Corpora quadrigemina
Appearance
| Corpora quadrigemina | |
|---|---|
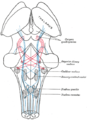
 Rhomboid fossa. ("Corpora quadrigemina" visible at top). | |
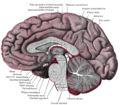
 Sagittal section through right cerebellar hemisphere. The right olive has also been cut sagittally. ("Corpora quadrigemina" visible at upper right). | |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroNames | 1279 |
| FMA | 242157 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
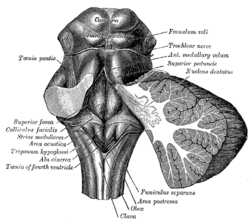
In the brain, the corpora quadrigemina (Latin for "quadruplet bodies") are the four colliculi—two inferior, two superior—located on the tectum of the dorsal aspect of the midbrain. They are respectively named the inferior and superior colliculus.
The corpora quadrigemina are reflex centers involving vision and hearing. It consists of groups of nerve cells-grey matter scattered in white matter. It basically connects the forebrain and the hind brain. It has four corpora quadrigemina which are the reflex centres of eye movement and auditory responses. The superior part of corpora quadrigemina are called superior colliculi, and inferior part as inferior colliculi.[1]
Additional images
-
Schematic representation of the chief ganglionic categories (I to V)
-
Transverse section through mid-brain
-
Scheme showing the course of the fibers of the lemniscus; medial lemniscus in blue, lateral in red
-
Dissection showing the ventricles of the brain
-
Median sagittal section of brain
-
Upper part of medulla spinalis and hind- and mid-brains; posterior aspect, exposed in situ
References
- ^ Marieb, Elaine N. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 6th ed. San Francisco: Daryl Fox, 2000. 210.
External links