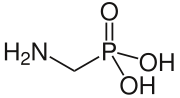
Aminomethylphosphonic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Aminomethyl)phosphonic acid | |
| Other names
Aminomethanephosphonic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | AMPA; AMeP |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.014 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH6NO3P | |
| Molar mass | 111.037 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Melting point | 338 to 344 °C (640 to 651 °F; 611 to 617 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) is a aminophosphonate with a weak phosphonic acid group.
Application
AMPA apparently can be used as biocide and pesticide.[1] AMPA is also used in research to assess the exposure of glyphosate.[2]

Environmental fate
AMPA is one of the primary degradation products of the herbicide glyphosate.[4][1] In addition, it is a degradation product of other aminophosphonates, which have applications as antiscalant and water treatment.[5]
AMPA was found in the final effluent of some wastewater treatment plants at concentrations of up to 10μg/l.[6] AMPA can be detected after membrane filtration.[7] AMPA has the potential to be broken down further by manganese oxide in laboratory conditions, however in soil manganese oxide is usually only present in trace amounts.[8] Microbial degradation of AMPA is the more likely degradation pathway, where it degrades into phosphoric acid[9][10] and ultimately to carbon dioxide and inorganic phosphate.[11]
Toxicity
AMPA has toxicity which is comparable to that of glyphosate and it is therefore considered to be of similar toxicological concern (harmful in greater than 0.5 parts per million) as glyphosate itself.[12]
References
- ^ a b "(Aminomethyl)phosphonic acid". PubChem. NLM. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ Fagan, John; Bohlen, Larry; Patton, Sharyle; Klein, Kendra (October 2020). "Organic diet intervention significantly reduces urinary glyphosate levels in U.S. children and adults". Environmental Research. 189: 109898. Bibcode:2020ER....189j9898F. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109898. PMID 32797996.
- ^ Zuliang Chen, Wenxiang He, Michael Beer, Mallavarapu Megharaj, Ravendra Naidu (2009-05-15). "Speciation of glyphosate, phosphate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in soil extracts by ion chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with an octopole reaction system". Talanta. 78 (3): 852–856. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2008.12.052. PMID 19269440.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Environmental Fate of Glyphosate Archived 2012-04-20 at the Wayback Machine, Jeff Schuette, Department of Pesticide Regulation, California
- ^ Schwientek, M.; Rügner, H.; Haderlein, S. B.; Schulz, W.; Wimmer, B.; Engelbart, L.; Bieger, S.; Huhn, C. (2024-07-23). "Glyphosate contamination in European rivers not from herbicide application?". Water Research: 122140. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2024.122140. ISSN 0043-1354.
- ^ Wang, Shu; Zhang, Bingliang; Shan, Chao; Yan, Xing; Chen, Hong; Pan, Bingcai (2020). "Occurrence and transformation of phosphonates in textile dyeing wastewater along full-scale combined treatment processes". Water Research. 184: 116173. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2020.116173.
- ^ Kuhn, Ramona; Vornholt, Carsten; Preuß, Volker; Bryant, Isaac Mbir; Martienssen, Marion (15 June 2021). "Aminophosphonates in Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Permeates". Membranes. 11 (6): 446. doi:10.3390/membranes11060446. ISSN 2077-0375. PMC 8232610. PMID 34203777.
- ^ K. A. Barrett and M. B. McBride. Oxidative Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonate by Manganese Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 39 (23), pp 9223–9228
- ^ Pipke R, Amrhein N. (1988) Isolation and characterization of a mutant of Arthrobacter sp. strain GLP-1 which utilizes the herbicide glyphosate as its sole source of phosphorus and nitrogen. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54(11): 2868-2870.
- ^ Forlani G, Mangiagalli A, Nielsen E, Suardi CM. (1999) Degradation of the phosphonate herbicide glyphosate in soil: Evidence for a possible involvement of unculturable microorganisms. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 31: 991-997
- ^ Backgrounder: Glyphosate does not degrade to phosphorous acid in the environment. Monsanto. 2005
- ^ Pesticide Residues in Food - 1997, FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide Residues in Food and the Environment and the WHO Core Assessment Group
