Asiatic Squadron: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
===Philippine-American War=== |
===Philippine-American War=== |
||
{{Main|Philippine-American War}} |
{{Main|Philippine-American War}} |
||
The Asiatic squadron participated in the [[Philippine-American War]] from 1899 to it's disbandment. American naval forces operated by sending landing parties ashore and by providing them with naval gunfire support. From 1899 to 1902, the squadron conducted several missions against the Filipinos. USS '' |
The Asiatic squadron participated in the [[Philippine-American War]] from 1899 to it's disbandment. American naval forces operated by sending landing parties ashore and by providing them with naval gunfire support. From 1899 to 1902, the squadron conducted several missions against the Filipinos. At the beginning of the war in February of 1899, several American warships were supporting the oocupation of the Philippines. Admirals Dewey's squadron engaged in naval operation against the Filipinos during and after the [[Battle of Manila (1899)|Battle of Manila]] while other vessels engaged in a campaign to take [[Caloocan]]. [[USS Monadnock|USS ''Monadock'']], [[USS Charleston|USS ''Charleston'']] USS Concord, [[USS Callao|USS ''Callao'']] and the former Spanish [[gunboat]] ''Laguna de Bay'' bombarded enemy position during the major [[Battle of Coolacan]] in February of 1899. Over 300 Filipnos were killed in battle and three times as many wounded, many of the casualties were attributed to accurate naval gunfire. USS ''Baltimore'' and USS ''Petrel'' served at the [[Battle of Iloilo]], over 1,000 Filipinos, were defeated by the two warships when they bombarded the fort there and sent marines and sailors ahore. Only minor skirmishing occured on land due to the Filipinos who retreated and burned the town as they left. |
||
===Boxer Rebellion=== |
===Boxer Rebellion=== |
||
Revision as of 07:05, 20 September 2010
| Asiatic Squadron | |
|---|---|
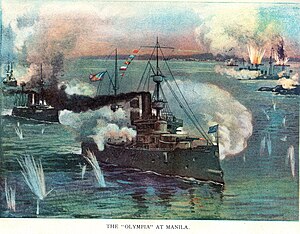 The Asiatic Squadron destroying the Spanish fleet off Manila in 1898. | |
| Active | 1868 - 1902 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | naval squadron |
The Asiatic Squadron was a squadron of United States Navy warships stationed in East Asia during the latter half of the 19th century, it was created in 1868 when the East India Squadron was disbanded. Vessels of this station were primarily involved in matters relating to American commerce with China and Japan though it participated in several conflicts over forty years of service until being merged into the the Asiatic Fleet in 1902.
History
Korean Expedition
In May of 1871, Rear Admiral John Rodgers went to Korea, commanding an expedition of five Asiatic Squadron vessels, USS Colorado, USS Monocacy, USS Benicia, USS Palos and USS Alaska. The objective of the operation was to ascertain the fate of the merchant ship SS General Sherman, establish trade relations and to recieve an assurance from the Joseon government that shipwrecked American sailors would be safely treated should they become stranded in Korea.

On June 1, while Rear Admiral Rodgers was negotiating in Inchon, one of the Selee River forts opened fire on USS Palos as she traversed Gangwha Straits. In the following engagement, the Palos and USS Monocacy bombarded the fort until it was silenced and on June 10, the expedition attacked in force. Five of the six hostile forts were captured and destroyed, over 200 Koreans were killed and dozens of cannons were captured. Ultimately, the Americans won a military victory but the Koreans refused to sign a trading treaty until 1882.
Spanish-American War
On April 27, 1898, the squadron, composed of the flagship Olympia under George Dewey, Baltimore, Raleigh, Petrel, Concord, Boston, and McCulloch, sailed from Mirs Bay, China, to the Philippines to participate in the Spanish-American War. The squadron proceeded to destroy the Spanish fleet guarding the Philippines, and effectively took control of Manila Bay. Eight Spanish ships were sunk and over 150 killed while the Americans suffered only slight damage.
Philippine-American War
The Asiatic squadron participated in the Philippine-American War from 1899 to it's disbandment. American naval forces operated by sending landing parties ashore and by providing them with naval gunfire support. From 1899 to 1902, the squadron conducted several missions against the Filipinos. At the beginning of the war in February of 1899, several American warships were supporting the oocupation of the Philippines. Admirals Dewey's squadron engaged in naval operation against the Filipinos during and after the Battle of Manila while other vessels engaged in a campaign to take Caloocan. USS Monadock, USS Charleston USS Concord, USS Callao and the former Spanish gunboat Laguna de Bay bombarded enemy position during the major Battle of Coolacan in February of 1899. Over 300 Filipnos were killed in battle and three times as many wounded, many of the casualties were attributed to accurate naval gunfire. USS Baltimore and USS Petrel served at the Battle of Iloilo, over 1,000 Filipinos, were defeated by the two warships when they bombarded the fort there and sent marines and sailors ahore. Only minor skirmishing occured on land due to the Filipinos who retreated and burned the town as they left.
Boxer Rebellion
The Asiatic Squadron also participated in the China Relief Expedition in 1900. An international legation including United States Marines and United States Navy sailors slowly fought their way to take control of Tientsin away from the Boxer rebels in order to relieve Peking. At the time, Peking was home to many foreigners who were under siege by Boxer rebels. The Asiatic Squadron subsequently became the Asiatic Fleet in 1902.
Commanders
Successive Commanders-in-Chief of the Asiatic Fleet were as follows[1].
- Henry H. Bell, ( - 11 January 1868)
- John R. Goldsborough, (11 January 1868 - 18 April 1868)
- Stephen C. Rowan, (18 April 1868 – 19 August 1870)
- John Rodgers, (19 August 1870 – 12 May1872)
- Thornton A. Jenkins, (1 September 1872 – 12 December 1873)
- Enoch Greenleafe Parrott, (12 December 1873 - 12 January 1874)
- Edmund Calhoun, (12 January 1874 - 29 May 1874)
- Alexander Mosely Pennock, (29 May 1874 - 24 June 1875)
- R. F. R. Lewis, (24 June 1875 - 16 August 1875)
- William Reynolds, (16 August 1875 - 12 August 1877)
- Jonathan Young, (12 August 1877 - 4 October 1877)
- Thomas H. Patterson, (12 August 1877 - 11 September 1880)
- John M. B. Clitz, (11 September 1880 - 21 April 1883)
- Peirce Crosby, (21 April 1883 - 30 October 1883)
- Joseph S. Skerrett, (30 October 1883 - 19 December 1883)
- John Lee Davis (19 December 1883 - 22 November 1886)
- Ralph Chandler, (22 November 1886 - 11 February 1889)
- George E. Belknap, (4 April 1889 – 20 February 1892)
- David B. Harmony, (20 February 1892 - 7 June 1893)
- John Irwin, (11 June 1893 – 11 December 1893)
- Joseph S. Skerrett, (11 December 1893 – 1 September 1894)
- Charles C. Carpenter, (1 September 1894 – 21 December 1895)
- Frederick V. McNair, Sr. (21 December 1895 - 3 January 1898)
- George Dewey, (3 January 1898 - 5 June 1899)
- John C. Watson, (5 June 1899 - 19 April 1900)
- George C. Remey (19 April 1900 - 1 March 1902)
See Also
- European Squadron
- Home Squadron
- Brazil Squadron
- Mediterranean Squadron
- North Atlantic Squadron
- West Indies Squadron
- Home Squadron
- New Orleans Squadron
- Pacific Squadron
References
- ^ Kemp Tolley, Yangtze Patrol: The U.S. Navy in China, pg 317
