea, Samaria and Idumea: Three Models of Ethnicity and Administration in the Persian Period' 2012
- ^ Shahîd, Irfan (1984). Rome and the Arabs: A Prolegomenon to the Study of Byzantium and the Arabs. Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection. p. 5. ISBN 9780884021155.
- ^ Kloner, Amos; Stern, Ian (2007). "Idumea in the Late Persian Period (Fourth Century b.c.e.)". In Lipschits, Oded; Knoppers, Gary N.; Albertz, Rainer (eds.). Judah and the Judeans in the Fourth Century B.C.E. Penn State University Press. pp. 139–143. ISBN 9781575065809.
- ^ Grabbe, Lester L. (2011). A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9780567381743.
- ^ Waterfield, Robin (2011). Dividing the Spoils – The War for Alexander the Great's Empire (hardback). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 273 pages. ISBN 978-0-19-957392-9.
- ^ a b c Van Maaren, John (2022). The Boundaries of Jewishness in the Southern Levant 200 BCE–132 CE: Power, Strategies, and Ethnic Configurations. De Gruyter. ISBN 9783110787481.
- ^ Berlin, Adele (2011). The Oxford Dictionary of the Jewish Religion. Oxford University Press. p. 330. ISBN 9780199730049.
John Hyrcanus I, who embarked upon further territorial conquests, forcing the non-Jewish populations of the conquered regions to adopt the Jewish way of life and destroying the Samaritan temple on Mount Gerizim.
. - ^ Jonathan Bourgel (2016). "The Destruction of the Samaritan Temple by John Hyrcanus: A Reconsideration". Journal of Biblical Literature. 135 (153/3). Society of Biblical Literature: 505. doi:10.15699/jbl.1353.2016.3129.
- ^ Bourgel, Jonathan (2014). "The Samaritans during the Hasmonean Period: The Affirmation of a Discrete Identity?". Religions. 10 (11): 628. doi:10.3390/rel10110628.
- ^ Schwartz, Daniel R. (1992). Studies in the Jewish Background of Christianity. Mohr Siebeck. ISBN 978-3-16-157327-9.
- ^ Faust, A., and Erlich, A., 2008, The Hasmonean Policy toward the Gentile Population in Light of the Excavations at Kh. er-Rasm and Additional Rural Sites, Jerusalem and Eretz Israel 6: 5-32 (HEBREW)
- ^ Leibner, Uzi. "Determining the Settlement History of Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine Sites in the Galilee, Israel: Comparing Surface, Subsurface, and Stratified Artifact Assemblages." Journal of Field Archaeology, vol. 39, no. 4, 2014, pp. 387–400. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/24408752. Accessed 11 Jan. 2024.
- ^ Horbury and Davies (2008) Preface. In: The Cambridge History of Judaism, Volume 3, The Early Roman Period. p. xi
- ^ Antiquities of the Jews, 17.42
- ^ James A. Sanders (2008) The canonical process In: The Cambridge History of Judaism, Volume 4, p. 235
- ^ E. Mary Smallwood (2008), The Diaspora in the Roman period before CE 70. In: The Cambridge History of Judaism, Volume 3. Editors Davis and Finkelstein.
- ^ a b c 'Jack Pastor, Land and Economy in Ancient Palestine, Routledge, 2013 p.6.
- ^ Magen Broshi, The Population of Western Palestine in the Roman-Byzantine Period, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, No. 236, p.7, 1979.
- ^ Magen Broshi, 'The Population of Western Palestine in the Roman-Byzantine Period,' Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, No. 236 (Autumn, 1979), pp.1–10, p.7.
- ^ Dio's Roman History (trans. Earnest Cary), vol. 8 (books 61–70), Loeb Classical Library: London 1925, pp. 449–451
- ^ Taylor, Joan E. (15 November 2012). The Essenes, the Scrolls, and the Dead Sea. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199554485.
Up until this date the Bar Kokhba documents indicate that towns, villages and ports where Jews lived were busy with industry and activity. Afterwards there is an eerie silence, and the archaeological record testifies to little Jewish presence until the Byzantine era, in En Gedi. This picture coheres with what we have already determined in Part I of this study, that the crucial date for what can only be described as genocide, and the devastation of Jews and Judaism within central Judea, was 135 CE and not, as usually assumed, 70 CE, despite the siege of Jerusalem and the Temple's destruction
ISBN 978-0-19-955448-5 - ^ a b c d David Goodblatt (2006). "The political and social history of the Jewish community in the Land of Israel, c. 235–638". In Steven Katz (ed.). The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. IV. Cambridge University Press. pp. 404–430. ISBN 978-0-521-77248-8.
- ^ Hanan Eschel (2008) The Bar Kochba Revolt. In: The Cambridge History of Judaism Volume 4. Editor: S. T. Katz. pp. 105–127
- ^ a b c Bar, Doron (2003). "The Christianisation of Rural Palestine during Late Antiquity". The Journal of Ecclesiastical History. 54 (3): 401–421. doi:10.1017/S0022046903007309.
The nomadic tribes that were scattered on the outer fringes of the country were converted quite easily, but on the other hand, in my opinion, in the rural sectors, where a population resided that assimilated sociological, technological and religious innovations at a far slower pace, the dominant religion spread far more gradually. Moreover, vast areas of rural Palestine, such as Galilee and Samaria, had an absolute Jewish or Samaritan majority. The influence of Christianity in these regions was therefore limited and came at a much later stage than in the pagan settlement areas.
- ^ Steven T.Katz (2008)Introduction. In: The Cambridge History of Judaism, Volume 4. Editor: Steven T. Katz.
- ^
Pastor, Jack (2013). Land and Economy in Ancient Palestine. Routledge. p. 6. ISBN 9781134722648. Retrieved 14 June 2016.
[...] the scholar is faced with a wide range of approximations arising from greatly varying systems of reckoning.
- ^ Robert Goldenberg (2008)The destruction of the Jerusalem Temple: its meaning and its consequences. In: The Cambridge History of Judaism Volume 4. Editor: S. T. Katz. p.198
- ^ Masalha, Nur (2016). "The Concept of Palestine: The Conception of Palestine from the Late Bronze Age to the Modern Period" (PDF). Journal of Holy Land and Palestine Studies. 15 (2). Edinburgh University Press: 143–202. doi:10.3366/hlps.2016.0140.
- ^ a b Safrai, Zeev (1998). Palestine in the Fifth Century : Growth and Decline. Peeters. pp. 51–81. ISBN 9789068319859.
- ^ a b c d e Stemberger, Gunter (1999). Jews and Christians in the Holy Land: Palestine in the Fourth Century. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-0567086990.
- ^ a b Goodblatt, David (2006). "The Political and Social History of the Jewish Community in the Land of Israel, c. 235–638". The Cambridge History of Judaism. Vol. IV. Cambridge University Press. pp. 404–430. ISBN 978-0-521-77248-8.
Immigration of Christians and the conversion of pagans, Samaritans and Jews eventually produced a Christian majority
- ^ a b Ehrlich, Michael (2022). The Islamization of the Holy Land, 634–1800. Leeds, UK: Arc Humanities Press. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-1-64189-222-3. OCLC 1302180905.
Samaritan rebellions during the fifth and sixth centuries were crushed by the Byzantines and as a result, the main Samaritan communities began to decline. Similarly, the Jewish community strove to recover from the catastrophic results of the Bar Kokhva revolt (132–135 ce). During the Late Roman and Byzantine periods, many Jews emigrated to thriving centres in the diaspora, especially Iraq, whereas some converted to Christianity and others continued to live in the Holy Land, especially in Galilee and the coastal plain.
- ^ a b c d e Taylor, Joan (1993). Christians and the Holy Places: The Myth of Jewish-Christian Origins. Clarendon Press. ISBN 9780198147855.
- ^ a b Lewin, Ariel (2005). The Archaeology of Ancient Judea and Palestine. J. Paul Getty Museum. p. 36. ISBN 9780892368006.
- ^ Crown, Alan David (1989). The Samaritans. Mohr Siebeck. ISBN 9783161452376.
- ^ Pummer, Reinhard (2016). The Samaritans. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0802867681.
- ^ Pummer, Reinhard (2002). Early Christian Authors on Samaritans and Samaritanism: Texts, Translations and Commentary. Mohr Siebeck. ISBN 978-3-161-47831-4.
- ^ Schwartz, Joshua (2018). Jews and Christians in Roman-Byzantine Palestine: History, Daily Life and Material Culture. Peter Lang. ISBN 9783034335874.
- ^ Levy, Thomas E. (1998). The Archaeology of Society in the Holy Land. Leicester University Press. ISBN 9780718501655.
- ^ Safrai, S., Ste, M., Flusser, D., & van Unnik, W.C. (1976). "Paganism in Palestine". In The Jewish People in the First Century. Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. https://doi.org/10rn.1163/9789004275096_014
- ^ Joan Taylor, A critical investigation of archaeological material assigned to Palestinian Jewish-Christians of the Roman and Byzantine periods, 1990
- ^ a b Kasher, Aryeh (1990). Jews and Hellenistic Cities in Eretz-Israel. Relations of the Jews in Eretz-Israel with the Hellenistic Cities During the Second Temple Period (332 BCE - 70 CE). J.C.B. Mohr. ISBN 9783161452413.
- ^ Doron Bar, 2008, Continuity and change in the cultic topography of late antique Palestine
- ^ Emmanuel, Friedheim (2006). Rabbinisme Et Paganisme en Palestine Romaine: Étude Historique Des Realia Talmudiques (Ier-IVème Siècles) (in French). Brill. ISBN 9789047408277.
- ^ a b c Bar, Doron (2003). "The Christianisation of Rural Palestine during Late Antiquity". The Journal of Ecclesiastical History. 54 (3): 401–421. doi:10.1017/s0022046903007309. ISSN 0022-0469.
All this, coupled with immigration and conversion, allegedly meant that the Christianisation of Palestine took place much more rapidly than that of other areas of the Roman Empire, brought in its wake the annihilation of the pagan cults and meant that by the middle of the fifth century there was a clear Christian majority.
- ^ a b Bar, Doron (2004). "Population, settlement and economy in Late Roman and Byzantine Palestine (70–641 AD)". Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies. 67 (3): 307–320. doi:10.1017/S0041977X04000217. S2CID 161411981.
- ^ Safrai, S., Stern, M., Flusser, D., & van Unnik, W.C. (1976). "Paganism in Palestine". In The Jewish People in the First Century. Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004275096_014
- ^ Bar, Doron (2005). "Rural Monasticism as a Key Element in the Christianization of Byzantine Palestine". The Harvard Theological Review. 98 (1): 49–65. doi:10.1017/S0017816005000854. ISSN 0017-8160. JSTOR 4125284. S2CID 162644246.
The phenomenon was most prominent in Judea, and can be explained by the demographic changes that this region underwent after the second Jewish revolt of 132–135 C.E. The expulsion of Jews from the area of Jerusalem following the suppression of the revolt, in combination with the penetration of pagan populations into the same region, created the conditions for the diffusion of Christians into that area during the fifth and sixth centuries. [...] This regional population, originally pagan and during the Byzantine period gradually adopting Christianity, was one of the main reasons that the monks chose to settle there. They erected their monasteries near local villages that during this period reached their climax in size and wealth, thus providing fertile ground for the planting of new ideas.
- ^ Schick, Robert (2021). The Christian Communities of Palestine from Byzantine to Islamic Rule: An Historical and Archaeological Study. Gerlach Press. ISBN 9783959940924.
- ^ a b Magness, Jodi. The Archaeology of the Early Islamic Settlement in Palestine. Penn State University Press, 2003. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.5325/j.ctv1bxh26b. Accessed 26 Nov. 2023.
- ^ Günter Stemberger (2000). Jews and Christians in the Holy Land: Palestine in the Fourth Century. T&T Clark Int'l. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-567-08699-0.
- ^ Lawrence H. Schiffman (August 2003). Understanding Second Temple and rabbinic Judaism. KTAV Publishing House, Inc. p. 336. ISBN 978-0-88125-813-4. Retrieved 28 June 2011.
- ^ Della Pergola 2001.
- ^ Mohr Siebeck. Editorial by Alan David Crown, Reinhard Pummer, Abraham Tal. A Companion to Samaritan Studies. p70-45.
- ^ שור, נתן (2006). "רדיפות השומרונים בידי העבאסים והיעלמות היישוב השומרוני החקלאי". In שטרן, אפרים; אשל, חנן (eds.). ספר השומרונים [Book of the Samaritans] (in Hebrew) (2 ed.). ירושלים: יד יצחק בן-צבי; רשות העתיקות. pp. 587–590. ISBN 965-217-202-2.
- ^ Gil, Moshe (1997). A History of Palestine, 634–1099. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521599849.
- ^ a b c d e Ehrlich, Michael (2022). The Islamization of the Holy Land, 634–1800. Arc Humanity Press. ISBN 978-1-64189-222-3. OCLC 1310046222.
- ^ a b Levy-Rubin, Milka (2000). "New Evidence Relating to the Process of Islamization in Palestine in the Early Muslim Period: The Case of Samaria". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 43 (3): 257–276. doi:10.1163/156852000511303. JSTOR 3632444.
- ^ a b c d Avni, Gideon (2014). The Byzantine-Islamic Transition in Palestine: An Archaeological Approach. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780191507342.
- ^ Ellenblum, Ronnie (2012). The Collapse of the Eastern Mediterranean: Climate Change and the Decline of the East, 950–1072. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139151054.
- ^ a b Ellenblum, Ronnie (2010). Frankish Rural Settlement in the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780511585340.
- ^ Levy-Rubin, Milka (21 January 2024). "New Evidence Relating to the Process of Islamization in Palestine in the Early Muslim Period: The Case of Samaria". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 43 (3): 263. JSTOR 3632444. Retrieved 21 January 2024.
- ^ Friedman, Yaron (2019). The Shīʿīs in Palestine: From the Medieval Golden Age Until the Present. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-42031-1.
- ^ Luz, Nimrod. "Aspects of Islamization of Space and Society in Mamluk Jerusalem and its Hinterland" (PDF). Mamlūk Studies Review. The Middle East Documentation Center (MEDOC): 1947–2404. 1036.
- ^ Ephrat, Daphna. “The Shaykh, the Physical Setting and the Holy Site: The Diffusion of the Qādirī Path in Late Medieval Palestine.” Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, vol. 19, no. 1, 2009, pp. 1–20. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/27756016.
- ^ Ephrat, Daphna (2008). Spiritual wayfarers, leaders in piety: Sufis and the dissemination of Islam in medieval Palestine (Illustrated ed.). Harvard CMES. ISBN 9780674032019.
- ^ Reuven Atimal and Ronnie Ellenblum. The Demographic Transformation in Palestine in the Post-Crusading Period (1187–1516 C.E.)
- ^ Ireton, Sean (2003). Strategies for Survival of an Ethno-religious Minority in the Twenty First Century (Thesis). Anthrobase/University of Kent at Canterbury MA Dissertation for Ethnicity, Nationalism and Identity.
- ^ Yousef, Hussein Ahmad; Barghouti, Iyad (24 January 2005). "The Political History of the Samaritans: Minority under Occupation: The Socio politics of the Samaritans in the Palestinian Occupied Territories". Zajel. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012.
- ^ Bernard Lewis, Studies in the Ottoman Archives—I, Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, Vol. 16, No. 3, pp. 469–501, 1954
- ^ Cohen, Amnon, and Bernard Lewis. Population and Revenue in the Towns of Palestine in the Sixteenth Century. Princeton University Press, 1978. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt13x196g. Accessed 11 Nov. 2023.
- ^ a b McCarthy 1990.
- ^ a b Grossman, D. (1986). "Oscillations in the Rural Settlement of Samaria and Judaea in the Ottoman Period". in Shomron studies. Dar, S., Safrai, S., (eds). Tel Aviv: Hakibbutz Hameuchad Publishing House. p. 314-317, 345-385
- ^ Grossman, David (2017). Distribution and Population Density During the Late Ottoman and Early Mandate Periods (9781315128825 ed.). New York: Routledge. pp. 44–52. doi:10.4324/9781315128825. ISBN 9781315128825.
They came from Circassia and Chechnya, and were refugees from territories annexed by Russia in 1864, and the Bosnian Muslims, whose province was lost to Serbia in 1878. Belonging to this category were the Algerians (Mughrabis), who arrived in Syria and Palestine in several waves after 1850 in the wake of France's conquest of their country and the waves of Egyptian migration to Palestine and Syria during the rule of Muhammad Ali and his son, Ibrahim Pasha. [...] In most cases the Egyptian army dropouts and the other Egyptian settlers preferred to settle in existing localities, rather than to establish new villages. In the southern coastal plain and Ramla zones there were at least nineteen villages which had families of Egyptian origin, and in the northern part of Samaria, including the 'Ara Valley, there are a number of villages with substantial population of Egyptian stock.
- ^ a b Grossman, David (2004). Arab Demography and Early Jewish Settlement in Palestine: Distribution and Population Density during the Late Ottoman and Early Mandate Periods (in Hebrew). Jerusalem: The Hebrew University Magness Press, Jerusalem. p. 146. ISBN 978-965-493-184-7.
- ^ Greene, Roberta R.; Hantman, Shira; Seltenreich, Yair; ʻAbbāsī, Muṣṭafá (2018). Living in Mandatory Palestine: personal narratives of resilience of the Galilee during the Mandate period 1918-1948. New York, NY: Routledge. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-138-06898-8.
In addition, there were 12 settlements in the Galilee of Algerian immigrants, who had come to the region during the second half of the nineteenth century after their emir, Abd al-Qader al-Jazairi, surrendered to the French in 1847.
- ^ a b Mendel, Yonatan (5 October 2014). The Creation of Israeli Arabic: Security and Politics in Arabic Studies in Israel. Palgrave Macmillan UK. p. 188. ISBN 978-1-137-33737-5.
Note 28: The exact percentage of Jews in Palestine prior to the rise of Zionism is unknown. However, it probably ranged from 2 to 5 per cent. According to Ottoman records, a total population of 462,465 resided in 1878 in what is today Israel/Palestine. Of this number, 403,795 (87 per cent) were Muslim, 43,659 (10 per cent) were Christian and 15,011 (3 per cent) were Jewish (quoted in Alan Dowty, Israel/Palestine, Cambridge: Polity, 2008, p. 13). See also Mark Tessler, A History of the Israeli–Palestinian Conflict (Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 1994), pp. 43 and 124.
- ^ Salmon, Yosef (1978). "Ideology and Reality in the Bilu "Aliyah"". Harvard Ukrainian Studies. 2 (4). [President and Fellows of Harvard College, Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute]: 431. ISSN 0363-5570. JSTOR 41035804. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
Jewish influx into Palestine. Between 1880 and 1907, the number of Jews in Palestine grew from 23,000 to 80,000. Most of the community resided in Jerusalem, which already had a Jewish majority at the beginning of the influx. [Footnote: Mordecai Elia, Ahavar Tziyon ve-Kolel Hod (Tel Aviv, 1971), appendix A. Between 1840 and 1880 the Jewish settlement in Palestine grew in numbers from 9,000 to 23,000.] The First Aliyah accounted for only a few thousand of the new-comers, and the number of the Biluim among them was no more than a few dozen. Jewish immigration to Palestine had begun to swell in the 1840s, following the liberalization of Ottoman domestic policy (the Tanzimat Reforms) and as a result of the protection extended to immigrants by the European consulates set up at the time in Jerusalem and Jaffa. The majority of immigrants came from Eastern and Central Europe – the Russian Empire, Romania, and Hungary – and were not inspired by modern Zionist ideology. Many were motivated by a blend of traditional ideology (e.g., belief in the sanctity of the land of Israel and in the redemption of the Jewish people through the return to Zion) and practical considerations (e.g., desire to escape the worsening conditions in their lands of origin and to improve their lot in Palestine). The proto-Zionist ideas which had already crystallized in Western Europe during the late 1850s and early 1860s were gaining currency in Eastern Europe.
- ^ Scholch, Alexander (November 1985). "The Demographic Development of Palestine, 1850–1882". International Journal of Middle East Studies. 17 (4): 485–505. doi:10.1017/s0020743800029445. JSTOR 163415. S2CID 154921401.
- ^ Dowty, Alan (16 April 2012). Israel / Palestine. Polity. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-7456-5611-3.
- ^ McCarthy 1990, p. 26.
- ^ On, Raphael R. Bar. "ISRAEL'S NEXT CENSUS OF POPULATION AS A SOURCE OF DATA ON JEWS." Proceedings of the World Congress of Jewish Studies / דברי הקונגרס העולמי למדעי היהדות ה (1969): 31*-41*. http://www.jstor.org/stable/23524099.
- ^ [1] pp. 625, 653
- ^ McCarthy 1990, pp. 37–38.
- ^ Population growth and demographic balance between Arabs and Jews in Israel and historic Palestine, Hussein Abu el Naml, Contemporary Arab Affairs, January 2010, Vol. 3, No. 1 (January 2010), pp. 71–82, University of California Press
- ^ The Tel Aviv Deportation
- ^ Qafisheh, Mutaz M. (2008). The International Law Foundations of Palestinian Nationality: A Legal Examination of Palestinian Nationality Under the British Rule. BRILL. pp. 94–. ISBN 978-90-04-16984-5.
- Earlier version of the work available at:
- —— (2007). The International Law Foundations of Palestinian Nationality: A Legal Examination of Palestinian Nationality under the British Rule (PDF) (Doctoral thesis). Université de Genève.
- Earlier version of the work available at:
- ^ Colonial Office, Great Britain (1922). Report by His Britannic Majesty's Government to the Council of the League of Nations on the Administration of Palestine and Transjordan. p. 53.
19,293 Provisional Certificates of Citizenship were granted in respect of 37,997 persons, wives and minor children being included on certificates issued to heads of families
- ^ The Jewish Telegraphic Agency, [2] and [3], stated: "Jerusalem, (J. T. A.) it is officially stated" that 19,293 naturalization certificates have been granted to Jews who had applied for Palestine Citizenship. As the naturalization of the husband applies also to the wife, the number of persons actually naturalized is 37,997. Only 100 members of other nationalities applied for naturalization. Very few British or American Jews renounced their citizenship in favor of Palestine, a fact which is causing unfavorable comment among Palestinian Jews"
- ^ Palestine Census ( 1922).
- ^ "Mandate for Palestine - Interim report of the Mandatory to the League of Nations/Balfour Declaration text (30 July 1921)". unispal.un.org.
- ^ Palestine & Near East Economic Magazine. Third Year. Vol. III, no 5–6 15 March 1928.
- ^ a b Afaf Lutfi, Al-Sayyid Marsot (1984). Egypt in the Reign of Muhammad Ali. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780511563478.
- ^ a b c d e f Grossman, David (2011). Rural Arab Demography and Early Jewish Settlement in Palestine: Distribution and Population Density during the Late Ottoman and Early Mandate Periods. Transaction Publishers. ISBN 9781412844543.
- ^ Büssow, Johann (2011). Hamidian Palestine: Politics and Society in the District of Jerusalem 1872–1908. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-21570-2.
- ^ Ayyad, Abd al-Aziz (1999). Arab nationalism and the Palestinians, 1850–1939. Palestinian Academic Society for the Study of International Affairs.
- ^ Manna, A. (2009). "Rereading the 1834 Revolt Against Muhammad Ali in Palestine and Rethinking Ottoman Rule". In Kamil Mansur; Leila Tarazi Fawaz (eds.). Transformed Landscapes: Essays on Palestine and the Middle East in Honor of Walid Khalid. American University of Cairo Press. ISBN 978-977-416-247-3.
- ^ 1922 Census of Palestine
- ^ U. Schmelz (1990). "Population characteristics of Jerusalem and Hebron regions according to Ottoman census of 1905". In G. Gilbar (ed.). Ottoman Palestine 1800–1914. Bill Leiden. pp. 5–67.
- ^ Jacob Metzer, The Divided Economy of Mandatory Palestine, Cambridge University Press, 1998 pp.31ff.
- ^ Bernstein, Deborah: Constructing Boundaries: Jewish and Arab Workers in Mandatory Palestine, pp. 20–21
- ^ Paul Blair (19 April 2002). "Special Report: The Origins of the Arab-Jewish Conflict Over Palestine". Capitalism Magazine. Archived from the original on 14 January 2010.
- ^ Anglo-American Commission report, Section 4.4. "Of this Moslem growth by 472,000, only 19,000 was accounted for by immigration."
- ^ a b "Palestine: Report on Immigration, Land Settlement and Development - UK Government report - Non-UN document (see attached also as PDF file at the end of the doc) (1 October 1930)". unispal.un.org. Archived from the original on 10 August 2014. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- ^ Passfield White Paper, para 17. "the Arab population, while lacking the advantages enjoyed by the Jewish settlers, has, by the excess of births over deaths, increased with great rapidity"
- ^ the Peel Commission report, pp. 125,282. "unlike the Jewish, the rise has been due in only a slight degree to immigration."
- ^ Survey of Palestine, p140. "the expansion of the Moslem and Christian populations is due mainly to natural increase, while that of the Jews is due mainly to immigration."
- ^ a b c Government of Palestine (1933). E. Mills (ed.). Census of Palestine 1931. Vol. I. Palestine Part I, Report. Alexandria. pp. 59, 61–65.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Henry Laurens, La Question de Palestine: Vol.2, 1922–1947, Fayard 2002 p.384.
- ^ a b Gottheil, Fred M. (1 January 2003). "The Smoking Gun: Arab Immigration into Palestine, 1922–1931". Middle East Quarterly.
- ^ Tessler, Mark: A History of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict, Second Edition, p. 211
- ^ a b c Bachi 1974, pp. 133, 390–394.
- ^ Bachi 1974, pp. 34–35.
- ^ McCarthy 1990, pp. 16, 33.
- ^ McCarthy 1990, p. 16.
- ^ McCarthy 1990, p. 38.
- ^ McCarthy 1990, pp. 16–17.
- ^ Gottheil, Fred M. (27 May 1982). "Arab Immigration into Pre-State Israel 1922–1931". In Kedourie, Elie; Haim, Sylvia G. (eds.). Palestine and Israel in the 19th and 20th Centuries. Routledge. ISBN 9781135168148.
- ^ Gilbar, Gad G. (1986). "The Growing Economic Involvement of Palestine with the West, 1865–1914". In David Kushner (ed.). Palestine in the Late Ottoman Period: political, social and economic transformation. Brill Academic Publishers. p. 188. ISBN 90-04-07792-8.
- ^ Gilbar, Gad: [Ottoman Palestine, 1800–1914: Studies in Economic and Social History], p. 3
- ^ Porath, Y. (1986). Mrs. Peters's Palestine. New York Review of Books. 16 January, 32 (21 & 22).
- ^ a b c d e Elhanan Miller,'Right-wing annexation drive fueled by false demographics, experts say,' The Times of Israel 5 January 2015.
- ^ Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Israel. "Population, by religion and population group" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 April 2006. Retrieved 2006-04-08.
- ^ Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Israel. "Jews and others, by origin, continent of birth and period of immigration" (PDF). Retrieved 8 April 2006.
- ^ Ian Lustick, 'What Counts is the Counting:Statistical Manipulation as a Solution to Israel's "Demographic Problem",' Archived 13 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine Middle East Journal, 67(2), pp. 29–35.
- ^ a b "Regional Statistics". Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 21 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Main Indicators by Type of Locality - Population, Housing and Establishments Census 2017" (PDF). Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS). Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d Gaza Strip and West Bank (except Jerusalem) estimate for mid-2023 as per "Estimated Population in the Palestine Mid-Year by Governorate,1997-2026". Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, State of Palestine. Retrieved 1 January 2024. Subtract 817,407 (Area C), 611,284 (East Jerusalem).
- ^ "The Separation Barrier – Statistics". B'Tselem. 16 July 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
Data source: Israel 's Central Bureau of Statistics, The PA Central Bureau of Statistics and OCHA. All data on population updated to the end of 2005.
- ^ Katz, Yaakov (1 January 2024). "WEST BANK Jewish Population Stats (not including eastern Jerusalem) UPDATED TO: JANUARY 1, 2024" (PDF). WestBankJewishPopulationStats.com. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ TIA GOLDENBERG (2 February 2023). "Jewish settler population in the West Bank surpasses half a million". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ Biard, Michel (26 June 2019). "Addressing the Needs of Palestinian Households in Area C of the West Bank - Findings of the First Comprehensive Household Survey (January 2019) - occupied Palestinian territory | ReliefWeb". ReliefWeb. Oxfam. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ "Occupied Palestinian Territory Area C of the West Bank" (PDF). UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. August 2014. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ Sum of Israeli and Palestinian estimates
- ^ a b BBC News. Regions and territories: The Golan Heights.
- ^ a b United Nations. Security Council Resolutions, 1981.
- ^ a b Council on Foreign Relations. UN Security Council Resolution 497.
- ^ a b c "Total" and "Jewish/Other" figures from "III/5 Population of Jerusalem by Population Group, Religious Identification, Quarter and Sub-Quarter, 2021 in Jerusalem Statistical Yearbook". Jerusalem Institute for Policy Research. 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2023.. From this number subtract 18,982 Arabs who have Israeli citizenship, viz. "Just 5 Percent of E. Jerusalem Palestinians Have Received Israeli Citizenship Since 1967". Haaretz. Retrieved 31 December 2023. East Jerusalem consists of Areas 2111–2911, all of Quarters 1, 4, and 16; in Quarter 5 Giv'at Shapira (French Hill), Ramat Eshkol, Giv'at Hamivtar and Ma'alot Dafna (but not Shmuel Hanavi), and in Quarter 13 East Talpiot.
- ^ "Estimated Population in the Palestine Mid-Year by Governorate,1997-2026". Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, State of Palestine. Retrieved 13 February 2024.
- ^ "The Legal Status of the West Bank and Gaza". Question of Palestine, United Nations. 1982.
The West Bank has an extension of 2,270 square miles
- ^ a b c Figure calculated from other sourced figures in table
- ^ Derived from total CBS Population of Israel 31-Dec-2023 minus estimates for East Jerusalem Israelis and non-Israeli Palestinians, minus Golan Heights, minus 1/1/24 estimate of settlers in Area C
- ^ Aji, Albert (26 March 2019). "Trump acceptance of Israeli control of Golan sparks protests". Associated Press. Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- ^ a b c "'This is our moment': Israel okays major plan to boost Golan, double its population". The Times of Israel. 26 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ "Home". Central Bureau for Statistics, State of Israel. December 2023. Retrieved 14 February 2024.
9.842 million population December 2023
- ^ ""Area of the State of Israel", All Terms". Central Bureau of Statistics, State of Israel. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ ""Population of Israel", All Terms". Central Bureau of Statistics, State of Israel. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
Bibliography
- Della Pergola, Sergio (2001). "Demography in Israel/Palestine: Trends, Prospects, Policy Implications" (PDF). International Union for the Scientific Study of Population, XXIV, General Population Conference, Salvador de Bahia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 December 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- Bachi, Roberto (1974). The Population of Israel (PDF). Institute of Contemporary Jewry, Hebrew University of Jerusalem. pp. 133, 390–394.
- McCarthy, Justin (1990). The Population of Palestine: Population History and Statistics of the Late Ottoman Period and the Mandate. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-07110-9.
- Jewish National Council (1947). "First Memorandum: historical survey of the waves of the number and density of the population of ancient Palestine; Presented to the United Nations in 1947 by Vaad Leumi on Behalf of the Creation of a Jewish State" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2012.
- Jewish National Council (1947). "Second Memorandum: historical survey of the Jewish population in Palestine from the fall of the Jewish state to the beginning of zionist pioneering; Presented to the United Nations in 1947 by Vaad Leumi on Behalf of the Creation of a Jewish State" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2012.
- Jewish National Council (1947). "Third Memorandum: historical survey of the waves of Jewish immigration into Palestine from the arab conquest to the first zionist pioneers; Presented to the United Nations in 1947 by Vaad Leumi on Behalf of the Creation of a Jewish State" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2011.
- Forbes, Andrew, and Henley, David, People of Palestine (Chiang Mai: Cognoscenti Books, 2012), ASIN: B0094TU8VY