Search results
Appearance
There is a page named "Baodiao movement" on Wikipedia
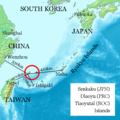
- Baodiao movement (simplified Chinese: 保钓运动; traditional Chinese: 保釣運動; lit. 'Defend the Diaoyu Islands movement') is a social movement originating among...10 KB (1,077 words) - 15:03, 20 November 2024
- transfer the islands to Japan prompted the development of the Baodiao movement.: 52 This movement began among students from Taiwan and Hong Kong studying in...159 KB (15,975 words) - 08:57, 29 March 2025
- born in Chaoyang, Guangdong, China. He was a prominent leader of the Baodiao movement in Hong Kong, which advocates Chinese sovereignty over the Senkaku...7 KB (681 words) - 17:19, 5 December 2024
- survived. David Chan Yuk-cheung (Chinese: 陈毓祥, born 1950), a leader of Baodiao movement in Hong Kong, drowned in the sea during a protest in 1996. Jeff Buckley...55 KB (6,023 words) - 08:13, 27 March 2025
- transfer the islands to Japan prompted the development of the Baodiao movement.: 52 This movement began among students from Taiwan and Hong Kong studying in...52 KB (4,993 words) - 19:59, 1 March 2025
- secretary-general of the university's student council, and encountered the baodiao movement. In his third year at the university, he was selected by the United...129 KB (12,421 words) - 22:03, 30 March 2025
- actor Sita Chan (陳僖儀), singer David Chan Yuk-cheung (陳毓祥), leader of Baodiao movement (保釣運動) William Chang (張叔平), art director, costume and production designer...23 KB (2,624 words) - 09:11, 2 February 2025
- coffin to protests to show his disapproval of Beijing. As part of the Baodiao movement, he landed on the Senkaku Islands, or Diaoyutai Islands, on 15 August...16 KB (1,626 words) - 02:10, 1 July 2024
- Democratic Movement in Taiwan (OSDMT) was a Chinese-American student-led organization which promoted democracy in Taiwan. The Baodiao movement that started...7 KB (583 words) - 15:46, 22 February 2024
- saw a wave of youth movements, which emerged from events like the Baodiao movement when the question of the sovereignty of the Diaoyu Islands appeared...34 KB (4,615 words) - 18:18, 21 February 2025
- participant in the left-wing Baodiao movement during the 1970s. Composed of overseas students from the Republic of China, this movement emerged in opposition...6 KB (665 words) - 18:08, 15 November 2024
- in Chemistry David Chan Yuk-cheung (陳毓祥) – prominent leader of the Baodiao movement in Hong Kong Deborah Chung (鍾端玲) – American scientist and author Hui...8 KB (747 words) - 07:52, 10 February 2025
- social movements, such as the Chinese Language Movement, the anti-corruption movement, the Baodiao movement and so on, in which many of the student leaders...61 KB (6,864 words) - 09:48, 14 March 2025
- (台湾同学会), Lin wrote that he had accepted Marxism while involved in the Baodiao movement in the United States. In addition, he wrote that he saw the Kuomintang...4 KB (441 words) - 07:00, 17 June 2024
- 1920) September 26 — David Chan Yuk-cheung, prominent leader of the Baodiao movement in Hong Kong (b. 1950) September 27 — Lee Tit, director (b. 1913) September...10 KB (871 words) - 04:49, 12 October 2024
- Tencent Weibo. Zhang, Ketian (Spring 2015). "Nationalist Motivations: "Baodiao" Activists, Tong Zeng, And The CFDD". MIT Center for International Studies...190 KB (20,085 words) - 20:00, 23 January 2025
- Hengtong Bus Co., Ltd. L1N XPeng Motors L10 Geely Emgrand L2B Jiangsu Baodiao Locomotive Co., Ltd. (motorcycles) L2C Chery Jaguar Land Rover L3H Shanxi