Continuation War: Difference between revisions
→See also: portal |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.6.2) (Manelolo) |
||
| Line 154: | Line 154: | ||
The Continuation War represents the only case of a genuinely democratic state participating in World War II on the side of the [[Axis powers of World War II|Axis powers]], albeit without being a signatory of the [[Tripartite Pact]]. The United Kingdom declared war on Finland on 6 December 1941 (Finnish Independence Day), with Canada and New Zealand declaring war on Finland on 7 December and Australia and South Africa declaring war the next day. U.S. Secretary of State [[Cordell Hull]] congratulated the Finnish envoy on 3 October 1941 for the liberation of Karelia but warned Finland not to enter Soviet territory; furthermore, the United States did not declare war on Finland when it went to war alongside the Axis countries and, together with the UK, approached Soviet Premier [[Joseph Stalin]] at the [[Tehran Conference]] about acknowledging Finnish independence. However, the U.S. government seized Finnish [[merchant vessel|merchant ships]] in American ports, and in the summer of 1944 shut down Finnish diplomatic and commercial offices in the United States as a result of President Ryti's treaty with Germany. The U.S. government later warned Finland about the consequences of continued adherence to the Axis.<ref>World War II: [http://worldwar2database.com/html/finland.htm Finland] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120212182348/http://worldwar2database.com/html/finland.htm |date=February 12, 2012 }}</ref> |
The Continuation War represents the only case of a genuinely democratic state participating in World War II on the side of the [[Axis powers of World War II|Axis powers]], albeit without being a signatory of the [[Tripartite Pact]]. The United Kingdom declared war on Finland on 6 December 1941 (Finnish Independence Day), with Canada and New Zealand declaring war on Finland on 7 December and Australia and South Africa declaring war the next day. U.S. Secretary of State [[Cordell Hull]] congratulated the Finnish envoy on 3 October 1941 for the liberation of Karelia but warned Finland not to enter Soviet territory; furthermore, the United States did not declare war on Finland when it went to war alongside the Axis countries and, together with the UK, approached Soviet Premier [[Joseph Stalin]] at the [[Tehran Conference]] about acknowledging Finnish independence. However, the U.S. government seized Finnish [[merchant vessel|merchant ships]] in American ports, and in the summer of 1944 shut down Finnish diplomatic and commercial offices in the United States as a result of President Ryti's treaty with Germany. The U.S. government later warned Finland about the consequences of continued adherence to the Axis.<ref>World War II: [http://worldwar2database.com/html/finland.htm Finland] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120212182348/http://worldwar2database.com/html/finland.htm |date=February 12, 2012 }}</ref> |
||
The best-known British action on Finnish soil was an aircraft carrier [[Raid on Kirkenes and Petsamo|strike on German and Finnish ships]] in the Finnish harbour of [[Pechenga (urban-type settlement), Murmansk Oblast|Petsamo]] on 31 July 1941.<ref name="pvfkvi">FAA archive: [http://www.fleetairarmarchive.net/RollofHonour/Battlehonour_crewlists/Petsamo_Kirkenes_1941.html Raid on Petsamo]</ref> This attack achieved little except the loss of three British aircraft, but it was intended as a demonstration of British support for its Soviet ally. Later in 1941, [[Hawker Hurricane|Hurricanes]] of [[No. 151 Wing RAF]], based at Murmansk, provided local air cover for Soviet troops and fighter escorts for Soviet bombers.<ref>The [[Royal Air Force]] in Russia :[http://ww2airfronts.org/Theaters/eto/rinr/pages/rinr-1.html Hurricanes at Murmansk] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140808144736/http://ww2airfronts.org/Theaters/eto/rinr/pages/rinr-1.html |date=August 8, 2014 }}</ref> |
The best-known British action on Finnish soil was an aircraft carrier [[Raid on Kirkenes and Petsamo|strike on German and Finnish ships]] in the Finnish harbour of [[Pechenga (urban-type settlement), Murmansk Oblast|Petsamo]] on 31 July 1941.<ref name="pvfkvi">FAA archive: [http://www.fleetairarmarchive.net/RollofHonour/Battlehonour_crewlists/Petsamo_Kirkenes_1941.html Raid on Petsamo] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040904030659/http://www.fleetairarmarchive.net/rollofhonour/Battlehonour_crewlists/Petsamo_Kirkenes_1941.html |date=4 September 2004 }}</ref> This attack achieved little except the loss of three British aircraft, but it was intended as a demonstration of British support for its Soviet ally. Later in 1941, [[Hawker Hurricane|Hurricanes]] of [[No. 151 Wing RAF]], based at Murmansk, provided local air cover for Soviet troops and fighter escorts for Soviet bombers.<ref>The [[Royal Air Force]] in Russia :[http://ww2airfronts.org/Theaters/eto/rinr/pages/rinr-1.html Hurricanes at Murmansk] {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140808144736/http://ww2airfronts.org/Theaters/eto/rinr/pages/rinr-1.html |date=August 8, 2014 }}</ref> |
||
[[Finnish radio intelligence]] is said to have participated effectively in German actions against British convoys to [[Murmansk]].<ref>Ahtokari, Reijo and Pale, Erkki: ''Suomen Radiotiedustelu 1927–1944'' (Finnish radio intelligence 1927–1944), Helsinki, Hakapaino Oy, pp. 191–98, {{ISBN|952909437X}}</ref> |
[[Finnish radio intelligence]] is said to have participated effectively in German actions against British convoys to [[Murmansk]].<ref>Ahtokari, Reijo and Pale, Erkki: ''Suomen Radiotiedustelu 1927–1944'' (Finnish radio intelligence 1927–1944), Helsinki, Hakapaino Oy, pp. 191–98, {{ISBN|952909437X}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 18:03, 1 February 2018
Template:Use Harvard referencing
This article or section is in a state of significant expansion or restructuring. You are welcome to assist in its construction by editing it as well. This template was placed by Manelolo (talk · contribs). If this article or section has not been edited in several days, please remove this template. If you are the editor who added this template and you are actively editing, please be sure to replace this template with {{in use}} during the active editing session. Click on the link for template parameters to use.
This article was last edited by InternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs) 6 years ago. (Update timer) |
| Continuation War | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Eastern Front of World War II | |||||||||
 Finnish soldiers, VT-line in 1944, Karelian offensive; "Alarm in VT-line positions". | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
(until 7 November 1941) (7 November 1941 – 23 June 1944) (from 28 June 1944) |
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
530,000 Finns[Note 1][7] 220,000 Germans[Note 2] |
In June 1941: 450,390 (Northern Front and Baltic Fleet)[8] In June 1944: 650,000[9] | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
Finnish: 14,000 dead or missing 37,000 wounded[7] unknown non-combat casualties Total 275,000+ casualties |
Finnish estimate based on Soviet data: 305,000 dead and missing[12](including 64,000 captured) 385,000 wounded 190,000 hospitalized due to sickness[13] 4,361 civilian deaths 697 tanks destroyed[14] 55 tanks captured 673 trucks captured 306 artillery pieces captured 300 tractors captured 303 aircraft destroyed[15] Multiple ships sunk Total ~835,000 casualties[13] not including civilian victims of the Siege of Leningrad | ||||||||
|
1 2 | |||||||||
The Continuation War (Finnish: jatkosota; Swedish: fortsättningskriget; 25 June 1941 – 19 September 1944) consisted of hostilities between Finland and the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1944. The Continuation War began 15 months after the end of the Winter War, which was also fought between Finland and the Soviet Union.[17] In the Soviet Union, the war was considered part of the Great Patriotic War.[18] Germany regarded its operations in the region as part of its overall war efforts on the Eastern Front, and it provided Finland with critical material support and military cooperation.
Acts of war between the Soviet Union and Finland recommenced on 22 June 1941, the day Germany launched its invasion of the Soviet Union. Open warfare began with a Soviet air offensive to Finland on 25 June. Subsequent Finnish operations undid its post-Winter War concessions to the Soviet Union on the Karelian Isthmus and Ladoga Karelia, and captured East Karelia by September 1941. On the Karelian Isthmus, the Finns halted their offensive 30 km from Leningrad, at the pre-World War II border between the Soviet Union and Finland. In 1944, Soviet air forces conducted air raids on Helsinki and other major Finnish cities.
Eventually, in mid-1944, the Soviet strategic offensive drove the Finns from most of the territories they had gained during the war, but the Finnish Army later brought the offensive to a standstill in July 1944. A ceasefire ended hostilities on 5 September and was followed by the Moscow Armistice on 19 September. The 1947 Paris peace treaty concluded the war formally. Finland ceded Pechengsky District to the Soviets, leased Porkkala peninsula to them and paid reparations, while retaining its independence.
Background
Winter War

On 23 August 1939, the Soviet Union (USSR) and Germany signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, whereby the parties divided the independent countries of Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Romania into spheres of interest, with Finland falling to the Soviet sphere of interest.[19] Shortly afterward, Germany invaded Poland and, as a result, the United Kingdom and France declared war against Germany. The Soviet Union invaded eastern Poland on 17 September.[20] Next, Moscow demanded that the Baltic states allow the establishment of Soviet military bases and the stationing of troops on their soil. The Baltic governments accepted these ultimatums, signing corresponding agreements in September and October.[21]
In October 1939, the Soviet Union attempted to negotiate with Finland for the cessation of Finnish territory on the Karelian Isthmus and the islands of the Gulf of Finland and for the establishment of a Soviet military base near the Finnish capital of Helsinki.[22] The Finnish government refused, and the Red Army invaded Finland on 30 November 1939.[23] The USSR was expelled from the League of Nations and condemned by the international community for the illegal attack.[24] Foreign support for Finland was planned, but very little actual help materialized, except from Sweden.[25] The Moscow Peace Treaty concluded the 105-day Winter War on 13 March 1940 and started the Interim Peace.[26] By the terms of the treaty, Finland ceded 11 per cent of its national territory and 13 percent of its economic capacity to the Soviet Union.[27] Finland avoided total conquest of the country by the Soviet Union and kept its sovereignty.[28]

Before the war, Finland's foreign policy had been based on multilateral guarantees for support from the League of Nations and Nordic countries and was considered a failure.[29] After the war, Finnish public opinion favored the reconquest of Finnish Karelia, the government declared national defense to be its first priority, and military expenditures rose to nearly half of public spending. Finland purchased and received donations of war materiel during and immediately after the Winter War. The Soviet Union had received a military base, which employed over 30,000 Soviet military personnel, in Hanko on Finland's southern coast near the capital Helsinki, [30]
Finland resettled some 420,000 evacuees from the lost territories. To ensure food supply, it was necessary to clear new land for the evacuees to cultivate, facilitated by the Rapid Settlement Act.[30] Finnish leadership wanted to preserve the spirit of unanimity that was commonly felt throughout the country during the Winter War. The divisive White Guard tradition of the Finnish Civil War's 16 May victory day celebration was therefore discontinued.[31] Relations between Finland and the Soviet Union remained strained after the signing of the one-sided peace treaty, and there were disputes regarding the implementation of the treaty. Finland sought security against further territorial depredations by the USSR and proposed mutual defence agreements with Norway and Sweden, but these initiatives were quashed by Moscow.[32][33]
German and Soviet expansion in Europe
After the Winter War, Germany was not popular in Finland as it was considered an ally of the Soviet Union. However, the Finnish government began to restore diplomatic relations with Germany. Finland continued its Western-oriented policy and negotiated a war trade agreement with the United Kingdom.[32] The agreement was renounced after the German invasion of Denmark and Norway on 9 April 1940, when Britain cut all trade and traffic communications with the Nordic countries. With the fall of France, a Western orientation was no longer considered an option in Finnish foreign policy.[34] On 15 and 16 June, the Soviet Union occupied the Baltic states without resistance. Soviet puppet regimes were installed, and within two months Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania were incorporated as Soviet republics within the USSR. By mid-1940, the two remaining northern democracies, Finland and Sweden, were encircled by the hostile states of Germany and the Soviet Union.[35]
On 23 June, shortly after the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states began, Soviet Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov contacted the Finns and demanded a mining licence for the Soviet Union at the nickel mines in Petsamo or, alternatively, establishing a joint Soviet-Finnish company to operate there. The licence to mine the deposit had earlier been granted to a British-Canadian company, and the proposition was rejected by Finland. The next month, the Soviets demanded that Finland destroy the fortifications built on the Åland islands and grant the USSR the right to use Finnish railways to transport Soviet troops to the newly-acquired Soviet base at Hanko. The Finns very reluctantly agreed to these demands.[36] On 24 July, Molotov accused the Finnish government of persecuting the Finland–Soviet Union Peace and Friendship Society, a pro-communist group, and soon afterwards he publicly supported the group. The society organized demonstrations in Finland, some of which turned into riots.[37][38]
Soviet sources maintain that Soviet policies up to the Continuation War were best explained as defensive measures by offensive means: The Soviet division of occupied Poland with Germany, the Soviet occupations of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia, and the Soviet invasion of Finland in the Winter War are described as elements in the Soviets' construction of a security zone or buffer region between the perceived threat from the capitalist powers of Western Europe. The Soviet sources see the post-World War II establishment of Soviet satellite states in the Warsaw Pact countries and the Finnish-Soviet Agreement of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance as the conclusion of this Soviet defense plan.[39][40][41] Western historians, such as Norman Davies and John Lukacs, dispute this view and describe the pre-war Soviet policy as an attempt to stay out of the war and regain land lost after the fall of the Russian Empire.[42]
Relations between Finland, Germany and the USSR

On 31 July 1940, German leader Adolf Hitler gave the order to start planning an assault on the Soviet Union. This meant that Germany had to reassess its position regarding both Finland and Romania. Until then, Germany had rejected Finnish appeals to purchase arms, but in August, Germans allowed the secret sale of weapons to Finland. Military authorities made an agreement on 12 September, and an official exchange of diplomatic notes was sent on 22 September. At the same time, German troops were allowed transit through Sweden and Finland.[43] In practice, this meant Germany had redrawn the border of German and Soviet spheres of influence.[44]
Due to the new situation, Molotov visited Berlin on 12–13 November.[45] He wanted Germany to withdraw its troops from Finland and stop enabling Finnish anti-Soviet sentiments. He also reminded the Germans of the 1939 Soviet–German non-aggression pact. Hitler asked how the USSR planned to settle the "Finnish question". Molotov answered that it would happen in the same manner as in Bessarabia and the Baltic states. Hitler rejected this.[46] In December, the Soviet Union, Germany and the United Kingdom all voiced opinions concerning suitable Finnish presidential candidates. Risto Ryti was the only candidate none of the three powers objected to and he was elected on 19 December.[47]
In January 1941, the USSR demanded control of the Petsamo mining area. Finland rejected the proposition as it had a rebuilt defense force and was encouraged by Germany to reject the Soviet demand.[47] On 18 December 1940, Hitler officially approved Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union.[48] He expected both Finland and Romania to join the German campaign.[49] Two days earlier, Finnish Major General Paavo Talvela had met German Colonel General Franz Halder and, a couple of days later, Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring, in Berlin. This was the first time the Germans advised the Finns, in carefully couched diplomatic terms, that they were preparing for a war with the Soviet Union. Outlines of the actual plan were revealed in January 1941 and regular contacts between Finnish and German military leaders started in February.[49]
In the late spring of 1941, the USSR made a number of goodwill gestures to prevent Finland from completely falling under German influence. Ambassador Ivan Zotov was replaced with the more flexible Pavel Orlov. Furthermore, the Soviet government announced that it no longer opposed a rapprochement between Finland and Sweden. These conciliatory measures, however, did not have any effect on Finnish policy.[50] Finland wished to re-enter World War II mainly because of the Soviet invasion of Finland during the Winter War, which had taken place after Finnish intentions of relying on the League of Nations and Nordic neutrality to avoid conflicts had failed from lack of outside support.[51] Finland primarily aimed to reverse its territorial losses from the March 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty and, depending on the success of the German invasion of the Soviet Union, to possibly expand its borders, especially into East Karelia. Some right-wing groups, such as the Academic Karelia Society, supported a Greater Finland ideology.[52]
On 20 May, the Germans invited some Finnish officers to discuss the coordination of Operation Barbarossa. The participants met on 25–28 May in Salzburg and Berlin, and continued their meeting in Helsinki from 3 to 6 June. They agreed upon the arrival of German troops, Finnish mobilization, and a general division of operations.[50] They also agreed that the Finnish Army would start mobilization on 15 June, but the Germans did not reveal the final date for the assault. The Finnish decisions were made by a small group of political and military leaders; the rest of the government was largely kept in the dark. The government was not informed until 9 June that the country would start mobilization of reservists due to tensions between Germany and the Soviet Union.[48][Note 7] Finland never signed the Tripartite Pact, which was signed by all de jure Axis powers. The Finns and Mannerheim, in particular, clearly stated they would fight against the Soviets only to the extent necessary to redress the balance of the 1940 treaty. For Hitler the matter was irrelevant; he saw Finland as an ally.[54]
Opposing forces

The Germans took responsibility for the 500 km (310 mi) stretch of the northern front in Finnish Lapland. The Finnish Army was now much stronger than it had been during the Winter War, boasting 475,000 men. Their artillery was strong, but there was only one armour battalion and a lack of motorized transportation.[55] At the beginning of the war, the Soviet Union had eighteen divisions in the region, against fifteen Finnish and four German divisions. The Finns had air supremacy. Furthermore, the Soviet Union needed its best units and latest materiel on its central European front.[56] On the Soviet side, the Karelian Isthmus was covered by the 23rd Army and Ladoga Karelia was defended by the 7th Army. In the Murmansk–Salla region, there was the 14th Army with the 42nd Corps. The Red Army also had around 40 battalions of separate regiments and fortification units present. Leningrad was garrisoned by three infantry divisions and one mechanized corps. As the initial devastating German strike against the Soviet Air Force did not affect air units located near Finland, the Soviets could deploy 700 planes as well as some aircraft from the Navy against 300 Finnish aircraft.[57]
Finnish offensive phase in 1941
Initial operations
In the late hours of 21 June 1941, German minelayers hiding in the Archipelago Sea laid two large minefields across the Gulf of Finland.[58][59] Later the same night, German bombers flew along the Gulf of Finland to Leningrad and mined the harbour and the river Neva. On the return trip, these bombers landed for refueling in Utti, Finland. In the early hours of 22 June, Finnish forces launched Operation Kilpapurjehdus, which deployd troops to the demilitarized Åland Islands. An international treaty on the status of the islands called for Finland to defend them in case of the threat of an attack.[60] However, the operation was coordinated with the German invasion, and the personnel of the Soviet consulate there were arrested. According to Finnish historian Mauno Jokipii, Finland knew that it had violated international protocol.[61]
After Axis powers launched Operation Barbarossa around 3:15 a.m. on 22 June 1941, the Soviet Union commenced an airstrike on Finland with 7 bombers, as reported at 6:06 a.m. by coastal defence ship Väinämöinen.[62] On the morning of 25 June, the Soviet Union launched another air offensive with 460 fighters and bombers targeting 19 airfields in Finland. Inaccurate intelligence and poor bombing accuracy caused several raids to hit Finnish cities or municipalities with considerable damage.[63] 23 Soviet bombers were lost[63] while the Finns did not lose aircraft.[64] The USSR stated that the airstrikes were directed against German targets, especially airfields, in Finland.[65] The bombings offered the Finnish government a ground for claiming that the country had become the target of a new assault, and the Finnish Parliament approved a "defensive war" as a fait accompli.[66] According to historian David Kirby, the message was intended more for public opinion in Finland than abroad, where it was seen that the country was in the Axis camp.[67]

Finnish advance in Karelia
In July, the Finnish military began its planned offensive. The Soviet Union struggled to contain the German invasion, and soon the Soviet High Command had to call all available units stationed along the Finnish border to the rapidly deteriorating front line.[68] Moreover, the 237th Infantry Division and, excluding the 198th Motorized Division, the Soviet 10th Mechanized Corps were withdrawn from Ladoga Karelia, thus stripping most of the reserves from the remaining defending Soviet units.[69]
The Finnish plans for the offensive in Ladoga Karelia were completed on 28 June.[70] The offensive was launched on 10 July[70][71] and by 16 July the Finns reached the shore of Lake Ladoga and cut the defending Soviet army in two, hindering the Soviets' defense of the area.[70]

The Finnish II Corps (II AK) started its offensive in the region of the Karelian Isthmus on 31 July.[72][73] Finnish troops reached the shores of Lake Ladoga on 9 August, surrounding most of three defending Soviet divisions on the northwestern coast of the lake; the Soviet divisions were evacuated across the lake. On 22 August, the Finnish IV AK Corps started its offensive from the 1940 border between the Gulf of Finland and the II AK, and advanced towards Viborg.[72] By 23 August, the Finnish II Corps had reached the Vuoksi waterway from the east and continued to surround the Soviet forces defending Viborg.[72] The Soviet withdrawal order came too late, and the Soviet divisions lost much of their equipment, although a sizable portion of their manpower was later evacuated via the Koivisto islands. The badly mauled defending Soviet army was unable to halt the Finnish offensive, and by 2 September the Finns had reached the 1939 border along its whole length. On 31 August, Finnish headquarters ordered the 2nd and 4th Army Corps, which had advanced the furthest, to halt their offensive after reaching a line just past the former border that ran from the mouth of the River Sestra via Retukylä, Aleksandrovka, and the eastern edge of the village of S. Beloostrov (Russian: Старого Белоо́стров) to Ohta and form for defense.[74][75] On 1 September the IV Corp defeated the Soviet 23rd Army at the Battle of Porlampi.[76]
According to Soviet sources, the Finns advanced and took the settlement of Novyi Beloostrov with its train station on 4 September, but a Soviet counter-attack threw them out the next day.[77][78][79] The war diary of the Finnish 12th Division facing this settlement[74][80] notes that it was quiet at the time,[80] while the neighboring 18th Division had orders on the morning of 4 September 1941 to form a line of defense north of N. Beloostrov,[81] and the Finnish 6th Regiment responsible for the Finnish 18th Division's front line facing N. Beloostrov[74] formed for defense along the small stream (Serebryanyy ruchey) north of N. Belootrov on 4 September 1941.[82][83] According to Finnish sources, Soviet forces advanced north from N. Beloostrov and attacked the Finnish positions along the small stream on the morning of 5 September 1941, but the Finns managed to repel them.[82][83] Staryi Beloostrov (Valkeasaari) was taken by the Finns on September 4 and the Soviet counterattacks failed to retake the settlement.[74] Finnish forces captured N. Beloostrov again on 10 or 11 September 1941.[74][78][79][84] According to the war diary of the Finnish 12th Division, this was done to strengthen their lines.[84] The Soviet war correspondent Luknitsky noted that this created a dangerous bulge in the Soviet defensive line.[78] According to Russian historian Nazarenko, the Finns were not able to advance further due to stronger Soviet defensive positions.[79] Fighting for the settlement continued until 20 September, when the Soviets managed to force the Finns out.[85] After that the front stabilized.[86][87]
Related to the Finnish advance to the Svir, the German Army Group North advanced from the south towards the Svir River and managed to capture Tikhvin before Soviet counterattacks forced the Germans to withdraw to the Volkhov River. Soviet forces also made several attempts to force the Finns out from their bridgehead south of the Svir during October and December 1941; however, the Soviet efforts to reduce the bridgehead were blocked by the Finns. Soviet forces also attacked the German 163rd Division, which was operating under Finnish command across the Svir in October 1941, but the Soviet forces that had crossed the river were pushed back soon after.[88]
The advance in East Karelia was halted on 6 December. The Finns had suffered 75,000 casualties, of whom 25,000 were Finnish deaths during the advance.[89]
Operation Silver Fox in Lapland
The German objective in northern Finland was to take Murmansk and seize control of the Murman Railway. Murmansk was the only year-round ice-free port in the north, and it was a threat to the nickel mine at Petsamo. Operation Silver Fox was run by the German AOK Norwegen and had two Finnish divisions under its command. The German soldiers were from central Europe and they had difficulty moving over the roadless terrain of swamp and forest. The troops managed to advance some distance with heavy casualties, but the terrain offered good defensive positions for the Soviet resistance.[90]
Politics and civilian aspects

Domestic
Germany's main forces advanced rapidly deep into Soviet territory during the first weeks of the Operation Barbarossa campaign. The Finns believed the Germans would defeat the Soviet Union quickly. President Ryti envisioned Greater Finland, where the country and other Finnic people would live inside a "natural defence borderline" by incorporating the Kola Peninsula, East Karelia, and perhaps even northern Ingria. In public, the proposed frontier was introduced by the slogan "A short border – a long peace".[91] Some members of the Finnish Parliament, such as the Social Democrats and the Swedish People's Party, opposed the idea, arguing that maintaining the 1939 frontier would be enough.[91] On 10 July, Finnish Commander-in-Chief C. G. E. Mannerheim gave an order of the day, the Sword Scabbard Declaration, in which he pledged to liberate Karelia. The Finnish government assured the Americans that it was unaware of the order.[92] According to Finnish historian Olli Vehviläinen, most Finns thought that the scope of the new offensive was only to regain what had been wrongly taken in the Winter War.[93]
Finland had prepared for a short war, but in late autumn it was clear that there would be no decisive outcome in the short term. Finnish troops suffered losses during their advance; and, overall, German victory became uncertain as German troops were halted near Moscow. The Finnish economy suffered from a lack of labour, food shortages, and increased prices. The Finnish government had to demobilize part of the army so that industrial and agricultural production would not collapse.[89] In October, Finland informed Germany that it would need 175,000 short tons (159,000 t) of grain to manage until next year's harvest. The German authorities would have rejected the request, but Hitler himself agreed. Annual grain deliveries of 200,000 short tons (180,000 t) equaled almost one half of the Finnish domestic crop. In November, Finland decided to join the Anti-Comintern Pact.[94]
International
Finland maintained good relations with the Western powers. The Finnish government stressed that Finland was fighting as a co-belligerent with Germany against the Soviet Union only to protect itself.[89] Furthermore, Finland stressed that it was still the same democratic country as it had been in the Winter War. However, on 12 July 1941, the United Kingdom signed an agreement of joint action with the Soviet Union. Furthermore, under German pressure, Finland had to close the British legation in Helsinki. As a result, diplomatic relations between Finland and the United Kingdom were broken on 1 August.[95] On 28 November, Britain presented Finland an ultimatum demanding that Finland cease military operations by 3 December.[96] Unofficially, Finland informed the Western powers that Finnish troops would halt their advance in the next few days. The reply did not satisfy the United Kingdom, which declared war on Finland on 6 December. The Commonwealth member states of Canada, Australia, British Raj, and New Zealand followed suit.[97][Note 8]
Relations between Finland and the United States were more complex; the American public was sympathetic to the "brave little democracy", and there were anti-communist feelings. At first, the United States empathised with the Finnish cause; however, the situation became problematic after Finnish troops crossed the 1939 border.[98] Finnish and German troops were a threat to the Murmansk Railway and northern communication supply line between the Western Allies and the Soviet Union.[99] On 25 October 1941, the United States demanded that Finland cease all hostilities against the Soviet Union and withdraw behind the 1939 border. In public, President Ryti rejected the demands, but in private he wrote to Mannerheim on 5 November, asking him to halt the offensive. Mannerheim agreed and secretly instructed General Hjalmar Siilasvuo to break off the assault against the Murmansk Railway.[96]
Trench warfare phase during 1942–43

Military operations
Although military operations during 1942 and 1943 were limited, the front did see some action. In early 1942, Soviet Karelian Front forces attempted to retake Medvezhyegorsk, which had been lost to the Finns in late 1941. As spring came, the Soviet forces also went on the offensive on the Svir front as well as in Kiestinki region. All Soviet offensives started promisingly, but due either to the Soviets overextending their lines or stubborn defensive resistance, the Soviet offensives were stopped and repulsed. After Finnish and German counterattacks in Kiestinki, the eventual front lines had moved very little. In September 1942, the Soviets tried again at Kriv near Medvezhyegorsk, but despite five days of fighting, the Soviets managed to push the Finnish lines back only 500 m (550 yd) on a roughly 1 km (0.62 mi)-long stretch of the front.[100]

Unconventional warfare was fought in both the Finnish and Soviet wilderness. Finnish long-range reconnaissance patrols, organized both by Finnish HQ—4th Separate Battalion (Er.P 4)—and by local units, patrolled beyond Soviet lines. In summer 1942, the Soviet Union formed the 1st Partisan Brigade. The unit was only 'partisan' in name, as it was essentially more than 600 men and women on long-range patrol. The 1st Partisan Brigade was able to infiltrate beyond Finnish patrol lines, but was found and largely destroyed.[101]
On the naval front, the Soviet Baltic Fleet still operated from the besieged city of Leningrad. In early 1942, Soviet forces recaptured the island of Gogland, but lost both Gogland and Bolshoy Tyuters to the Finns later in spring 1942. During the winter of 1941/1942, the Soviet Baltic Fleet made the decision to use the large submarine fleet to carry the fight to the enemy. Though initial submarine operations in the summer of 1942 were successful, the German Kriegsmarine and Finnish Navy soon stepped up their anti-submarine efforts, making Soviet submarine operations later in 1942 very costly. The underwater offensive carried out by the Soviets convinced the Germans to lay anti-submarine nets as well as supporting minefields between Porkkala and Naissaar which proved to be an insurmountable obstacle for Soviet submarines.[102]


Soviet partisans conducted a number of operations in Finland and in Eastern Karelia from 1941 to 1944. The major one failed when the 1st Partisan Brigade was destroyed in the beginning of August 1942 at Lake Seesjärvi. Partisans distributed propaganda newspapers, Pravda in Finnish and Lenin's Banner in Russian. One of the leaders of the partisan movement in Finland and Karelia was Yuri Andropov.[103]
Finnish sources state that partisan activity in East Karelia focused mainly on Finnish military supply and communication targets, but almost two thirds of the attacks on the Finnish side of the border targeted civilians,[104] killing 200 and injuring 50, including children and the elderly.[105][106][107]
Politics and civilian aspects
Domestic

On 19 July 1941, the Finns set up the military administration in occupied East Karelia. The goal of the administration was to prepare the region for eventual incorporation into Finland. In the early stage, the Finns aimed at ethnic cleansing where the Russian population would be expelled from the area once the war was over.[109] They would be replaced with Finnic peoples such as Karelians, Finns, Estonians, Ingrians, and Vepsians. The Russian population was deemed "non-national".[110] Most of the East Karelian population had been evacuated before the Finnish forces arrived. About 85,000 people—mostly the elderly, women, and children—were left behind, and less than half of them were Karelians. A significant number of civilians—almost 30% of the remaining Russians—were interned in concentration camps.[110]
The winter of 1941–42 was an ordeal for the Finnish urban population, due to poor harvests and a shortage of agricultural laborers.[110] However, for the Russians captured in Finnish concentration camps it was disastrous; more than 3,500 people died, mostly from starvation. This figure amounted to 13.8% of the inmates, while the corresponding figure for the free population of the occupied territories was 2.6%, and for Finland proper 1.4%.[111] Conditions gradually improved; ethnic discrimination in wage levels and food rations was terminated the following year after the Red Cross commission from Switzerland inspected the camps, and new schools were established for the Russian-speaking population.[112] By the end of the occupation, mortality rates dropped to the same levels as in Finland proper.[111]
Operation Barbarossa was planned as a blitzkrieg intended to last a few weeks. By the autumn of 1941 it was clear that this the operation would not accomplish its goals, and leading Finnish military officers started to doubt Germany's capability to finish the war quickly. German troops in northern Finland faced circumstances they were not properly prepared for, and failed to reach their targets, most importantly Murmansk. As the lines stabilized, Finland sent out peace feelers to the Soviet Union several times.[113]
International
The Continuation War represents the only case of a genuinely democratic state participating in World War II on the side of the Axis powers, albeit without being a signatory of the Tripartite Pact. The United Kingdom declared war on Finland on 6 December 1941 (Finnish Independence Day), with Canada and New Zealand declaring war on Finland on 7 December and Australia and South Africa declaring war the next day. U.S. Secretary of State Cordell Hull congratulated the Finnish envoy on 3 October 1941 for the liberation of Karelia but warned Finland not to enter Soviet territory; furthermore, the United States did not declare war on Finland when it went to war alongside the Axis countries and, together with the UK, approached Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin at the Tehran Conference about acknowledging Finnish independence. However, the U.S. government seized Finnish merchant ships in American ports, and in the summer of 1944 shut down Finnish diplomatic and commercial offices in the United States as a result of President Ryti's treaty with Germany. The U.S. government later warned Finland about the consequences of continued adherence to the Axis.[114]
The best-known British action on Finnish soil was an aircraft carrier strike on German and Finnish ships in the Finnish harbour of Petsamo on 31 July 1941.[16] This attack achieved little except the loss of three British aircraft, but it was intended as a demonstration of British support for its Soviet ally. Later in 1941, Hurricanes of No. 151 Wing RAF, based at Murmansk, provided local air cover for Soviet troops and fighter escorts for Soviet bombers.[115]
Finnish radio intelligence is said to have participated effectively in German actions against British convoys to Murmansk.[116]
Foreigners to Finland from Sweden and Estonia were among international personnel who fought during the Continuation war.[117]
Jews in Finland
Finland had a small (approx. 2,300) Jewish population. They had full civil rights and fought with other Finns in the ranks of the Finnish Army. The Germans mentioned the Finnish Jews at the Wannsee Conference in Germany during January 1942, wishing to transport them to Majdanek in General Government. SS leader Heinrich Himmler mentioned the Finnish Jews during his visit in Finland in the summer of 1942. Finnish Prime Minister Jukka Rangell replied that Finland had no "Jewish question".[54] However, there were differences for Jewish refugees in Finland. In November 1942, the Finns handed eight Jewish refugees over to the Gestapo. This raised protests among the Finnish Social Democrat ministers, and after this event no more refugees were handed over.[118] Over 500 Jewish refugees were granted asylum.[119]
The field synagogue in Eastern Karelia was one of the very few functioning synagogues on the Axis side during the war. There were even several cases of Jewish officers of Finland's army being awarded the German Iron Cross, which they declined. German soldiers were treated by Jewish medical officers who sometimes saved the soldiers' lives.[120][121][122][123]
Soviet offensive phase in 1944


Military operations
On 9 June 1944, the Soviet Union opened a major offensive against Finnish positions on the Karelian Isthmus and in the area of Lake Ladoga (it was timed to accompany D-Day[124]). On the 21.7 km (13.5 mi)-wide breakthrough segment the Red Army had concentrated 3,000 guns and mortars. In some places, the concentration of artillery pieces exceeded 200 guns for every kilometer of the front (one every 5 m (5.5 yd)). On that day, Soviet artillery fired over 80,000 rounds along the front on the Karelian Isthmus. On the second day of the offensive, the Soviet forces broke through the Finnish front lines. The Soviets penetrated the second line of defence by the sixth day. The Soviet pressure on the Karelian Isthmus forced the Finns to reinforce the area. This allowed the second Soviet offensive in Eastern Karelia to meet less resistance and to capture Petrozavodsk by 28 June 1944. According to Erickson (1991), James Gebhardt (1989), and Glantz (1998), the main objective of the Soviet offensives was to force Finland from the war.[125][126][127] The Allied invasion of France (Battle of Normandy) was coordinated with the Soviet major offensive against Finland (9 June–15 July 1944).[113]
Finland especially lacked modern antitank weaponry which could stop Soviet heavy tanks, and German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop offered these in exchange for a guarantee that Finland would not seek a separate peace again. On 26 June, President Risto Ryti gave this guarantee as a personal undertaking, which he intended to last only for the remainder of his presidency. In addition to delivering thousands of hand-held Panzerfaust and Panzerschreck antitank weapons, Hitler sent the 122nd Infantry Division, the half-strength 303rd Assault Gun Brigade, and Luftwaffe Detachment Kuhlmey to provide temporary support in the most threatened defense sectors.
With new supplies from Germany, the Finnish army halted the Soviet advance in early July 1944. At this point, the Finnish forces had retreated about one hundred kilometres, which brought them to approximately the same line of defence they had held at the end of the Winter War. This line was known as the VKT-line (short for "Viipuri–Kuparsaari–Taipale"; it ran from Viborg to the River Vuoksi to Lake Ladoga at Taipale), where the Finnish Army stopped the Soviet offensive in the Battle of Tali-Ihantala in spite of Soviet numerical and materiel superiority.[128][129][130] The front stabilized once again.[128][129][130]
A few battles were fought in the latter stages of the war. The last of them was the Battle of Ilomantsi, a Finnish victory, from 26 July to 13 August 1944.[131][132][133][134] The struggle to contain the Soviet offensive was exhausting Finnish resources. The German support under the Ryti-Ribbentrop Agreement had prevented a disaster, but it was believed the country would not be able to hold another major attack.[135] The Soviet advances against German Army Groups Center and North further complicated matters for Finland.[135]
With the front being stable so far, it was a good time for Finland to seek a way out of the war.[135][136][137] At the beginning of August President Ryti resigned to allow Finland to sue for peace again, which the new government did in late August.[126][136][138] The Soviet peace terms were harsh, but the $600,000,000 reparations demanded in the spring were reduced to $300,000,000,[131] most likely due to pressure from the United States and Britain.[139] However, after the ceasefire the Soviets insisted that the payments should be based on 1938 prices, which doubled the amount.[139]
Politics and civilian aspects
Finland began to actively seek a way out of the war after the disastrous German defeat at the Battle of Stalingrad in February 1943. Edwin Linkomies formed a new cabinet with peace as the top priority. Negotiations were conducted intermittently in 1943–44 between Finland and its representative, Juho Kusti Paasikivi, on one side, and the Western Allies and the Soviet Union on the other, but no agreement was reached. Stalin decided to force Finland to surrender; a bombing campaign on Helsinki followed. The air campaign in February 1944 included three major air attacks involving a total of over 6,000 sorties. Finnish anti-aircraft defences managed to repel the raids as only five percent of the dropped bombs hit their planned targets. Helsinki's air defense included the strategic placing of searchlights and fires as decoys outside the city to lure the Soviet bombers to drop their payloads in what were actually unpopulated areas. Major air attacks also hit Oulu and Kotka, but because of radio intelligence and effective anti-aircraft defences, the number of casualties was small.[140]
Meanwhile, the lengthy and ferocious German defence in Narva aided by the Estonians eliminated Soviet-occupied Estonia as a favorable base for Soviet amphibious invasions and air attacks against Helsinki and other Finnish cities. The tactical success of the army detachment "Narwa" from mid-February to April diminished the hopes of the Stavka to assault Finland and force it into capitulation from Estonia.[141][142][143] Finland terminated the negotiations in mid-April 1944,[144] because they considered the Soviet terms to be impossible to fulfill.[131]
Several Western historians, while noting the Soviets' assertion of their alleged need for a Soviet security buffer, contend the Soviet designs on Finland were no different from their designs on other Baltic countries. American Dan Reiter (1990) notes, “[Finland recognized] that the Soviet Union was unlikely to be satisfied with territorial concessions as a means to increase its security. [T]he Soviets viewed the control of small buffer states as critical to their security...This was the motivation", he asserts, "behind the de facto 1940 Soviet annexation of the Baltic States, and Moscow saw the control of Finland also as ultimately being necessary." Reiter and British historian Victor Rothwell quote Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov as telling his Lithuanian counterpart at the time Lithuania was effectively absorbed into the USSR, “[S]mall states will disappear...Baltic states, including Finland, will be included within the honourable family of Soviet peoples.[145][146] However, contends Reiter, "[T]he fear of rising costs of fighting pushed Stalin to accept a limited war outcome with Finland, rather than pursue absolute victory",[147] although a contemporary "Soviet document... called for the brutal military occupation of Finland at war’s end."[148] “The Finnish victory [at Ilomantsi] ended the Soviet offensive in Finland and persuaded the Soviets to give up their demand for Finland's unconditional surrender".[149] Peter Provis (1999) concludes his essay on point, “By following [self-censorship and limited appeasement] policies and fulfilling the Soviet Union's demands [for great reparations]...Finland avoided the same fate as other nations that were 'liberated' by the Red Army...Finland had once again defended her independence in a global conflict that engulfed and destroyed many other nations...The Finns had once again demonstrated their determination to avoid defeat by the Soviet Union and maintained their independence".[5]
Russian historian Nikolai Baryshnikov disputes the view that the Soviet Union wanted to deprive Finland of its independence, and that Finnish "defensive victories" prevented this. He argues that there is no documentary evidence for such claims and that the Soviet government was always open for negotiations. Baryshnikov cites the former head of the Office of Information of the Finnish General Staff, Kalle Lehmus, and other Finnish sources to show that the Finnish leaders already knew of the limited Soviet plans for Finland in the first half of July 1944, after intelligence indicated that some Soviet divisions were to be transferred to reserve in Leningrad.[150][151]
Aftermath
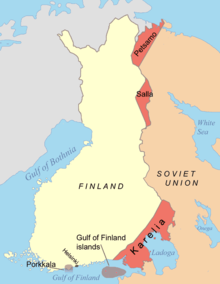
Mannerheim had repeatedly reminded the Germans that in case their troops in Estonia retreated, Finland would be forced to make peace even on extremely unfavourable terms.[152]
As sizable numbers of civilians who had been relocated into Finland from Karelia in 1939–40 had moved back into Karelia during the war, they had to be evacuated again; of the 260,000 civilians who had moved back into the Karelia, only 19 chose to remain and become Soviet citizens.[153] Most of the Ingrian Finns together with Votes and Izhorians living in German-occupied Ingria had been evacuated to Finland in 1943–1944. After armistice Finland was forced to return the evacuees.[154] Soviet authorities did not allow the 55,733 people who had been handed over to settle back in Ingria, and instead deported them to central regions of Russia.[154][155]
The number of Soviet prisoners of war was estimated to be around 64,000. Of these, 56,000 were captured in 1941.[156] Around 2,600 to 2,800 Soviet prisoners of war were handed over to the Germans in exchange for roughly 2,200 Finnic prisoners of war.[157] Out of 64,188 Soviet POWs, at least 18,318 were documented to have died in Finnish prisoner of war camps.[158]
Henrik Lunde notes that unlike many of Germany's allies, Finland survived World War II without losing its independence.[159] Although the price for war was high in war casualties, reparation payments, territorial loss, a bruised international reputation according to Olli Vehviläinen, and according to some, subsequent Soviet influence on Finland's foreign policy during the Cold War. According to Tuulikki Vuonokari, the Finnish–German alliance was different from most of the other Axis relationships, an example of which was the participation of Finnish Jews in the fight against the Soviet Union.[160] The Finnish government did not take any anti-Jewish measures, despite repeated requests from Nazi Germany.[161]
See also
- List of Finnish corps in the Continuation War
- List of Finnish divisions in the Continuation War
- Finnish prisoners of war in the Soviet Union
- Co-belligerence
- Einsatzkommando Finnland
- Finlandization
- Finnish Waffen-SS volunteers
- Paasikivi–Kekkonen line
- Salpalinja
- No. 151 Wing RAF
- Karelian question in Finnish politics
- Russo-Finnish wars
- The Unknown Soldier (novel)
- Army of Karelia
Notes
- ^ Most of the Finns served during the Finnish offensive in 1941 (approx. 500,000 men) and the Soviet offensive in August 1944 (528,000 men). Army strength varied from 260,000 to 360,000, Air Force 8,000–22,000, Navy 14,000–40,000 and directly under the HQ command 15,000–36,000. In addition, some people were obliged by law to provide supporting tasks, like 19,000 in labour groups and 25,000 men in air-raid defence (fire brigades, air-raid shelter maintenance, etc.), and 43,000 women volunteers in various non-military tasks (clerks, radio-operators, air-observers, supply).
- ^ Germans were located in Finnish Lapland executing the Operation Silver Fox.
- ^ Finnish detailed death casualties: Dead, buried 33,565; Wounded, died of wounds 12,820; Dead, not buried later declared as dead 4,251; Missing, declared as dead 3,552; Died as prisoners of war 473; Other reasons (diseases, accidents, suicides) 7,932; Unknown 611
- ^ The official Soviet number was 2,377 POWs. Finnish researchers have estimated 3,500 POWs.
- ^ Italian participation was limited to four motor torpedo boats and their crews which were used alongside already obsolete Finnish motor torpedo boat Sisu and four German minelaying KM-boats to form international Naval Detachment K which operated on Lake Ladoga during the summer and autumn of 1942.
- ^ Although the United Kingdom formally declared war on Finland on 6 December 1941, there was only one British attack on Finnish soil — a carrier strike on Petsamo[16] carried out on 31 July 1941 four months before the declaration of war. Additional British participation in the Continuation War was limited to supply aid, aerial support for its Arctic operations and a British airwing (No. 151 Wing RAF) under Soviet command, which supported Soviet air raids in the Murmansk area and trained Soviet crews for roughly a month in the autumn of 1941 — a couple of months before the declaration of war against Finland by the United Kingdom.
- ^ The matter of when and why Finland prepared for war is still somewhat opaque. Historian William R. Trotter has analysed the issue as follows:[53]
Despite exhaustive efforts by Finnish historians, it is so far proven impossible to pinpoint the exact date on which Finland was taken into confidence about Operation Barbarossa. The "paper trail" is tantalizing but leads only to dead ends and side paths, not to any benchmark conference or dates. Probably no formal agreements were necessary. The Finnish Generals who were privy to joint planning were mostly German trained and intimately familiar with the German way of waging war. There was also a certain amount of coyness on both sides. Joint operations were discussed, all during the spring of 1941, in purely hypothetical terms, and neither the Finns nor the Germans were entirely candid with one another as to their national aims and methods. In any case, the step from contingency planning to actual operations, when it came, was little more than a formality. Three days after the start of Barbarossa, Stalin handed the Finns a perfect excuse by launching some air raids. War was declared on June 25, 1941
- ^ See also the Statute of Westminster 1931.
References
Citations
- ^ Mouritzen, Hans (1997). External Danger and Democracy: Old Nordic Lessons and New European Challenges. Dartmouth. p. 35. ISBN 1855218852.
- ^ Nordstrom, Byron (2000). Scandinavia Since 1500. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press. p. 316. ISBN 978-0816620982.
- ^ Morgan, Kevin; Cohen, Gidon; Flinn, Andrew (2005). Agents of the Revolution: New Biographical Approaches to the History of International Communism in the Age of Lenin and Stalin. Bern: Peter Lang. p. 246. ISBN 978-3039100750.
- ^ https://books.google.fr/books?id=96X7piasCDkC&pg=PA246&dq=continuation+war+soviet+victory&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiJpbqR0rXTAhVFHxoKHbJYCDYQ6AEINDAC#v=onepage&q=continuation%20war%20soviet%20victory&f=false
- ^ a b Provis, Peter (1999). "Nordic Notes: Finnish achievement in the Continuation War and after". Celsius Centre for Scandinavian Studies. ISSN 1442-5165. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Provis, Peter (1999). "Nordic Notes: Finnish achievement in the Continuation War and after". Celsius Centre for Scandinavian Studies. ISSN 1442-5165. Archived from the original on 2013-11-03.
- ^ a b Maanpuolustuskorkeakoulun historian laitos, Jatkosodan historia 1–6 ("The History of the Continuation War, 1–6"), 1994
- ^ Кривошеев, ed. (2001). Россия и СССР в войнах ХХ века (in Russian). Олма-Пресс. pp. 269–71. ISBN 5224015154.
- ^ Manninen (1994) pp. 277–82
- ^ a b c Kurenmaa, Pekka; Lentilä, Riitta (2005). "Sodan tappiot". In Leskinen, Jari; Juutilainen, Antti (eds.). Jatkosodan pikkujättiläinen (in Finnish) (1st ed.). Werner Söderström Osakeyhtiö. pp. 1150–62. ISBN 9510286907.
- ^ Malmi, Timo (2005). "Jatkosodan suomalaiset sotavangit". In Leskinen, Jari; Juutilainen, Antti (eds.). Jatkosodan pikkujättiläinen (in Finnish) (1st ed.). Werner Söderström Osakeyhtiö. pp. 1022–32. ISBN 9510286907.
- ^ Finland at War p. 320
- ^ a b Manninen (1994) pp. 306–13
- ^ Philip Jowett & Brent Snodgrass p. 14
- ^ Koskimaa, Matti, Veitsenterällä, 1993, ISBN 9510188115, WSOY
- ^ a b FAA archive: Raid on Petsamo Archived 4 September 2004 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lavery, Jason Edward. The history of Finland. Greenwood Press. p. 126.
- ^ Great Soviet Encyclopedia, Finland, Moscow, 1974. ISBN 0028800109
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 30
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 31
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 33
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 39
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 44
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 49
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 65
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 69
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 215
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 70
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 74
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 75
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 76
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 77
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 216
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 78
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 79
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 80
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 81
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 218
- ^ Template:Ru iconThe problem of ensuring the security of Leningrad from the north in light of Soviet war planning of 1932–1941 by V. N. Baryshnikov: The actual war with Finland began first of all due to unresolved issues in Leningrad's security from the north and Moscow's concerns for the perspective of Finland's politics. At the same time, a desire to claim better strategic positions in case of a war with Germany had surfaced within the Soviet leadership.
- ^ Template:Ru iconФинская война. Взгляд "с той стороны" ("The Finnish war. A look from the 'other side'") by A. I. Kozlov: "After the rise of National Socialism to power in Germany, the geopolitical importance of the former 'buffer states' had drastically changed. Both the Soviet Union and Germany vied for the inclusion of these states into their spheres of influence. Soviet politicians and military considered it likely, that in case of an aggression against the USSR, German armed forces will use the territory of the Baltic states and Finland as staging areas for invasion—by either conquering or coercing these countries. None of the states of the Baltic region, excluding Poland, had sufficient military power to resist a German invasion".
- ^ Template:Ru icon Stalin's Missed Chance, by Mikhail Meltyukhov: "The English–French influence in the Baltics, characteristic for the '20s–early '30s was increasingly limited by the growth of German influence. Due to the strategic importance of the region, the Soviet leadership also aimed to increase its influence there, using both diplomatic means as well as active social propaganda. By the end of the '30s, the main contenders for influence in the Baltics were Germany and the Soviet Union. Being a buffer zone between Germany and the USSR, the Baltic states were bound to them by a system of economic and non-aggression treaties of 1926, 1932 and 1939".
- ^ Norman Davies, Europe at War 1939–1945: No Simple Victory, 2007, ISBN 978-0670018321
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 220
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 83
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 219
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 84
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 85
- ^ a b Kirby 2006, p. 221
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 86
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 87
- ^ Lunde 2011, p. 9
- ^ Jokipii 1999, pp. 145–16
- ^ Trotter, Willian R. (1991). A Frozen Hell: The Russo-Finnish Winter War of 1939–1940. Algonquin Books. p. 226.
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 102
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 90
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 91
- ^ Jokipii 1999, p. 301
- ^ Template:Fi icon Nordberg, Erkki, Arvio ja ennuste Venäjän sotilaspolitiikasta Suomen suunnalla, 2003, ISBN 9518843627
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica Premium, 2006, Finland
- ^ "Ahvenanmaansaarten linnoittamattomuutta ja puolueettomuutta koskeva sopimus". Finlex – Finnish legislation. 28 January 1922. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
7th Article, section II. If a surprise attack against Åland or against the Finnish mainland via Åland could place the neutrality of the zone in jeopardy, Finland must take necessary precautions in the zone to halt or ward off the attacker...
- ^ Jokipii 1999, p. 282
- ^ "Digitaaliarkisto". digi.narc.fi. Retrieved 25 April 2017.
- ^ a b Хазанов, Дмитрий Борисович (2006). "Chapter 3: Первая воздушная операция советских ВВС в Великой Отечественной войне". 1941. Война в воздухе. Горькие уроки [1941. The war in the air. Bitter lessons.] (in Russian). Moscow. ISBN 5699178465. Retrieved 10 August 2011.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Hyvönen, Jaakko (2001). Kohtalokkaat lennot 1939–1944 [Fateful flights 1939–1944] (in Finnish). Apali Oy. ISBN 9525026213.
- ^ Platonov, S. P., ed. (1964). Битва за Ленинград [The Battle for Leningrad]. Voenizdat Ministerstva oborony SSSR.
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 88
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 222
- ^ Lunde, Henrik O. (19 March 2011). Finland's War of Choice. Casemate Pub. p. 159. ISBN 978-1935149484.
- ^ Raunio, Ari; Kilin, Juri (2007). Jatkosodan hyökkäystaisteluja 1941. Keuruu: Otavan Kirjapaino Oy. pp. 34, 62. ISBN 978-9515930699.
- ^ a b c Lunde (2011) pp. 154–59
- ^ Коллектив Института истории СССР Академии Наук СССР (1970). Непокоренный Ленинград (in Russian). Наука. p. 19.
- ^ a b c Lunde (2011) pp. 167–72
- ^ "1941: Germany attacks, Finland follows". 13 April 2005. Archived from the original on 3 October 2011. Retrieved 28 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Raunio, Ari; Kilin, Juri (2007). Jatkosodan hyökkäystaisteluja 1941. Keuruu: Otavan Kirjapaino Oy. pp. 151–55. ISBN 978-9515930699.
- ^ Jatkosodan historia. 2, Hyökkäys Itä-Karjalaan ja Karjalan kannakselle [History of the Continuation War, part 2: Offensive to East Karelia and to Karelian Isthmus]. Sotatieteen laitoksen julkaisuja (in Finnish). Written by Department of Military History of the Maanpuolustuskorkeakoulu. Porvoo, Finland: WSOY. 1989. p. 261. ISBN 9510153281.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "Memorial Battle of Porlammi 1941 – Sveklovichnoye". www.tracesofwar.com. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
- ^ Werth 1999, p. 294
- ^ a b c Luknitsky 1988, p. 58
- ^ a b c Nazarenko, Kirill (14 April 2005). "Северный щит Ленинграда: Карельский укрепленный район (1928–1995 гг.)" [The Northern Shield of Leningrad: The Karelian Fortified Region (1928–1995)] (in Russian). КаУР – Карельский Укрепрайон (KaUR – Karelian Fortified Region). Retrieved 24 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b "Os.2/12.DE, sotapäiväkirja, 4.9.41 – 18.1.42" [War diary of 12th Divisions headquarters, section 2]. War diary collection (in Finnish). National Archives Services of Finland. pp. 3–4. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "18.D:n Op.käskyt ajalla 28.7.41 – 6.9.41" [Operational orders of 18th Division between 28.7.41 – 6.9.41]. War diary collection (in Finnish). National Archives Services of Finland. pp. 184–85. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b Häkkinen, Edvin, Ilmari (1986). Kannaksen kahlaajat – JR 6 Jatkosodassa [Waders of the Isthmus – 6th Infantry Regiment in the Continuation War] (in Finnish). Turku: Koteva Oy. pp. 176–79, 182–83. ISBN 9519978798.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "E/JR6 Taistelukertomus v. 1941" [War Diary of the headquarters of the 6th Infantry Regiment for 1941]. War diary collection (in Finnish). National Archives Services of Finland. pp. 206, 209, 324. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b "Os.2/12.DE, sotapäiväkirja, 4.9.41 – 18.1.42" [War diary of 12th Divisions headquarters, section 2]. War diary collection (in Finnish). National Archives Services of Finland. p. 8. Retrieved 25 February 2013.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ Luknitsky 1988, p. 72
- ^ Salisbury 2003, p. 246
- ^ Werth 1999, pp. 360–61
- ^ Raunio, Ari; Kilin, Juri (2008). Jatkosodan torjuntataisteluja 1942–44 [Defensive battles of Continuation War 1942–44] (in Finnish). Keuruu: Otavan Kirjapaino Oy. pp. 10–11. ISBN 978-9515930705.
- ^ a b c Vehviläinen 2002, p. 96
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 95
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 92
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 224
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 89
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 101
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 97
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 99
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 100
- ^ Vehvilainen 2002, p. 98
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 98
- ^ Raunio, Ari; Kilin, Juri (2008). Jatkosodan torjuntataisteluja 1942–44 [Defensive battles of Continuation War 1942–44] (in Finnish). Keuruu: Otavan Kirjapaino Oy. pp. 76–81. ISBN 978-9515930705.
- ^ Tikkanen, Pentti, H. (1973). Sissiprikaatin tuho [Destruction of Partisan Brigade] (in Finnish). Arvi A. Karisto Osakeyhtiö. ISBN 9512307545.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kijanen, Kalervo (1968). Suomen Laivasto 1918–1968, II [Finnish Navy 1918–1967, Part II] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Meriupseeriyhdistys/Otava. p. 123.
- ^ Template:Ru iconAndropov Yuri Vladimirovich. Biography.
- ^ Template:Fi icon Eino Viheriävaara, Partisaanien jäljet 1941–1944. Oulun Kirjateollisuus Oy, 1982. ISBN 9519939660
- ^ Erkkilä, Veikko, Vaiettu sota ("The Silenced War"). Arator Oy. ISBN 9529619189
- ^ Lauri Hannikainen, (1992). Implementing Humanitarian Law Applicable in Armed Conflicts: The Case of Finland, Martinuss Nijoff Publishers, Dordrecht. ISBN 0792316118.
- ^ Template:Fi icon Tyyne Martikainen, (2002). Partisaanisodan siviiliuhrit, PS-Paino Värisuora Oy. ISBN 9529143273.
- ^ Geust, Carl-Fredrik (2007). "Murjottavat ja nauravat Äänislinnan lapset" [Sulking and laughing children of Petrozavodsk]. Sotilasaikakauslehti (11): 44–45.
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 105
- ^ a b c Kirby 2006, p. 225
- ^ a b Vehviläinen 2002, p. 107
- ^ Kirby 2006, p. 226
- ^ a b Jutikkala 1988, p. 248
- ^ World War II: Finland Archived February 12, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Royal Air Force in Russia :Hurricanes at Murmansk Archived August 8, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Ahtokari, Reijo and Pale, Erkki: Suomen Radiotiedustelu 1927–1944 (Finnish radio intelligence 1927–1944), Helsinki, Hakapaino Oy, pp. 191–98, ISBN 952909437X
- ^ Jowett, Philip; Snodgrass, Brent; Ruggeri, Raffaele (2006). Finland at War 1939–45. Oxford: Osprey Publishing Ltd. pp. 29–31. ISBN 978-1841769691.
- ^ Vehviläinen 2002, p. 103
- ^ "Finland" (PDF). Yad Vashem. Retrieved 29 October 2010.
- ^ Template:Fi icon Rautkallio, Hannu, Suomen juutalaisten aseveljeys (Finnish Jews as German Brothers in Arms), Tammi, 1989
- ^ Tuulikki Vuonokari (2003), Jews in Finland During the Second World War, Finnish Institutions Student Paper: FAST Area Studies Program Department of Translation Studies, University of Tampere, Autumn 2003 "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Retrieved 2009-02-06. - ^ Poljakoff in Torvinen, Kadimah: Suomen juutalaisten historia 35 Smolar 155–57
- ^ Torvinen, Taimi, Kadimah: Suomen juutalaisten historia Helsinki: Otava, 1989 pp. 117–67 Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 2009-02-06.
- ^ Declaration of the Three Powers, December 1, 1943, Tehran Conference
- ^ Erickson 1993, p. 197
- ^ a b Gebhardt 1989, p. 2
- ^ Glantz 1998, p. 202
- ^ a b 500 Days: The War in Eastern Europe ... – Google Books
- ^ a b Finland at War 1939–45 – Google Books
- ^ a b Dictionary of Battles and Sieges: F–O – Google Books
- ^ a b c Moisala 1988
- ^ Lunde 2011, p. 299
- ^ Ilomantsin mottitaistelut 26.7. – 13.8.1944[permanent dead link] (The motti-battle in Ilomantsi). Ilomantsi sodassa (Ilomantsi at war). In Finnish: Nykyisen Ilomantsin itäosissa käytiin kesällä 1944 yli viikon mittainen kiivas torjuntataistelu, jossa kaksi viivyttämällä kulutettua neuvostodivisioonaa pysäytettiin, paloiteltiin motteihin ja lyötiin lähes täydellisesti. Tämä suurtaistelu varmisti armeijamme puolustuksen pitävyyden jatkosodan raskaina viimeisinä päivinä. "A week-long vehement defensive battle was fought in the eastern parts of what is now Ilomantsi, where two Soviet divisions were stopped, cut up into mottis, and almost completely destroyed. This operation secured our army's defence in the tough final days of the Continuation war".
- ^ Juutilainen 1994
- ^ a b c Grier 2007, p. 31
- ^ a b Erickson 1993, pp. 329–30
- ^ Glantz 1998, p. 229
- ^ Glantz 1998, pp. 201–03
- ^ a b Ziemke (2002), p. 390
- ^ Mäkelä, Jukka (1967). Helsinki liekeissä. Helsinki: Werner Söderström osakeyhtiö. p. 20.
- ^ Paulman, F. I. (1980). "Nachalo osvobozhdeniya Sovetskoy Estoniy". Ot Narvy do Syrve [From Narva to Sõrve] (in Russian). Tallinn: Eesti Raamat. pp. 7–119.
- ^ Laar, Mart (2005). Estonia in World War II. Tallinn: Grenader. pp. 32–59.
- ^ Jackson, Robert (2007). Battle of the Baltic: The Wars 1918–1945. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Maritime.
- ^ Gebhardt 1989, p. 1
- ^ Dan Reiter, How Wars End, Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey USA (2009), p. 131.
- ^ Rothwell, Victor (2006). War Aims in the Second World War: The War Aims of the Key Belligerents 1939–1945. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 143, 145. ISBN 978-0748615032.
- ^ Dan Reiter, How Wars End, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (2009), pp. 138, 135.
- ^ Dan Reiter, How Wars End, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (2009), p. 135.
- ^ Dan Reiter, How Wars End, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (2009), p. 136.
- ^ Baryshnikov (2002), pp. 222–23 (Section heading "Стремительный прорыв," paragraph #48 et seq., after cit. 409)
- ^ Baryshnikov (2006)
- ^ Howard D. Grier. Hitler, Dönitz, and the Baltic Sea, Naval Institute Press, 2007, ISBN 1591143454. p. 121
- ^ Hietanen, Silvo (1992). "Evakkovuosi 1944 – jälleen matkassa" [Evacuation of year 1944 – again on the road]. Kansakunta sodassa. 3. osa. Kuilun yli (in Finnish). Helsinki: Valtion Painatuskeskus. pp. 130–39.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b Taagepera (2013), p. 144
- ^ Scott and Liikanen (2013), pp. 59–60
- ^ Juutilainen & Leskinen (ed.); Kujansuu, Juha (2005), p. 1036
- ^ Helsingin Sanomat: "Wartime refugees made pawns in cruel diplomatic game." Archived 2011-06-04 at the Wayback Machine 8 November 2003
- ^ Template:Fi icon Ylikangas, Heikki, Heikki Ylikankaan selvitys Valtioneuvoston kanslialle, Government of Finland Archived August 8, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lunde 2011, p. 379
- ^ Vuonokari, Tuulikki (21 November 2003). "Jews in Finland During the Second World War". University of Tampere. Archived from the original on 10 January 2008. Retrieved 29 October 2010.
- ^ Letter to the New York Times by Mark Cohen, Executive Director of Holocaust Publications in New York, 28 April, 1987
Bibliography
- Baryshnikov, Nikolai I. (2002). Блокада Ленинграда и Финляндия 1941–1944 [Finland and the Siege of Leningrad, 1941–1944] (in Russian). St. Petersburg: Johan Beckman Institute. ISBN 9525412105.
- Baryshnikov, Nikolai I. (2006). Феномен фальши: 'Победа в противостоянии' [The Phenomenon of Lies: 'The Victory in the Confrontation']. St. Petersburg and the Countries of Northern Europe (in Russian). St. Petersburg: Russian Christian Humanitarian Academy. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
- Erickson, John (1993). The Road to Berlin: Stalin's War with Germany. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 0300078137.
- Gebhardt, James (1990). "The Petsamo-Kirkenes Operation: Soviet Breakthrough and Pursuit in the Arctic, October 1944" (PDF). Leavenworth Papers (17). Fort Leavenworth: Combat Studies Institute. ISSN 0195-3451. Retrieved 10 May 2010.
- Glantz, David; House, Jonathan (1998). When Titans Clashed: How the Red Army Stopped Hitler. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0700608997.
- Grier, Howard (2007). Hitler, Dönitz, and the Baltic Sea: the Third Reich's last hope, 1944–1945. Annapolis: US Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1591143451.
- Jokipii, Mauno (1999). Финляндия на пути к войне [The Launching of the Continuation War] (in Russian). Petrozavodsk: Karelia. ISBN 5754507356.
- Jutikkala, Eino; Pirinen, Kauko (1988). A History of Finland. Dorset Press. ISBN 0880292601.
- Juutilainen, Antti (1994). Ilomantsi – lopultakin voitto (in Finnish). Rauma: Kirjapaino Oy West Point. ISBN 9519521852.
- Kirby, David (2006). A concise history of Finland. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 343. ISBN 978-0521539890.
- Krosby, H. Peter (1968). Finland, Germany, and the Soviet Union, 1940–1941: The Petsamo Dispute. University of Wisconsin Press.
- Leskinen, Jari; Juutilainen, Antti (ed.) (2005). Jatkosodan pikkujättiläinen (in Finnish) (1st ed.). WSOY. ISBN 9510286907.
{{cite book}}:|first2=has generic name (help) - Leskinen, Jari; Juutilainen, Antti, eds. (1999). Talvisodan pikkujättiläinen (in Finnish) (1st ed.). Werner Söderström Osakeyhtiö. p. 976. ISBN 9510235369.
- Luknitsky, Pavel (1988). Сквозь всю блокаду [Through the Siege] (in Russian). Leningrad: Lenizdat.
- Lunde, Henrik O. (2011). Finland's War of Choice: The Troubled German-Finnish Alliance in World War II. Newbury: Casemate Publishers. ISBN 978-1612000374.
- Manninen, Ohto (1994). Molotovin cocktail- Hitlerin sateenvarjo [Molotov's cocktail – Hitler's umbrella] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Painatuskeskus. ISBN 9513714950.
- Moisala, U.E.; Alanen, Pertti (1988). Kun hyökkääjän tie pysäytettiin (in Finnish). Keuruu: Otava. ISBN 9511103865.
- Raunio, Ari (ed.); Maanpuolustuskorkeakoulun Historian laitos (1994). Jatkosodan historia 1–6 (in Finnish) (1st ed.). WSOY.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help) - Salisbury, Harrison E. (2003). The 900 Days: The Siege of Leningrad (2 ed.). Cambridge: Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0306812989.
- Scott, James Wesley; Liikanen, Ilkka (2013). European Neighbourhood Through Civil Society Networks?: Policies, Practices and Perceptions. Routledge. ISBN 978-1317983453.
- Taagepera, Rein (2013). The Finno-Ugric Republics and the Russian State. Routledge. ISBN 978-1136678080.
- Vehviläinen, Olli (2002). Finland in the Second World War: Between Germany and Russia. New York: Palgrave. ISBN 0333801490.
- Werth, Alexander (1999). Russia at War, 1941–1945 (2 ed.). New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0786707225.
- Ziemke, Earl (2002). Stalingrad to Berlin. The German Defeat in the East (PDF). Washington DC: Government Printing Office. ISBN 978-0160019623.
- Finland at War: The Continuation and Lapland Wars 1941–45 by Vesa Nenye, Peter Munter, Toni Wirtanen, and Chris Birks
Further reading
- Krosby, Hans Peter (1966). Nikkelidiplomatiaa Petsamossa 1940–1941. Kirjayhtyma.
- Krosby, Hans Peter (1967). Suomen valinta 1941. Kirjayhtyma.
- Platonov, S.P., ed. (1964). Битва за Ленинград. Voenizdat Ministerstva oborony SSSR. ISBN 0125581807.
- Polvinen, Tuomo I. (1979). Suomi kansainvälisessä politiikassa 1941–1947, osa 1: 1941–1943: Barbarossasta Teheraniin. WSOY.
- Polvinen, Tuomo I. (1980). Suomi kansainvälisessä politiikassa 1941–1947, osa 2: 1944: Teheranista Jaltaan. WSOY.
- Polvinen, Tuomo I. (1981). Suomi kansainvälisessä politiikassa 1941–1947, osa 3: 1945–1947: Jaltasta Pariisin rauhaan. WSOY.
- Sana, Elina (1994). Luovutetut: Suomen ihmisluovutukset Gestapolle [The Extradited: Finland's Extraditions to Gestapo]. WSOY. ISBN 9510279757.
- Schwartz, Andrew J. (1960). America and the Russo-Finnish War. Washington, D.C.: Public Affairs Press. ISBN 0837179645.
- Seppinen, Ilkka (1983). Suomen Ulkomaankaupan ehdot 1939–1944 [Finnish Foreign Trade Conditions, 1939–44]. Suomen Historiallinen Seura. ISBN 951925448X.
- Taylor, Alan (23 May 2013). "Finland in World War II". The Atlantic.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - Wuorinen, John H., ed. (1948). Finland and World War II 1939–1944. The Ronald Press Company. ISBN 0313241333.
External links
- Военный альбом (photographs of World War II and the Great Patriotic War 1939–1945)
- Finna.fi (search service for information from Finnish archives, libraries and museums)
- Finnish Wartime Photograph Archive (under CC BY 4.0)
