Haswell (microarchitecture): Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary Tag: Reverted |
No edit summary Tags: Manual revert nowiki added |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Intel processor microarchitecture}} |
{{short description|Intel processor microarchitecture}} |
||
{{Use American English|date=December 2022}} |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=December 2022}} |
|||
{{Infobox CPU |
{{Infobox CPU |
||
| name |
| name = Haswell |
||
| image |
| image = Haswell Chip.jpg |
||
| caption |
| caption = A Haswell [[Wafer (electronics)|wafer]] with several [[Die (integrated circuit)|dies]], with a pin for scale |
||
| produced-start = {{ |
| produced-start = {{start date and age|June 4, 2013}} |
||
| produced-end = |
| produced-end = |
||
| brand1 = {{unbulleted list|Core i3|Core i5|Core i7|Xeon E3 v3|Xeon E5 v3|Xeon E7 v3|Pentium|Celeron}} |
|||
| soldby = [[Intel]] |
|||
| model = {{unbulleted list|Haswell|Haswell Refresh|Haswell-E|Haswell-EP|Haswell-EX}} |
|||
| designfirm = [[Intel]] |
|||
| numcores = {{unbulleted list|2–4 (mainstream)|6–8 (enthusiast)|2–18 (Xeon)}} |
|||
| manuf1 = [[Intel]] |
|||
| size-from = [[22 nanometer|22 nm]] ([[FinFET|Tri-Gate]]) |
|||
| brand1 = {{unbulleted list|Core i3|Core i5|Core i7|Xeon E3 v3|Xeon E5 v3|Xeon E7 v3|Pentium|Celeron}} |
|||
| size-to = |
|||
| model = {{unbulleted list|Haswell|Haswell Refresh|Haswell-E|Haswell-EP|Haswell-EX}} |
|||
| l1cache = 64 [[Kibibyte|KB]] per core |
|||
| numcores = {{unbulleted list|2–4 (mainstream)|6–8 (enthusiast)|2–18 (Xeon)}} |
|||
| l2cache = 256 KB per core |
|||
| size-from = [[Intel]] [[22 nanometer|22 nm]] ([[FinFET|Tri-Gate]]) |
|||
| l3cache = 2–45 [[Mebibyte|MB]] (shared) |
|||
| size-to = |
|||
| |
| l4cache = 128 MB of [[eDRAM]] (Iris Pro models only) |
||
| |
| cpuid = 0306C3h |
||
| code = {{unbulleted list|80646 (desktop [[LGA 1150]])|80647 (mobile [[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]])|80648 (desktop [[LGA 2011|LGA 2011-3]])|80644 (server LGA 2011-3)}} |
|||
| l3cache = 2–45{{nbsp}}MB (shared) |
|||
| dmi = |
|||
| l4cache = 128{{nbsp}}MB of [[eDRAM]] (Iris Pro models only) |
|||
| gpu = {{unbulleted list|[[Intel HD Graphics|HD Graphics]] 4200|HD Graphics 4400|HD Graphics 4600|HD Graphics 5000|Iris 5100|Iris Pro 5200}} |
|||
| cpuid = 0306C3h |
|||
| arch1 = [[x86-64]] |
|||
| code = {{unbulleted list|80646 (desktop [[LGA 1150]])|80647 (mobile [[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]])|80648 (desktop [[LGA 2011|LGA 2011-3]])|80644 (server LGA 2011-3)}} |
|||
| |
| microarch = Haswell |
||
| instructions = [[x86]], [[x86-64]] |
|||
| gpu = {{unbulleted list |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD Graphics]] |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD Graphics 4200]] |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD Graphics 4400]] |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD Graphics 4600]] |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD Graphics 5000]] |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris 5100]] |[[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris Pro 5200]]}} |
|||
| extensions = [[AES instruction set|AES-NI]], [[CLMUL instruction set|CLMUL]], [[RDRAND]], [[Trusted Execution Technology|TXT]] |
|||
| arch1 = [[x86-64]] |
|||
| extensions1 = [[MMX (instruction set)|MMX]], [[Streaming SIMD Extensions|SSE]], [[SSE2]], [[SSE3]], [[SSSE3]], [[SSE4]], [[SSE4.1]], [[SSE4.2]], [[FMA instruction set|FMA3]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions|AVX]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2#Advanced Vector Extensions 2|AVX2]], and [[Transactional Synchronization Extensions|TSX]] (disabled via [[microcode]], except for Haswell-EX) |
|||
| microarch = Haswell |
|||
| |
| extensions3 = [[Intel VT-x|VT-x]], [[Intel VT-d|VT-d]] |
||
| sock1 = [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
| extensions = [[AES instruction set|AES-NI]], [[CLMUL instruction set|CLMUL]], [[RDRAND]], [[Trusted Execution Technology|TXT]] |
|||
| sock2 = [[rPGA 947]] |
|||
| extensions1 = [[MMX (instruction set)|MMX]], [[Streaming SIMD Extensions|SSE]], [[SSE2]], [[SSE3]], [[SSSE3]], [[SSE4]], [[SSE4.1]], [[SSE4.2]], [[FMA instruction set|FMA3]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions|AVX]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2#Advanced Vector Extensions 2|AVX2]], and [[Transactional Synchronization Extensions|TSX]] (disabled via [[microcode]], except for Haswell-EX) |
|||
| sock3 = BGA 1364 |
|||
| extensions3 = [[Intel VT-x|VT-x]], [[Intel VT-d|VT-d]] |
|||
| sock4 = BGA 1168 |
|||
| sock1 = '''Desktop''' {{bulleted list |[[LGA 1150]] |BGA 1364 |[[LGA 2011-v3]] |<br>}} |
|||
| sock5 = [[LGA 2011-v3]] |
|||
| sock2 = '''Mobile''' {{bulleted list |[[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]] |BGA 1364 |BGA 1168 |<br>}} |
|||
| predecessor = [[Sandy Bridge]] (Tock)<br>[[Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Ivy Bridge]] ([[Tick–tock model|Tick]]) |
|||
| sock5 = '''Server''' {{bulleted list |[[LGA 2011-v3]]}} |
|||
| |
| successor = [[Broadwell (microarchitecture)|Broadwell]] (Tick/Process)<br>[[Skylake (microarchitecture)|Skylake]] (Tock) |
||
| successor = [[Broadwell (microarchitecture)|Broadwell]] (Tick/Process)<br>[[Skylake (microarchitecture)|Skylake]] (Tock) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 41: | Line 38: | ||
Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the [[Intel 8 Series chipsets]], [[Intel 9 Series chipsets]], and [[Intel Xeon chipsets#Haswell-based Xeon chipsets|Intel C220 series chipsets]]. |
Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the [[Intel 8 Series chipsets]], [[Intel 9 Series chipsets]], and [[Intel Xeon chipsets#Haswell-based Xeon chipsets|Intel C220 series chipsets]]. |
||
At least one Haswell-based processor is still being sold as of 2022, the Pentium G3420.<ref>{{Cite web |
At least one Haswell-based processor is still being sold as of 2022, the Pentium G3420.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Haswell is back: Intel reverses decision to discontinue 22nm Pentium CPUs|url=https://www.techspot.com/news/83078-haswell-back-intel-reverses-decision-discontinue-22nm-pentium.html|access-date=2021-04-12|website=TechSpot|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Shilov|first=Anton|title=Intel Un-Discontinues Pentium G3420 'Haswell' CPU|url=https://www.anandtech.com/show/15211/intel-undiscontinues-pentium-g3420-haswell-cpu-because-people-need-it|access-date=2021-04-12|website=www.anandtech.com}}</ref> |
||
== |
==Design== |
||
The Haswell architecture is specifically designed<ref>{{cite web |
The Haswell architecture is specifically designed<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pcper.com/reviews/Processors/IDF-2012-Intel-Haswell-Architecture-Revealed |title=IDF 2012: Intel Haswell Architecture Revealed |publisher = PC Perspective |last=Shrout |first=Ryan|date=11 September 2012 }}</ref> to optimize the power savings and performance benefits from the move to [[FinFET]] (non-planar, "3D") transistors on the improved 22 nm process node.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/2206077/idf-intel-says-haswell-wont-use-ivy-bridge-transistors |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120920221812/http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/2206077/idf-intel-says-haswell-wont-use-ivy-bridge-transistors |url-status=unfit |archive-date=September 20, 2012 |title=IDF: Intel says Haswell won't use Ivy Bridge transistors |publisher=The Inquirer |date=2012-09-17 |access-date=2013-10-12}}</ref> |
||
Haswell has been launched in three major forms:<ref>{{cite web |
Haswell has been launched in three major forms:<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.techpowerup.com/177817/Intel-Haswell-and-Broadwell-Silicon-Variants-Detailed.html |title=Intel Haswell and Broadwell Silicon Variants Detailed |publisher=techPowerUp |date=2012-12-26 |access-date=2013-10-12}}</ref> |
||
* Desktop version ([[LGA 1150]] socket and the [[LGA 2011-v3]] socket): ''Haswell-DT'' |
* Desktop version ([[LGA 1150]] socket and the [[LGA 2011-v3]] socket): ''Haswell-DT'' |
||
* Mobile/Laptop version ([[Pin grid array|PGA]] socket): ''Haswell-MB'' |
* Mobile/Laptop version ([[Pin grid array|PGA]] socket): ''Haswell-MB'' |
||
| Line 54: | Line 51: | ||
** 10 W TDP class (SoC): ''Haswell-ULX'' (for tablets and certain UltraBook-class implementations) |
** 10 W TDP class (SoC): ''Haswell-ULX'' (for tablets and certain UltraBook-class implementations) |
||
=== |
===Notes=== |
||
* ULT = ''Ultra Low TDP''; ULX = ''Ultra Low eXtreme'' TDP |
* ULT = ''Ultra Low TDP''; ULX = ''Ultra Low eXtreme'' TDP |
||
* Only certain quad-core variants and BGA R-series [[stock keeping unit]]s (SKUs) receive GT3e ([[Intel Iris Pro]] 5200) integrated graphics. All other models have GT3 ([[Intel HD]] 5000 or [[Intel Iris]] 5100), GT2 (Intel HD 4200, 4400, 4600, P4600 or P4700) or GT1 (Intel HD Graphics) integrated graphics.<ref>{{cite web |
* Only certain quad-core variants and BGA R-series [[stock keeping unit]]s (SKUs) receive GT3e ([[Intel Iris Pro]] 5200) integrated graphics. All other models have GT3 ([[Intel HD]] 5000 or [[Intel Iris]] 5100), GT2 (Intel HD 4200, 4400, 4600, P4600 or P4700) or GT1 (Intel HD Graphics) integrated graphics.<ref>{{cite web |
||
| url = http://www.anandtech.com/show/6926/intel-iris-iris-pro-graphics-haswell-gt3gt3e-gets-a-brand |
|||
| title = Intel Iris & Iris Pro Graphics: Haswell GT3/GT3e Gets a Brand |
|||
| date = 2013-05-01 | access-date = 2013-10-22 |
|||
| author = Anand Lal Shimpi | publisher = [[AnandTech]] |
|||
}}</ref> See also [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics]] for more details. |
|||
* Due to the low power requirements of tablet and UltraBook platforms, Haswell-ULT and Haswell-ULX are only available in dual-core configurations. All other versions come as dual- or quad-core variants. |
* Due to the low power requirements of tablet and UltraBook platforms, Haswell-ULT and Haswell-ULX are only available in dual-core configurations. All other versions come as dual- or quad-core variants. |
||
=== |
===Performance=== |
||
Compared to [[Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Ivy Bridge]]: |
Compared to [[Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Ivy Bridge]]: |
||
* Approximately 8% faster [[Vector processor|vector processing]]<ref name="vs">{{cite web |
* Approximately 8% faster [[Vector processor|vector processing]]<ref name="vs">{{cite web|last=Shvets|first=Gennadiy|title=Intel Core i5-3570K vs i5-4670K|url=http://www.cpu-world.com/Compare/579/Intel_Core_i5_i5-3570K_vs_Intel_Core_i5_i5-4670K.html|access-date=23 July 2013|date=9 July 2013}}</ref> |
||
* Up to 5% higher single-threaded performance |
* Up to 5% higher single-threaded performance |
||
* 6% higher multi-threaded performance |
* 6% higher multi-threaded performance |
||
* Desktop variants of Haswell draw between 8% and 23% more power under load than Ivy Bridge.<ref name="vs" /><ref>{{cite web |title=Intel Core i7-4770K CPU Review. Intel Haswell for Desktops: Ruin of Our Hopes?. Page 11 | |
* Desktop variants of Haswell draw between 8% and 23% more power under load than Ivy Bridge.<ref name="vs" /><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.xbitlabs.com/articles/cpu/display/core-i7-4770k_11.html |title=Intel Core i7-4770K CPU Review. Intel Haswell for Desktops: Ruin of Our Hopes?. Page 11 |publisher=X-bit labs |access-date=2013-10-12}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://translate.google.com/translate?sl=auto&tl=en&js=n&prev=_t&hl=en&ie=UTF-8&u=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.inpai.com.cn%2Fdoc%2Fhard%2F198653_34.htm&act=url |title=Google Translate |website=Translate.Google.com |access-date=2014-01-16}}</ref> |
||
* A 6% increase in sequential CPU [[Computer performance|performance]] (eight execution ports per core versus six)<ref name="vs" /> |
* A 6% increase in sequential CPU [[Computer performance|performance]] (eight execution ports per core versus six)<ref name="vs" /> |
||
* Up to 20% performance increase over the integrated HD4000 [[Graphics processing unit|GPU]] (Haswell HD4600 vs Ivy Bridge's built-in [[Intel HD Graphics|Intel HD4000]])<ref name="vs" /> |
* Up to 20% performance increase over the integrated HD4000 [[Graphics processing unit|GPU]] (Haswell HD4600 vs Ivy Bridge's built-in [[Intel HD Graphics|Intel HD4000]])<ref name="vs" /> |
||
* Total performance improvement on average is about 3%<ref name="vs" /> |
* Total performance improvement on average is about 3%<ref name="vs" /> |
||
* Around 15 °C hotter than Ivy Bridge, while clock frequencies of over 4.6 |
* Around 15 °C hotter than Ivy Bridge, while clock frequencies of over 4.6 GHz are achievable<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pcpro.co.uk/news/382267/intel-haswell-hotter-and-slower-than-expected|title = Intel Haswell hotter and slower than expected| publisher = PC Pro| access-date = 2013-10-12}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bit-tech.net/news/hardware/2013/06/06/haswell-heat/|title=Haswell heat surprises system builders|work=bit-tech|access-date=13 September 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.xbitlabs.com/news/cpu/display/20130606231316_Retail_Versions_of_Intel_Core_i_Haswell_Are_Hotter_and_Slower_Than_Expected_Report.html|title=Retail Versions of Intel Core i "Haswell" Are "Hotter and Slower" Than Expected – Report|access-date=13 September 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.xbitlabs.com/articles/cpu/display/core-i7-4770k_12.html|title=Intel Core i7-4770K CPU Review. Intel Haswell for Desktops: Ruin of Our Hopes?. Page 12|access-date=13 September 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author=Koen Crijns |url=http://us.hardware.info/reviews/4855/9/workshop-how-to-overclock-haswell-processors-in-practice |title=Workshop: How to overclock Haswell processors — In practice |publisher=Us.hardware.info |date=2013-10-21 |access-date=2014-04-02}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.anandtech.com/show/7063/overclocking-haswell-on-asus-8series-motherboards-video |title=<nowiki>Overclocking Haswell on ASUS' 8-Series Motherboards [video</nowiki>] |publisher=AnandTech |date=2013-06-12 |access-date=2014-04-02}}</ref> |
||
== |
==Technology== |
||
{{see also|Intel HD Graphics}} |
{{see also|Intel HD Graphics}} |
||
=== |
===Features carried over from Ivy Bridge=== |
||
* [[22 nanometer|22 nm]] manufacturing process<ref name="Haswell" /> |
* [[22 nanometer|22 nm]] manufacturing process<ref name="Haswell" /> |
||
* 3D [[Tri-Gate transistor|''Tri-Gate'' FinFET transistor]]s<ref>{{cite web |
* 3D [[Tri-Gate transistor|''Tri-Gate'' FinFET transistor]]s<ref>{{cite web|title=Haswell: 4th Gen Intel HD Graphics - All's Well for the new IGP?|url=http://www.hardwarezone.com.sg/feature-haswell-4th-gen-intel-hd-graphics-alls-well-new-igp|publisher=Hardware Zone|access-date=August 2, 2015}}</ref> |
||
* [[Micro-operation cache]] (Uop Cache) capable of storing 1.5 |
* [[Micro-operation cache]] (Uop Cache) capable of storing 1.5 K [[micro-operation]]s (approximately 6 KB in size)<ref name="anandtech-haswell">{{cite web |
||
| url = http://www.anandtech.com/show/6355/intels-haswell-architecture/6 |
|||
* 14- to 19-stage [[instruction pipeline]], depending on the micro-operation cache hit or miss (an approach used in the even earlier [[Sandy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Sandy Bridge]] microarchitecture)<ref name="anandtech-haswell"/> |
|||
| title = Intel's Haswell Architecture Analyzed |
|||
*Improve OoO window from 168 to 192<ref>{{Cite web |title=Haswell - Microarchitectures - Intel |url=https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/intel/microarchitectures/haswell_(client) |website=WikiChip |language=en-US |access-date=January 19, 2021}}</ref> |
|||
| date = 2012-10-05 | access-date = 2013-10-20 |
|||
| author = Anand Lal Shimpi | publisher = [[AnandTech]] |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
* 14- to 19-stage [[instruction pipeline]], depending on the micro-operation cache hit or miss (an approach used in the even earlier [[Sandy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Sandy Bridge]] microarchitecture)<ref name="anandtech-haswell" /> |
|||
*Improve OoO window from 168 to 192<ref>{{Cite web|title=Haswell - Microarchitectures - Intel - WikiChip|url=https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/intel/microarchitectures/haswell_(client)|access-date=2021-01-19|website=en.wikichip.org|language=en}}</ref> |
|||
*Queue Allocation from 28/threads to 56 |
*Queue Allocation from 28/threads to 56 |
||
* Mainstream variants are up to quad-core.<ref name="softpedia" /> |
* Mainstream variants are up to quad-core.<ref name="softpedia" /> |
||
* Native support for [[Multi-channel memory architecture|dual-channel]] [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3/DDR3L]] memory,<ref>{{cite web | |
* Native support for [[Multi-channel memory architecture|dual-channel]] [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3/DDR3L]] memory,<ref>{{cite web | url = http://media.bestofmicro.com/Intel-CPU-Haswell-LGA1150-iGPU,R-J-326287-13.jpg | title = Haswell | format = slide | publisher = Intel | access-date = 2012-02-15 | archive-date = 2012-09-15 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120915235424/http://media.bestofmicro.com/Intel-CPU-Haswell-LGA1150-iGPU,R-J-326287-13.jpg | url-status = dead }}</ref> with up to 32 GB of [[RAM]] on LGA 1150 variants |
||
* 64 KB (32 KB Instruction + 32 KB Data) L1 cache and 256 KB L2 cache per core<ref>{{cite web |format |
* 64 KB (32 KB Instruction + 32 KB Data) L1 cache and 256 KB L2 cache per core<ref>{{cite web | format = blog | url = http://www.anandtech.com/show/6263/intel-haswell-architecture-disclosure-live-blog | title = Intel Haswell Architecture Disclosure: Live Blog | quote = 01:58PM – Same sizes L1/L2 caches as SNB/IVB }}</ref> |
||
* A total of 16 [[PCI Express |
* A total of 16 [[PCI Express]] 3.0 lanes on LGA 1150 variants<ref>{{cite web|last1=Edwards|first1=Nathan|title=Theoretical vs. Actual Bandwidth: PCI Express and Thunderbolt|url=http://www.tested.com/tech/457440-theoretical-vs-actual-bandwidth-pci-express-and-thunderbolt/|publisher=Tested|access-date=August 2, 2015}}</ref> |
||
=== |
==={{Anchor|HASWELL-E}}New features=== |
||
[[File:Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator.svg|thumb|Haswell featured a [[Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator]].]] |
[[File:Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator.svg|thumb|Haswell featured a [[Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator]].]] |
||
==== CPU ==== |
==== CPU ==== |
||
* Wider core:<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.anandtech.com/show/6355/intels-haswell-architecture/8|title = Intel's Haswell Architecture Analyzed: Building a New PC and a New Intel}}</ref> fourth [[arithmetic logic unit]] (ALU), third [[address generation unit]] (AGU),<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.realworldtech.com/haswell-cpu/6/|title=Intel's Haswell CPU Microarchitecture|last=Kanter|first=David|date=2012-11-13|website=Real World Technologies|language=en-US|access-date=2017-04-07}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Jain|first1=Tarush|last2=Agrawal|first2=Tanmay|year=2013|title=The Haswell Microarchitecture - 4th Generation Processor|url=http://www.ijcsit.com/docs/Volume%204/vol4Issue3/ijcsit2013040321.pdf|journal=International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies|volume=4|issue=3|pages=477–480|issn=0975-9646}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |
* Wider core:<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.anandtech.com/show/6355/intels-haswell-architecture/8|title = Intel's Haswell Architecture Analyzed: Building a New PC and a New Intel}}</ref> fourth [[arithmetic logic unit]] (ALU), third [[address generation unit]] (AGU),<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.realworldtech.com/haswell-cpu/6/|title=Intel's Haswell CPU Microarchitecture|last=Kanter|first=David|date=2012-11-13|website=Real World Technologies|language=en-US|access-date=2017-04-07}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Jain|first1=Tarush|last2=Agrawal|first2=Tanmay|year=2013|title=The Haswell Microarchitecture - 4th Generation Processor|url=http://www.ijcsit.com/docs/Volume%204/vol4Issue3/ijcsit2013040321.pdf|journal=International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies|volume=4|issue=3|pages=477–480|issn=0975-9646}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |
||
| url = http://www.hotchips.org/wp-content/uploads/hc_archives/hc25/HC25.80-Processors2-epub/HC25.27.820-Haswell-Hammarlund-Intel.pdf |
|||
| title = Fourth-Generation Intel Core Processor, codenamed Haswell |
|||
| date = August 2013 |
|||
| access-date = 2014-12-08 |
|||
| author = Per Hammarlund |
|||
| website = hotchips.org |
|||
| page = 25 |
|||
| archive-date = 2016-07-05 |
|||
| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160705081212/http://www.hotchips.org/wp-content/uploads/hc_archives/hc25/HC25.80-Processors2-epub/HC25.27.820-Haswell-Hammarlund-Intel.pdf |
|||
| url-status = dead |
|||
* [[Haswell New Instructions|New instructions]]<ref>{{cite web |title=Haswell New Instruction Descriptions Now Available! | Intel Developer Zone |url=http://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2011/06/13/haswell-new-instruction-descriptions-now-available |website=Intel |language=en-US |date=June 13, 2011 |access-date=October 12, 2013}}</ref> (HNI, includes [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2]] (AVX2), [[Gather-scatter (vector addressing)|gather]], [[Bit Manipulation Instruction Sets|BMI1, BMI2, ABM]] and [[FMA instruction set|FMA3]] support).<ref>{{cite web |title=Haswell new instruction descriptions now available |url=http://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2011/06/13/haswell-new-instruction-descriptions-now-available/ |website=Intel |language=en-US |date=June 13, 2011 |access-date=January 4, 2012}}</ref> |
|||
}}</ref> second [[branch execution unit]] (BEU), deeper buffers, higher cache bandwidth, improved front-end and [[memory controller]], higher load/store bandwidth. |
|||
* [[Haswell New Instructions|New instructions]]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2011/06/13/haswell-new-instruction-descriptions-now-available |title=Haswell New Instruction Descriptions Now Available! | Intel Developer Zone |publisher=Software.intel.com |date=2011-06-13 |access-date=2013-10-12}}</ref> (HNI, includes [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2]] (AVX2), [[Gather-scatter (vector addressing)|gather]], [[Bit Manipulation Instruction Sets|BMI1, BMI2, ABM]] and [[FMA instruction set|FMA3]] support).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2011/06/13/haswell-new-instruction-descriptions-now-available/ |title=Haswell new instruction descriptions now available |publisher=Intel |date = 2011-06-13 |access-date=2012-01-04}}</ref> |
|||
* The instruction decode queue, which holds instructions after they have been decoded, is no longer statically partitioned between the two threads that each core can service.<ref name="anandtech-haswell" /> |
* The instruction decode queue, which holds instructions after they have been decoded, is no longer statically partitioned between the two threads that each core can service.<ref name="anandtech-haswell" /> |
||
* Intel [[Transactional Synchronization Extensions]] (TSX) for the Haswell-EX variant. In August 2014 Intel announced that a bug exists in the TSX implementation on the current [[Stepping level|steppings]] of Haswell, Haswell-E, Haswell-EP and early Broadwell CPUs, which resulted in disabling the TSX feature on affected CPUs via a [[microcode]] update.<ref name="anandtech-8376">{{cite web |
|||
* Intel [[Transactional Synchronization Extensions]] (TSX) for the Haswell-EX variant. In August 2014 Intel announced that a bug exists in the TSX implementation on the current [[Stepping level|steppings]] of Haswell, Haswell-E, Haswell-EP and early Broadwell CPUs, which resulted in disabling the TSX feature on affected CPUs via a [[microcode]] update.<ref name="anandtech-8376">{{cite web |last=Cutress |first=Ian |date=August 12, 2014 |title=Intel Disables TSX Instructions: Erratum Found in Haswell, Haswell-E/EP, Broadwell-Y |url=http://www.anandtech.com/show/8376/intel-disables-tsx-instructions-erratum-found-in-haswell-haswelleep-broadwelly |website=AnandTech |language=en-US |access-date=August 30, 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Transactional Synchronization in Haswell |url=http://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2012/02/07/transactional-synchronization-in-haswell |website=Intel |language=en-US |date=February 7, 2012 |access-date=February 7, 2012}}</ref><ref name="techreport-26911">{{cite web |last=Wasson |first=Scott |date=August 12, 2014 |title=Errata prompts Intel to disable TSX in Haswell, early Broadwell CPUs |url=http://techreport.com/news/26911/errata-prompts-intel-to-disable-tsx-in-haswell-early-broadwell-cpus |website=Tech Report |language=en-US |access-date=August 12, 2014}}</ref><ref name="intel-spec-update">{{cite web |title=Desktop 4th Generation Intel Core Processor Family, Desktop Intel Pentium Processor Family, and Desktop Intel Celeron Processor Family: Specification Update (Revision 014) |url=http://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/4th-gen-core-family-desktop-specification-update.pdf |page=46 |website=Intel |language=en-US |date=June 2014 |access-date=August 13, 2014 |quote=Under a complex set of internal timing conditions and system events, software using the Intel TSX (Transactional Synchronization Extensions) instructions may observe unpredictable system behavior.}}</ref> |
|||
| url = http://www.anandtech.com/show/8376/intel-disables-tsx-instructions-erratum-found-in-haswell-haswelleep-broadwelly |
|||
| title = Intel Disables TSX Instructions: Erratum Found in Haswell, Haswell-E/EP, Broadwell-Y |
|||
| date = 2014-08-12 | access-date = 2014-08-30 |
|||
| author = Ian Cutress | publisher = [[AnandTech]] |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://software.intel.com/en-us/blogs/2012/02/07/transactional-synchronization-in-haswell |title=Transactional Synchronization in Haswell |publisher=[[Intel]] |date=2012-02-07 |access-date=2012-02-07}}</ref><ref name="techreport-26911">{{cite web |
|||
| url = http://techreport.com/news/26911/errata-prompts-intel-to-disable-tsx-in-haswell-early-broadwell-cpus |
|||
| title = Errata prompts Intel to disable TSX in Haswell, early Broadwell CPUs |
|||
| date = 2014-08-12 | access-date = 2014-08-12 |
|||
| first = Scott | last = Wasson | publisher = The Tech Report |
|||
}}</ref><ref name="intel-spec-update">{{cite web |
|||
| url = http://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/4th-gen-core-family-desktop-specification-update.pdf |
|||
| title = Desktop 4th Generation Intel Core Processor Family, Desktop Intel Pentium Processor Family, and Desktop Intel Celeron Processor Family: Specification Update (Revision 014) |
|||
| date = June 2014 | access-date = 2014-08-13 |
|||
| publisher = [[Intel]] |
|||
| page = 46 |
|||
| quote = Under a complex set of internal timing conditions and system events, software using the Intel TSX (Transactional Synchronization Extensions) instructions may observe unpredictable system behavior. |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
* [[Fully integrated voltage regulator]] (FIVR), thereby moving some of the components from [[motherboard]] onto the CPU.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://static2.fileconnect.net/sites/default/files/resize/imagecache/tcm-inline-default/images/tcm/inline/intelhaswellnovsl01-575x429.jpg | format = JPEG | publisher = File connect | title = Intel Haswell | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120425152334/http://static2.fileconnect.net/sites/default/files/resize/imagecache/tcm-inline-default/images/tcm/inline/intelhaswellnovsl01-575x429.jpg | archive-date = 2012-04-25 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.anandtech.com/show/7003/the-haswell-review-intel-core-i74770k-i54560k-tested/2 | title = The Haswell Review: Intel Core i7-4770K & i5-4670K Tested | date = 2013-06-01 | publisher = AnandTech | access-date = 2013-11-14}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://hothardware.com/News/Haswell-Takes-A-Major-Step-Forward-Integrates-Voltage-Regulator/ | title = Intel's Haswell Takes A Major Step Forward, Integrates Voltage Regulator | date = 2013-05-13 | publisher = hothardware.com | access-date = 2013-11-14 | archive-date = 2013-10-20 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131020205158/http://hothardware.com/News/Haswell-Takes-A-Major-Step-Forward-Integrates-Voltage-Regulator/ | url-status = dead }}</ref> |
* [[Fully integrated voltage regulator]] (FIVR), thereby moving some of the components from [[motherboard]] onto the CPU.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://static2.fileconnect.net/sites/default/files/resize/imagecache/tcm-inline-default/images/tcm/inline/intelhaswellnovsl01-575x429.jpg | format = JPEG | publisher = File connect | title = Intel Haswell | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120425152334/http://static2.fileconnect.net/sites/default/files/resize/imagecache/tcm-inline-default/images/tcm/inline/intelhaswellnovsl01-575x429.jpg | archive-date = 2012-04-25 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.anandtech.com/show/7003/the-haswell-review-intel-core-i74770k-i54560k-tested/2 | title = The Haswell Review: Intel Core i7-4770K & i5-4670K Tested | date = 2013-06-01 | publisher = AnandTech | access-date = 2013-11-14}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://hothardware.com/News/Haswell-Takes-A-Major-Step-Forward-Integrates-Voltage-Regulator/ | title = Intel's Haswell Takes A Major Step Forward, Integrates Voltage Regulator | date = 2013-05-13 | publisher = hothardware.com | access-date = 2013-11-14 | archive-date = 2013-10-20 | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20131020205158/http://hothardware.com/News/Haswell-Takes-A-Major-Step-Forward-Integrates-Voltage-Regulator/ | url-status = dead }}</ref> |
||
* New advanced power-saving system; due to Haswell's new low-power C6 and C7 sleep states, not all [[Power supply unit (computer)|power supply units]] (PSUs) are suitable for computers with Haswell CPUs.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://techreport.com/news/24738/few-psus-support-haswell-c6-c7-low-power-states |title=Few PSUs support Haswell's C6/C7 low-power states |publisher=The Tech Report |date=2013-04-30 |access-date=2014-04-02}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://techreport.com/review/24897/the-big-haswell-psu-compatibility-list |title=The big Haswell PSU compatibility list |publisher=The Tech Report |date=2013-06-04 |access-date=2014-04-02}}</ref> |
* New advanced power-saving system; due to Haswell's new low-power C6 and C7 sleep states, not all [[Power supply unit (computer)|power supply units]] (PSUs) are suitable for computers with Haswell CPUs.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://techreport.com/news/24738/few-psus-support-haswell-c6-c7-low-power-states |title=Few PSUs support Haswell's C6/C7 low-power states |publisher=The Tech Report |date=2013-04-30 |access-date=2014-04-02}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://techreport.com/review/24897/the-big-haswell-psu-compatibility-list |title=The big Haswell PSU compatibility list |publisher=The Tech Report |date=2013-06-04 |access-date=2014-04-02}}</ref> |
||
| Line 199: | Line 234: | ||
Windows Vista support is also dropped with this processor as well. People who have installed x64 version of Vista have reported various problems such as services not starting automatically. The KB4493471 update (officially intended only for [[Windows Server 2008]], but can be installed on Vista) contains a HAL driver that fixes most of these issues. Windows XP and earlier and x86 version of Vista is unaffected by this bug. |
Windows Vista support is also dropped with this processor as well. People who have installed x64 version of Vista have reported various problems such as services not starting automatically. The KB4493471 update (officially intended only for [[Windows Server 2008]], but can be installed on Vista) contains a HAL driver that fixes most of these issues. Windows XP and earlier and x86 version of Vista is unaffected by this bug. |
||
== |
=={{Anchor|CPUS-LIST}}List of Haswell processors== |
||
=== |
==={{Anchor|PENTIUM-AE}}Desktop processors=== |
||
[[File:Intel Haswell 4771 CPU.jpg|thumb|right|Intel Haswell i7-4771 CPU, sitting atop its original packaging that contains an OEM fan-cooled [[heatsink]] ]] |
[[File:Intel Haswell 4771 CPU.jpg|thumb|right|Intel Haswell i7-4771 CPU, sitting atop its original packaging that contains an OEM fan-cooled [[heatsink]] ]] |
||
* All models support: ''[[MMX (instruction set)|MMX]], [[Streaming SIMD Extensions|SSE]], [[SSE2]], [[SSE3]], [[SSSE3]], [[SSE4.1]], [[SSE4.2]], [[F16C]], Enhanced Intel [[SpeedStep]] Technology (EIST), [[Intel 64]], XD bit (an [[NX bit]] implementation), [[Intel VT-x]],'' and ''[[Smart Cache]].'' |
* All models support: ''[[MMX (instruction set)|MMX]], [[Streaming SIMD Extensions|SSE]], [[SSE2]], [[SSE3]], [[SSSE3]], [[SSE4.1]], [[SSE4.2]], [[F16C]], Enhanced Intel [[SpeedStep]] Technology (EIST), [[Intel 64]], XD bit (an [[NX bit]] implementation), [[Intel VT-x]],'' and ''[[Smart Cache]].'' |
||
** Core i3, i5 and i7 support ''[[Advanced Vector Extensions|AVX]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2|AVX2]], [[X86 Bit manipulation instruction set|BMI1]], [[BMI2]], [[FMA3]],'' and ''[[AES instruction set|AES-NI]].''<ref name="comparison">{{cite web |
** Core i3, i5 and i7 support ''[[Advanced Vector Extensions|AVX]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2|AVX2]], [[X86 Bit manipulation instruction set|BMI1]], [[BMI2]], [[FMA3]],'' and ''[[AES instruction set|AES-NI]].''<ref name="comparison">{{cite web|url=https://ark.intel.com/compare/77773,77775,77777,77480,77769,77771,75036,75037,75043,76640,75044,75045,75047,75048,76641,75049,75050,75121,75122,75123,76642,75124,75125|title=Intel Comparison Table of Haswell Celeron, Pentium, i3, i5, and i7 models|website=Intel.com|access-date=2013-09-02}}</ref> |
||
** Core i3 and i7, as well as the Core i5-4570T and i5-4570TE, support ''[[Hyper-Threading]] (HT)''.<ref name="comparison" /> |
** Core i3 and i7, as well as the Core i5-4570T and i5-4570TE, support ''[[Hyper-Threading]] (HT)''.<ref name="comparison" /> |
||
** Core i5 and i7 support ''[[Turbo Boost]] 2.0.''<ref name="comparison" /> |
** Core i5 and i7 support ''[[Turbo Boost]] 2.0.''<ref name="comparison" /> |
||
** Although it was initially supported on selected models, since August 2014 desktop variants no longer support ''[[Transactional Synchronization Extensions|TSX]]'' due to a bug that was discovered in its implementation; as a workaround, a microcode update disabled the TSX feature.<ref name="anandtech-8376" /><ref name="techreport-26911" /><ref name="intel-spec-update" /><ref name="comparison" /> |
** Although it was initially supported on selected models, since August 2014 desktop variants no longer support ''[[Transactional Synchronization Extensions|TSX]]'' due to a bug that was discovered in its implementation; as a workaround, a microcode update disabled the TSX feature.<ref name="anandtech-8376" /><ref name="techreport-26911" /><ref name="intel-spec-update" /><ref name="comparison" /> |
||
** SKUs below 45xx as well as R-series and K-series SKUs do not support ''[[Trusted Execution Technology]]'' or ''[[Intel vPro|vPro]].''<ref name="comparison" /> |
** SKUs below 45xx as well as R-series and K-series SKUs do not support ''[[Trusted Execution Technology]]'' or ''[[Intel vPro|vPro]].''<ref name="comparison" /> |
||
** ''[[Intel VT-d]]'', which is Intel's [[IOMMU]], is supported on all i5 and i7 SKUs except the i5-4670K and i7-4770K.<ref name="comparison" /><ref>{{cite web |
** ''[[Intel VT-d]]'', which is Intel's [[IOMMU]], is supported on all i5 and i7 SKUs except the i5-4670K and i7-4770K.<ref name="comparison" /><ref>{{cite web|url=https://ark.intel.com/products/80807/Intel-Core-i7-4790K-Processor-8M-Cache-up-to-4_40-GHz |title=ARK | Intel Core i7-4790K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz) |publisher=[[Intel]] |access-date=2014-07-15}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://ark.intel.com/products/80811/Intel-Core-i5-4690K-Processor-6M-Cache-up-to-3_90-GHz |title=ARK | Intel Core i5-4690K Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz) |publisher=[[Intel]] |access-date=2014-07-18}}</ref> Support for VT-d requires the chipset and motherboard to also support VT-d. |
||
** Models i5-4690K and i7-4790K, codenamed Devil's Canyon, have a better internal [[thermal grease]] to help heat escape and an improved internal [[voltage regulator]] ("FIVR"), to help deliver cleaner power in situations like overclocking. |
** Models i5-4690K and i7-4790K, codenamed Devil's Canyon, have a better internal [[thermal grease]] to help heat escape and an improved internal [[voltage regulator]] ("FIVR"), to help deliver cleaner power in situations like overclocking. |
||
* Transistors: 1.4 billion<ref name="anandtech">{{cite web |
* Transistors: 1.4 billion<ref name="anandtech">{{cite web|last1=Shimpi|first1=Lal|title=The Haswell Review: Intel Core i7-4770K & i5-4670K Tested|url=http://www.anandtech.com/show/7003/the-haswell-review-intel-core-i74770k-i54560k-tested/5|website=anandtech|access-date=20 November 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Smith|first1=Tony|title=Inside Intel's Haswell: What do 1.4 BEELLION transistors get you?|url=https://www.theregister.co.uk/Print/2013/06/03/feature_inside_haswell_intel_4g_core/|website=theregister.co.uk|access-date=20 November 2014}}</ref> |
||
* [[Die (integrated circuit)|Die]] size: 177 |
* [[Die (integrated circuit)|Die]] size: 177 mm<sup>2</sup><ref name="anandtech" /> |
||
* [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics#Haswell|Intel HD and Iris Graphics]] in following variants: |
* [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics#Haswell|Intel HD and Iris Graphics]] in following variants: |
||
** R-series desktop processors feature Intel Iris Pro 5200 graphics (GT3e).<ref>{{cite web |
** R-series desktop processors feature Intel Iris Pro 5200 graphics (GT3e).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://chinese.vr-zone.com/58507/intel-haswell-will-have-three-bga-cpu-for-core-i7-4770r-4670r-and-i5-4570r-with-graphics-5200-04052013/|title=Intel Haswell R-series CPU Lineup Leaked|website=VR Zone|date=5 April 2013|access-date=2013-04-05|archive-date=2013-04-07|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130407124213/http://chinese.vr-zone.com/58507/intel-haswell-will-have-three-bga-cpu-for-core-i7-4770r-4670r-and-i5-4570r-with-graphics-5200-04052013/|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
||
** All other currently known i3, i5 and i7 desktop processors include Intel HD 4600 graphics (GT2).<ref>{{cite web |
** All other currently known i3, i5 and i7 desktop processors include Intel HD 4600 graphics (GT2).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://wccftech.com/intel-haswell-cpu-lineup-leaked-core-i74770k-flagship-fourth-generation-processor/|title=Intel Haswell CPU Lineup Leaked, Core i7-4770K Flagship Fourth Generation Processor|website=wccftech.com|date=12 December 2012|access-date=2013-04-01}}</ref> |
||
** The exceptions are processors 41xxx, which include HD 4400 graphics (GT2). |
** The exceptions are processors 41xxx, which include HD 4400 graphics (GT2). |
||
** Celeron and Pentium processors contain Intel HD Graphics (GT1). |
** Celeron and Pentium processors contain Intel HD Graphics (GT1). |
||
* Pentium G3258, also known as the ''Pentium Anniversary Edition'', has an unlocked multiplier. Its release marks 20 years of "Pentium" as a brand.<ref>{{cite news |
* Pentium G3258, also known as the ''Pentium Anniversary Edition'', has an unlocked multiplier. Its release marks 20 years of "Pentium" as a brand.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://techreport.com/review/26189/intel-to-renew-commitment-to-desktop-pcs-with-a-slew-of-new-cpus |title=Intel to renew commitment to desktop PCs with a slew of new CPUs |newspaper=The Tech Report |publisher=techreport.com |date=2014-03-19|access-date=2014-03-25}}</ref> |
||
The following table lists available desktop processors. |
|||
SKU suffixes to denote: |
|||
* K{{snd}} unlocked <span style="color: #969696">(adjustable CPU multiplier up to 63x)</span> |
|||
**The Pentium G3258 CPU is unlocked despite not having the K-suffix. |
|||
* S{{snd}} performance-optimized lifestyle <span style="color: #969696">(low power with 65 W TDP)</span> |
|||
* T{{snd}} power-optimized lifestyle <span style="color: #969696">(ultra low power with 35–45 W TDP)</span> |
|||
* R{{snd}} BGA packaging / High-performance GPU <span style="color: #969696">(currently Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e))</span> |
|||
* X{{snd}} extreme edition <span style="color: #969696">(adjustable CPU ratio with no ratio limit)</span> |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
|||
==== Haswell-DT ==== |
|||
|- |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan=" |
! rowspan="2" | Target<br />segment |
||
! rowspan=" |
! rowspan="2" | Cores<br />(threads) |
||
! rowspan=" |
! colspan="2" rowspan="2" | Processor<br />branding and model |
||
! rowspan=" |
! rowspan="2" | GPU model |
||
! |
! colspan="2" | CPU [[clock rate]] |
||
! |
! colspan="2" | Graphics [[clock rate]] |
||
! colspan="3" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! colspan="2" | Cache |
! colspan="2" | Cache |
||
! rowspan=" |
! rowspan="2" data-sort-type="number" | [[Thermal Design Power|TDP]] |
||
! rowspan |
! rowspan="2" | PCIe 3.0 lane<br />configurations{{ref label|PCIeChipsetDependence|a}} |
||
! rowspan=" |
! rowspan="2" | VT-d{{ref label|VTdChipsetDependence|b}} |
||
! rowspan="2" class="unsortable" | Release<br />date |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Release<br />price<br />(USD) |
|||
! colspan="3" | Motherboard |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Normal |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Model |
|||
! [[Intel Turbo Boost|Turbo]] |
|||
! rowspan="2" | {{abbr|EUs|Execution Units}} |
|||
! Normal |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Max GPU <br/> clock rate <br/>([[Hertz|GHz]]) |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | Turbo |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[CPU Cache|L3]] |
|||
! |
! data-sort-type="number" | [[L3 cache|L3]] |
||
! [[L4 cache|L4]]{{Efn|Implemented as [[eDRAM]] and serving primarily to increase the performance of integrated [[GPU]], while being shared with the CPU.}} |
|||
! Socket |
|||
! Interface |
|||
! Memory |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="3" | Enthusiast / High-End |
|||
! [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3]] |
|||
| 8 (16) |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | Core i7<br />Extreme |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/82930 5960X] |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{N/a}} |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{N/a}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{N/a}} |
|||
| 20 MB |
|||
| rowspan="12" {{N/a}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 140 W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2×16 + 1×8 |
|||
| rowspan="9" {{Yes}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | {{Start date|2014|08|29}}<ref>{{cite news |author=Chris.L |url=http://chinese.vr-zone.com/118744/intel-haswell-e-and-x99-platform-embargo-day-confirm-06202014/ |title=確定 9 月 14 日解禁,Intel Haswell-E 與 X99 平台已在路上 - VR-Zone 中文版 |newspaper=Vr-Zone 中文版 |publisher=Chinese.vr-zone.com |language=zh |date=2014-06-20 |access-date=2014-06-26 |archive-date=2014-06-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140625231347/http://chinese.vr-zone.com/118744/intel-haswell-e-and-x99-platform-embargo-day-confirm-06202014/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
| $999 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | [[LGA 2011-v3]] |
|||
| rowspan="86" | [[Direct Media Interface|DMI 2.0]]<br />[[PCI Express 3.0|PCIe 3.0]] |
|||
| rowspan="3" |Up to quad<br />channel<br />DDR4-2133 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="2" | 6 (12) |
|||
! colspan="17" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59c4f0; color:#fff;" | Celeron |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/82931 5930K] |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15 MB |
|||
| $583 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/82932 5820K] |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | December 1, 2013 |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| $42 |
|||
| |
| 1×16 + 1×8 + 1×4 |
||
| |
| $389 |
||
| rowspan="7" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="7" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 10 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.05 |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="7" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
| rowspan="7" | DDR3-1333 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{yes}} |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78956/intel-celeron-processor-g1820t-2m-cache-2-40-ghz.html G1820T] |
|||
| $42 |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78957/intel-celeron-processor-g1820te-2m-cache-2-20-ghz.html G1820TE] |
|||
| $42 |
|||
| 2.2 |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78954/intel-celeron-processor-g1830-2m-cache-2-80-ghz.html G1830] |
|||
| $52 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 1.05 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80800/intel-celeron-processor-g1840-2m-cache-2-80-ghz.html G1840] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $42 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80801/intel-celeron-processor-g1840t-2m-cache-2-50-ghz.html G1840T] |
|||
| $42 |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80798/intel-celeron-processor-g1850-2m-cache-2-90-ghz.html G1850] |
|||
| $52 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="17" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59c4f0; color:#fff;" | Pentium |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77773/intel-pentium-processor-g3220-3m-cache-3-00-ghz.html G3220] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $54 |
|||
| rowspan="20" | 2 (2) |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| rowspan="20" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="20" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| rowspan="20" | 10 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="20" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="20" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="20" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
| rowspan="20" | DDR3-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="20" {{yes}} |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77774/intel-pentium-processor-g3220t-3m-cache-2-60-ghz.html G3220T] |
|||
| $54 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80796/intel-pentium-processor-g3240-3m-cache-3-10-ghz.html G3240] |
|||
| $54 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80797/intel-pentium-processor-g3240t-3m-cache-2-70-ghz.html G3240T] |
|||
| May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $54 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/83538/intel-pentium-processor-g3250-3m-cache-3-20-ghz.html G3250] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | July 21, 2014 |
|||
| $50 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="13" | Performance |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/83539/intel-pentium-processor-g3250t-3m-cache-2-80-ghz.html G3250T] |
|||
| $50 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/82723/intel-pentium-processor-g3258-3m-cache-3-20-ghz.html G3258] |
|||
| June 2, 2014 |
|||
| $72 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/87356/intel-pentium-processor-g3260-3m-cache-3-30-ghz.html G3260] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | March 30, 2015 |
|||
| $64 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/87357/intel-pentium-processor-g3260t-3m-cache-2-90-ghz.html G3260T] |
|||
| $64 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78007/intel-pentium-processor-g3320te-3m-cache-2-30-ghz.html G3320TE] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $70 |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77775/intel-pentium-processor-g3420-3m-cache-3-20-ghz.html G3420] |
|||
| $75 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| rowspan="10" | 1.1 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77776/intel-pentium-processor-g3420t-3m-cache-2-70-ghz.html G3420T] |
|||
| $75 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77777/intel-pentium-processor-g3430-3m-cache-3-30-ghz.html G3430] |
|||
| $93 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80794/intel-pentium-processor-g3440-3m-cache-3-30-ghz.html G3440] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $82 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80795/intel-pentium-processor-g3440t-3m-cache-2-80-ghz.html G3440T] |
|||
| $82 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80792/intel-pentium-processor-g3450-3m-cache-3-40-ghz.html G3450] |
|||
| $82 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80793/intel-pentium-processor-g3450t-3m-cache-2-90-ghz.html G3450T] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | July 21, 2014 |
|||
| $82 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/83428/intel-pentium-processor-g3460-3m-cache-3-50-ghz.html G3460] |
|||
| $82 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/83429/intel-pentium-processor-g3460t-3m-cache-3-00-ghz.html G3460T] |
|||
| $82 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/87358/intel-pentium-processor-g3470-3m-cache-3-60-ghz.html G3470] |
|||
| March 30, 2015 |
|||
| $86 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| 53{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="17" style="text-align:left; background-color:#00a4e6; color:#fff;" | Core i3 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77480/intel-core-i34130-processor-3m-cache-3-40-ghz.html 4130] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| rowspan="19" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| rowspan="19" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="8" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| rowspan="19" | 20 |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 1.15 |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="19" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="19" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
| rowspan="19" | DDR3-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="19" {{yes}} |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77481/intel-core-i34130t-processor-3m-cache-2-90-ghz.html 4130T] |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77486/intel-core-i34150-processor-3m-cache-3-50-ghz.html 4150] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77487/intel-core-i34150t-processor-3m-cache-3-00-ghz.html 4150T] |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77488/intel-core-i34160-processor-3m-cache-3-60-ghz.html 4160] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | July 21, 2014 |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77489/intel-core-i34160t-processor-3m-cache-3-10-ghz.html 4160T] |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77490/intel-core-i34170-processor-3m-cache-3-70-ghz.html 4170] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | March 30, 2015 |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/81209/intel-core-i34170t-processor-3m-cache-3-20-ghz.html 4170T] |
|||
| $117 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77769/intel-core-i34330-processor-4m-cache-3-50-ghz.html 4330] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $138 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| rowspan="11" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 1.15 |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77770/intel-core-i34330t-processor-4m-cache-3-00-ghz.html 4330T] |
|||
| $138 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77778/intel-core-i34330te-processor-4m-cache-2-40-ghz.html 4330TE] |
|||
| $122 |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77771/intel-core-i34340-processor-4m-cache-3-60-ghz.html 4340] |
|||
| $157 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77492/intel-core-i34350t-processor-4m-cache-3-10-ghz.html 4340TE] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $138 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77491/intel-core-i34350-processor-4m-cache-3-60-ghz.html 4350] |
|||
| $147 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77492/intel-core-i34350t-processor-4m-cache-3-10-ghz.html 4350T] |
|||
| $138 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77493/intel-core-i34360-processor-4m-cache-3-70-ghz.html 4360] |
|||
| $138 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77494/intel-core-i34360t-processor-4m-cache-3-20-ghz.html 4360T] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | July 21, 2014 |
|||
| $138 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77495/intel-core-i34370-processor-4m-cache-3-80-ghz.html 4370] |
|||
| $147 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
| 54{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/81207/intel-core-i34370t-processor-4m-cache-3-30-ghz.html 4370T] |
|||
| March 30, 2015 |
|||
| $147 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="17" style="text-align:left; background-color:#1e83cb; color:#fff;" | Core i5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75036/intel-core-i54430-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4430] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $187 |
|||
| rowspan="10" | 4 (4) |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| rowspan="8" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 20 |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="8" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="8" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
| rowspan="24" | DDR3-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="24" {{no}} |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75037/intel-core-i54430s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4430S] |
|||
| $187 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75038/intel-core-i54440-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4440] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $187 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75040/intel-core-i54440s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4440S] |
|||
| $187 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80817/intel-core-i54460-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4460] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $182 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80818/intel-core-i54460s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4460S] |
|||
| $182 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78927/intel-core-i54460t-processor-6m-cache-up-to-2-70-ghz.html 4460T] |
|||
| $182 |
|||
| 1.9 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75043/intel-core-i54570-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-60-ghz.html 4570] |
|||
| rowspan="5" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $192 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76640/intel-core-i54570r-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4570R] |
|||
| {{resize|OEM}} <br/> $288 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>Pro<br>5200]] |
|||
| 40 |
|||
| 1.3 |
|||
| 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 128{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75044/intel-core-i54570s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-60-ghz.html 4570S] |
|||
| $192 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| rowspan="8" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 20 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.15 |
|||
| 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="8" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="8" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75045/intel-core-i54570t-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-60-ghz.html 4570T] |
|||
| $195 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75468/intel-core-i54570te-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4570TE] |
|||
| $192 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80815/intel-core-i54590-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-70-ghz.html 4590] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $202 |
|||
| rowspan="12" | 4 (4) |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.15 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80816/intel-core-i54590s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-70-ghz.html 4590S] |
|||
| $192 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78928/intel-core-i54590t-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-00-ghz.html 4590T] |
|||
| $192 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75047/intel-core-i54670-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-80-ghz.html 4670] |
|||
| rowspan="5" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $224 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75048/intel-core-i54670k-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-80-ghz.html 4670K] |
|||
| $243 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76641/intel-core-i54670r-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-70-ghz.html 4670R] |
|||
| {{resize|OEM}} <br/> $310 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>Pro<br>5200]] |
|||
| 40 |
|||
| 1.3 |
|||
| 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 128{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75049/intel-core-i54670s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-80-ghz.html 4670S] |
|||
| $213 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 20 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75050/intel-core-i54670t-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4670T] |
|||
| $213 |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80810/intel-core-i54690-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-90-ghz.html 4690] |
|||
| May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $224 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80811/intel-core-i54690k-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-90-ghz.html 4690K] |
|||
| June 2, 2014 |
|||
| $243 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| 88{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80812/intel-core-i54690s-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-90-ghz.html 4690S] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| $224 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80813/intel-core-i54690t-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-50-ghz.html 4690T] |
|||
| $224 |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="17" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964c7; color:#fff;" | Core i7 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75121/intel-core-i74765t-processor-8m-cache-up-to-3-00-ghz.html 4765T] |
|||
| rowspan="7" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| |
|||
| rowspan="13" | 4 (8) |
| rowspan="13" | 4 (8) |
||
| rowspan="13" | Core i7 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80807 4790K] |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="9" | HD 4600 <br />(GT2) |
||
| 4.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 20 |
|||
| 4.4 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 350 MHz<ref name="4th Generation">{{cite web|url=https://ark.intel.com/products/family/75024/4th-Generation-Intel-Core-i5-Processors/desktop|title=4th Generation Intel® Core™ i5 Processors (Desktop)|access-date=2013-06-02}}</ref> |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 8{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 1.25 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="9" | 8 MB |
||
| 88 W |
|||
| rowspan="13" | DDR3-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="83" | 1×16<br />2×8<br />1×8 + 2×4 |
||
| {{Start date|2014|06|02}} |
|||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| $339 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | [[LGA 1150|LGA<br />1150]] |
|||
| rowspan="66" | Up to dual<br />channel<br />DDR3-1600<ref>{{cite web|url=https://ark.intel.com/products/80807 |title=Intel® Core™ i7-4790K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz) |publisher=Ark.intel.com |access-date=2014-08-20}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80806 4790] |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| $312 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 4.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 1.2 GHz |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| 84 W |
|||
| rowspan="4" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | $303 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80808 4790S] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| $350 |
|||
| 65 W |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| 1.25 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80809 4790T] |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| {{resize|OEM}} |
|||
| 3. |
| 3.9 GHz |
||
| 45 W |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>Pro<br>5200]] |
|||
| 40 |
|||
| 1.3 |
|||
| 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 128{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80814 4785T] |
|||
| 2.2 GHz |
|||
| $303 |
|||
| 3. |
| 3.2 GHz |
||
| 35 W |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 20 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 8{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="9" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="9" | [[LGA 1150]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77656 4771] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.5 GHz |
|||
| $303 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 3.9 GHz |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 84 W |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 45{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75610/intel-core-i74770te-processor-8m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4770TE] |
|||
| $303 |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77656/intel-core-i74771-processor-8m-cache-up-to-3-90-ghz.html 4771] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $320 |
| $320 |
||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.2 |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75123 4770K] |
|||
| 1.25 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| |
| {{No}} |
||
| rowspan="7" | {{Start date|2013|06|2}}<ref name="presence-pc">{{cite web|url=http://www.tomshardware.com/news/Intel-Haswell-Ivy-Bridge-E-CPU,20590.html | title=Intel Core i5, i7 Haswell Processors to be Released in June| date=22 January 2013| access-date=2013-02-05}}</ref> |
|||
| 2.2 |
|||
| |
| $339 |
||
| 35{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75122 4770] |
|||
| 3.4 GHz |
|||
| $312 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 GHz |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| rowspan="10" {{Yes}} |
|||
| 4.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $303 |
|||
| 84{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75124 4770S] |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65 W |
|||
| $350 |
|||
| 4.0 |
|||
| 4.4 |
|||
| 1.25 |
|||
| 88{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76642 4770R] |
|||
| Iris Pro 5200 <br />(GT3e) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | May 11, 2014 |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| $303 |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| |
| 1.3 GHz |
||
| 6 MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 |
|||
| |
| 128 MB |
||
| $392 |
|||
| BGA<br />1364 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75125 4770T] |
|||
| rowspan="10" | HD 4600 <br />(GT2) |
|||
| $303 |
|||
| 2. |
| 2.5 GHz |
||
| 3. |
| 3.7 GHz |
||
| rowspan="10" | 350 MHz<ref name="4th Generation" /> |
|||
| 45{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 8 MB |
|||
| rowspan="10" {{N/a}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 45 W |
|||
| rowspan="3" | $303 |
|||
| rowspan="10" | [[LGA 1150|LGA<br />1150]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75610 4770TE] |
|||
|} |
|||
| 2.3 GHz |
|||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
{{efn|name="32GB RAM" | Up to 32{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
==== Haswell-E (HEDT) ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Release date |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Price <br/> (USD){{efn|name="RCP"}} |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[CPU core|Cores]] <br/>([[Thread (computing)|Threads]]) |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Base Clock <br/>(GHz) |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Turbo Clock <br/>(GHz) |
|||
! rowspan="1" colspan="2" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[CPU cache|L3 <br> Cache]] |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Socket |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[PCI Express|PCIe]] <br> lanes |
|||
! rowspan="1" colspan="2" | Memory<br>support{{efn|name="64GB RAM"}} |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Thermal design power|TDP]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75121 4765T] |
|||
! rowspan="1" | Model |
|||
| 2.0 GHz |
|||
! rowspan="1" | Max GPU<br>clock rate <br/>(GHz) |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
! [[DDR4 SDRAM|DDR4]] |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 1.2 GHz |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
| 35 W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="43" | Mainstream |
|||
! colspan="21" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964C7; color:#FFFFFF;" | Core i7 |
|||
| rowspan="15" | 4 (4) |
|||
| rowspan="24" | Core i5 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80811 4690K] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 3.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 6 MB |
|||
| 88 W |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|06|02}} |
|||
| $242 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80810 4690] |
|||
| 84 W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | August 28, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $389 |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="3" | $213 |
||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| colspan="2" rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[LGA 2011|LGA 2011-3]] |
|||
| 28 <br><small>[[PCI Express#PCI Express 3.0|PCIe 3.0]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="2" | DDR4-2133 <br><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture|quad-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 140W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80812 4690S] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| $583 |
|||
| 65 W |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| 40 <br><small>[[PCI Express#PCI Express 3.0|PCIe 3.0]]</small> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80813 4690T] |
|||
! colspan="21" style="text-align:left; background-color:#454547; color:#F3D680;" | Core i7 Extreme |
|||
| 2.5 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| 45 W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75048 4670K] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.4 GHz |
|||
| August 28, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 3.8 GHz |
|||
| $999 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 84 W |
|||
| 8 (16) |
|||
| |
| {{No}} |
||
| rowspan="5" | {{Start date|2013|06|2}} |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| $242 |
|||
| colspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| 20{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| [[LGA 2011|LGA 2011-3]] |
|||
| 40 <br><small>[[PCI Express#PCI Express 3.0|PCIe 3.0]]</small> |
|||
| DDR4-2133 <br><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture|quad-channel]]</small> |
|||
| {{no}} |
|||
| 140W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75047 4670] |
|||
|} |
|||
| rowspan="19" {{Yes}} |
|||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $213 |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
{{efn|name="64GB RAM" | Up to 64{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
=== {{Anchor|MOBILE}} Mobile === |
|||
* All models support: ''[[MMX (instruction set)|MMX]], [[Streaming SIMD Extensions|SSE]], [[SSE2]], [[SSE3]], [[SSSE3]], [[SSE4.1]], [[SSE4.2]], F16C, Enhanced Intel [[SpeedStep]] Technology (EIST), [[Intel VT-x]], [[Intel 64]], XD bit (an [[NX bit]] implementation)'', and ''Smart Cache''. |
|||
** Core i3, i5 and i7 support ''[[Advanced Vector Extensions|AVX]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2|AVX2]], BMI1, BMI2, [[FMA3]]'', and ''[[hyper-threading]] (HT)''. |
|||
** Core i3, i5 and i7 except the Core i3-4000M support ''[[AES instruction set|AES-NI]]''.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Intel® Core™ i3-4000M Processor (3M Cache, 2.40 GHz) Product Specifications |url=https://ark.intel.com/products/75104/Intel-Core-i3-4000M-Processor-3M-Cache-2_40-GHz |website=Intel |language=en-US |access-date=December 14, 2022}}</ref> |
|||
** Core i5 and i7 except the Core i5-4410E, i5-4402EC, i7-4700EC, and i7-4702EC support ''[[Turbo Boost]] 2.0.'' |
|||
* Platform Controller Hub (PCH) integrated into the CPU package, slightly reducing the amount of space used on motherboards.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Cunningham |first=Andrew |date=June 4, 2013 |title=The U is for Ultrabook: Intel's low-power, dual-core Haswell CPUs unveiled |url=https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/06/the-u-is-for-ultrabook-intels-low-power-dual-core-haswell-cpus-unveiled/ |website=Ars Technica |language=en-US |access-date=October 22, 2013}}</ref> |
|||
* Transistors: 1.3 billion<ref name="techarp">{{cite web |title=Mobile CPU Comparison Guide Rev. 11.9 |url=http://www.techarp.com/showarticle.aspx?artno=347&pgno=6 |url-status=dead |website=Tech ARP |date=April 9, 2015 |access-date=April 9, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
* Die size: 181{{nbsp}}mm<sup>2</sup><ref name="techarp" /> |
|||
SKU suffixes to denote: |
|||
* M{{snd}} mobile processor ([[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]]) |
|||
* Q{{snd}} quad-core |
|||
* U{{snd}} ultra-low power (BGA{{nbsp}}1168 packaging) |
|||
* X{{snd}} "extreme" |
|||
* Y{{snd}} extreme low-power (BGA{{nbsp}}1168 packaging) |
|||
* E / H{{snd}} BGA1364 packaging |
|||
==== Haswell-M ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Release date |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Price <br/> (USD){{efn|name="RCP"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU core|Cores]] <br> ([[Thread (computing)|threads]]) |
|||
! colspan="2" | CPU clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU Cache|L3 <br/> Cache]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Socket |
|||
! colspan="2" | Memory<br>support{{efn|name="32GB RAM"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[Thermal design power|TDP]] |
|||
! colspan="3" rowspan="2" | Configurable TDP |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75049 4670S] |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Base |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Intel Turbo Boost|Turbo <br> Boost]] <br> 2.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65 W |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Max GPU <br> clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76641 4670R] |
|||
! [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3]] |
|||
| Iris Pro 5200 <br />(GT3e) |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
! {{abbr|SDP|Scenaro Design Power}} |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
! Down |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
! Up |
|||
| 1.3 GHz |
|||
| 4 MB |
|||
| 128 MB |
|||
| $310 |
|||
| BGA<br />1364 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75050 4670T] |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59C4F0; color:#fff;" | Celeron |
|||
| rowspan="6" | HD 4600 <br />(GT2) |
|||
| 2.3 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 350 MHz<ref name="4th Generation" /> |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 6 MB |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{N/a}} |
|||
| 45 W |
|||
| $213 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | [[LGA 1150|LGA<br />1150]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80815 4590] |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| October 1, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.7 GHz |
|||
| $86 |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="7" | 1.15 GHz |
||
| 84 W |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="3" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="5" | $192 |
||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Socket G3|Socket <br> G3]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80816 4590S] |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| 65 W |
|||
| $75 |
|||
| 2.2 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78928 4590T] |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59C4F0; color:#fff;" | Pentium |
|||
| 2.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 35 W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75043 4570] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| October 1, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.6 GHz |
|||
| $134 |
|||
| 84 W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2 (2) |
|||
| rowspan="5" | {{Start date|2013|06|2}} |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Socket G3|Socket <br> G3]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75044 4570S] |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65 W |
|||
| $134 |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76640 4570R] |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#00A4E6; color:#fff;" | Core i3 |
|||
| Iris Pro 5200 <br />(GT3e) |
|||
|- |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75104/intel-core-i34000m-processor-3m-cache-2-40-ghz.html 4000M] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 200 MHz |
|||
| $240 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | |
| rowspan="3" | 4 MB |
||
| 128 MB |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| $288 |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{NA}} |
|||
| BGA<br />1364 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="3" | [[Intel Socket G3|Socket <br> G3]] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76346/intel-core-i34100m-processor-3m-cache-2-50-ghz.html 4100M] |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/77483/intel-core-i34110m-processor-3m-cache-2-60-ghz.html 4110M] |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#1E83CB; color:#fff;" | Core i5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76348/intel-core-i54200m-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-10-ghz.html 4200M] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $240 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.15 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="6" | [[Intel Socket G3|Socket <br> G3]] |
|||
| rowspan="6" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/81012/intel-core-i54210m-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4210M] |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76347/intel-core-i54300m-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4300M] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $227 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 1.25 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80373/intel-core-i54310m-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4310M] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| 1.1 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76750/intel-core-i54330m-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-50-ghz.html 4330M] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $266 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.25 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80344/intel-core-i54340m-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-60-ghz.html 4340M] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $266 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964C7; color:#fff;" | Core i7 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76349/intel-core-i74600m-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-60-ghz.html 4600M] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $346 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2 (2) |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| rowspan="12" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.3 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="12" | [[Intel Socket G3|Socket <br> G3]] |
|||
| rowspan="12" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="12" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="12" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="12" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/80345/intel-core-i74610m-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-70-ghz.html 4610M] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $346 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75117/intel-core-i74700mq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4700MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $383 |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 4 (8) |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 1.15 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75119/intel-core-i74702mq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4702MQ] |
|||
| $383 |
|||
| 2.2 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 45{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78931/intel-core-i74710mq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-50-ghz.html 4710MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
| 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78933/intel-core-i74712mq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4712MQ] |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 45{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75128/intel-core-i74800mq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-70-ghz.html 4800MQ] |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $380 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 1.3 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78937/intel-core-i74810mq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-80-ghz.html 4810MQ] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75131/intel-core-i74900mq-processor-8m-cache-up-to-3-80-ghz.html 4900MQ] |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $570 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 8{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78939/intel-core-i74910mq-processor-8m-cache-up-to-3-90-ghz.html 4910MQ] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $570 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75133/intel-core-i74930mx-processor-extreme-edition-8m-cache-up-to-3-90-ghz.html 4930MX] |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $1096 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 3.9 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.35 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 57{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 65{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78940/intel-core-i74940mx-processor-extreme-edition-8m-cache-up-to-4-00-ghz.html 4940MX] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $1096 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| 4.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
{{efn|name="32GB RAM" | Up to 32{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
==== Haswell-E/EQ ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Release date |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Price <br/> (USD){{efn|name="RCP"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU core|Cores]] <br> ([[Thread (computing)|threads]]) |
|||
! colspan="2" | CPU clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU Cache|L3 <br/> Cache]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Socket |
|||
! colspan="2" | Memory<br>support{{efn|name="16GB RAM"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[Thermal design power|TDP]] |
|||
! colspan="3" rowspan="2" | Configurable TDP |
|||
|- |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Base |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Intel Turbo Boost|Turbo <br> Boost]] <br> 2.0 |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Max GPU <br> clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3]] |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
! {{abbr|SDP|Scenaro Design Power}} |
|||
! Down |
|||
! Up |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#00A4E6; color:#fff;" | Core i3 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76293/intel-core-i34100e-processor-3m-cache-2-40-ghz.html 4100E] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 0.9 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="4" | BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76294/intel-core-i34102e-processor-3m-cache-1-60-ghz.html 4102E] |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/79197/intel-core-i34110e-processor-3m-cache-2-60-ghz.html 4110E] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/79198/intel-core-i34112e-processor-3m-cache-1-80-ghz.html 4112E] |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| 1.8 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#1E83CB; color:#fff;" | Core i5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76292/intel-core-i54400e-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4400E] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $266 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="5" | BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="5" {{no}} |
|||
| 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="5" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="5" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="5" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76307/intel-core-i54402e-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-70-ghz.html 4402E] |
|||
| $266 |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| 0.9 |
|||
| 25{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/79199/intel-core-i54410e-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-90-ghz.html 4410E] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $266 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
| 37{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/79201/intel-core-i54422e-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-90-ghz.html 4422E] |
|||
| $266 |
|||
| 1.8 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 0.9 |
|||
| 25{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75554/intel-core-i54402ec-processor-4m-cache-up-to-2-50-ghz.html 4402EC] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $324 |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| colspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| 27{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964C7; color:#fff;" | Core i7 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75555/intel-core-i74700ec-processor-8m-cache-up-to-2-70-ghz.html 4700EC] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $459 |
|||
| 2 (4) |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| colspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| 8{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="6" | BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{no}} |
|||
| 43{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75469/intel-core-i74700eq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4700EQ] |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 4 (8) |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76297/intel-core-i74701eq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4701EQ] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $415 |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75556/intel-core-i74702ec-processor-8m-cache-up-to-2-00-ghz.html 4702EC] |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $459 |
|||
| 2 (4) |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| colspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| 8{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| 27{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76299/intel-core-i74850eq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4850EQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | August 29, 2013 |
|||
| $466 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 4 (8) |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>Pro<br>5200]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76298/intel-core-i74860eq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-20-ghz.html 4860EQ] |
|||
| $508 |
|||
| 1.8 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
{{efn|name="16GB RAM" | Up to 16{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
==== Haswell-H/HQ ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Release date |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Price <br/> (USD){{efn|name="RCP"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU core|Cores]] <br> ([[Thread (computing)|threads]]) |
|||
! colspan="2" | CPU clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU Cache|L3 <br/> Cache]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Socket |
|||
! colspan="2" | Memory<br>support{{efn|name="32GB RAM"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[Thermal design power|TDP]] |
|||
! colspan="3" rowspan="2" | Configurable TDP |
|||
|- |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Base |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Intel Turbo Boost|Turbo <br> Boost]] <br> 2.0 |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Max GPU <br> clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3]] |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
! {{abbr|SDP|Scenaro Design Power}} |
|||
! Down |
|||
! Up |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#1E83CB; color:#fff;" | Core i5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75027/intel-core-i54200h-processor-3m-cache-up-to-3-40-ghz.html 4200H] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $257 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2 (4) |
| rowspan="2" | 2 (4) |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75045 4570T] |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| rowspan="20" | HD 4600 <br />(GT2) |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.15 |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="55" {{N/a}} |
||
| rowspan="2" | |
| rowspan="2" | 35 W |
||
| rowspan="2" | $192 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan=" |
| rowspan="55" | [[LGA 1150|LGA<br />1150]] |
||
| rowspan="2" | 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75468 4570TE] |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| July 20, 2014 |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| $225 |
|||
| rowspan="13" | 350 MHz<ref name="4th Generation" /> |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="7" | 4 (4) |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964C7; color:#fff;" | Core i7 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80817 4460] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.4 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 6 MB |
|||
| 84 W |
|||
| rowspan="3" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| rowspan="7" | $182 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80818 4460S] |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| 65 W |
|||
| $383 |
|||
| rowspan="14" | 4 (8) |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4600]] |
|||
| rowspan="14" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="14" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="14" | BGA 1364 |
|||
| rowspan="14" | DDR3L-1600 <br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="14" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="14" | 47{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="14" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="14" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78927 4460T] |
|||
| 1.9 GHz |
|||
| $383 |
|||
| 2. |
| 2.7 GHz |
||
| 35 W |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|[https://ark.intel.com/products/75038 4440] |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | April 14, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.3 GHz |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| 84 W |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75040 4440S] |
|||
| 2.8 GHz |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| 65 W |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75036 4430] |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| January 1, 2015 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.2 GHz |
|||
| $378 |
|||
| 84 W |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|06|2}}<ref name="presence-pc" /> |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75037 4430S] |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| 65 W |
|||
| $440 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| 3.2 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris <br> Pro <br> 5200]] |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="19" | 2 (4) |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76090/intel-core-i74760hq-processor-6m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4760HQ] |
|||
| rowspan="19" | Core i3 |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77495 4370] |
|||
| $434 |
|||
| |
| 3.8 GHz |
||
| rowspan="46" {{N/a}} |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 1.15 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 4 MB |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 54 W |
|||
| rowspan="46" {{No}} |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $149 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77493 4360] |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
| July 21, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $434 |
|||
| 2.2 |
|||
| 3.4 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77491 4350] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.6 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $ |
| $138 |
||
| 2.3 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77771 4340] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| $ |
| $149 |
||
| 2.4 |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77769 4330] |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| July 21, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | $138 |
|||
| $434 |
|||
| 2.5 |
|||
| 3.7 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81207 4370T] |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 200 MHz |
|||
| $623 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 35 W |
|||
| 2.4 |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
| 3.6 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 55{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77494 4360T] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| $623 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| 3.8 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77492 4350T] |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| July 21, 2014 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $623 |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| 4.0 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77770 4330T] |
|||
|} |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
{{efn|name="32GB RAM" | Up to 32{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
==== Haswell-U (Low power) ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Release date |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Price <br/> (USD){{efn|name="RCP"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU core|Cores]] <br> ([[Thread (computing)|threads]]) |
|||
! colspan="2" | CPU clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU Cache|L3 <br/> Cache]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Socket |
|||
! colspan="2" | Memory<br>support{{efn|name="16GB RAM"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[Thermal design power|TDP]] |
|||
! colspan="3" rowspan="2" | Configurable TDP |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77492 4340TE] |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Base |
|||
| 2.6 GHz |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Intel Turbo Boost|Turbo <br> Boost]] <br> 2.0 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 350 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1 GHz |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $138 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77778 4330TE] |
|||
! [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3]] |
|||
| 2.4 GHz |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
! {{abbr|SDP|Scenaro Design Power}} |
|||
| $122 |
|||
! Down |
|||
! Up |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77490 4170] |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59C4F0; color:#fff;" | Celeron |
|||
| rowspan="8" | HD 4400 <br />(GT2) |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="8" | 1.15 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="28" | 3 MB |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 54 W |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | $117 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77488 4160] |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| $132 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 2 (2) |
|||
| 1.4 |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="4" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77486 4150] |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| December 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $132 |
|||
| 1.4 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77480 4130] |
|||
| 3.4 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
| $137 |
|||
| |
| $122 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81209 4170T] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| December 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 200 MHz |
|||
| $137 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 35 W |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | $117 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77489 4160T] |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59C4F0; color:#fff;" | Pentium |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77487 4150T] |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{ |
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
||
| rowspan="2" | 2 (2) |
|||
| 1.7 |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77481 4130T] |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| December 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|9|1}} |
|||
| $161 |
|||
| |
| $122 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="27" | Budget |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#00A4E6; color:#fff;" | Core i3 |
|||
| rowspan="27" | 2 (2) |
|||
| rowspan="20" | Pentium |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/87358 G3470] |
|||
| rowspan="27" | HD Graphics |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 350 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 53 W |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | $86 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83428 G3460] |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| $281 |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 2 (2) |
|||
| 1.7 |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="7" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="7" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="7" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80792 G3450] |
|||
| 3.4 GHz |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| 1.7 |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80794 G3440] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | |
| rowspan="2" | 3.3 GHz |
||
| $ |
| $75 |
||
| 1.9 |
|||
| 0.95 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77777 G3430] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|12|1}} |
|||
| $275 |
|||
| |
| $86 |
||
| rowspan="3" | 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77775 G3420] |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | $75 |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| 1.8 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83429 G3460T] |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 200 MHz |
|||
| $281 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 35 W |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80793 G3450T] |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| $342 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| 1.1 |
|||
| 28{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 23{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80795 G3440T] |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#1E83CB; color:#fff;" | Core i5 |
|||
| 2.8 GHz |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77776 G3420T] |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|12|1}} |
|||
| $281 |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.0 |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="11" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="11" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="11" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="11" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 25{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78007 G3320TE] |
|||
| 2.3 GHz |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 350 MHz |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| 1 |
| 1 GHz |
||
| rowspan="17" | Up to dual<br />channel<br />DDR3-1333 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| rowspan="10" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/87356 G3260] |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| $342 |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 53 W |
|||
| 1.3 |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| $64 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4500]] |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/82723 G3258]{{ref label|Anniversary|c}} |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75990/intel-core-i54258u-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-90-ghz.html 4258U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.2 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|06|02}} |
|||
| $342 |
|||
| |
| $72 |
||
| 2.9 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>5100]] |
|||
| 1.1 |
|||
| 28{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 23{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83538 G3250] |
|||
| |
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
||
| rowspan="7" | $64 |
|||
| $315 |
|||
| 1.4 |
|||
| 2.7 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>5000]] |
|||
| 1.0 |
|||
| 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80796 G3240] |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $342 |
|||
| 2.6 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>5100]] |
|||
| 1.2 |
|||
| 28{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 23{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77773 G3220] |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|12|1}} |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| 1.9 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| 1.1 |
|||
| 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/87357 G3260T] |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| July 20, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 200 MHz |
|||
| $315 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 35 W |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| {{Start date|2015|03|30}} |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>5100]] |
|||
| 1.2 |
|||
| 28{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 23{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83539 G3250T] |
|||
| 2.8 GHz |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| $281 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80797 G3240T] |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $342 |
|||
| 1.4 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>5000]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77774 G3220T] |
|||
| 2.6 GHz |
|||
| January 21, 2014 |
|||
| {{Start date|2013|12|1}} |
|||
| $315 |
|||
| 1.5 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan="7" | Celeron |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964C7; color:#fff;" | Core i7 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80798 G1850] |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 350 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 1.05 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 2 MB |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 53 W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| $52 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80800 G1840] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2.8 GHz |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $ |
| $42 |
||
| rowspan="7" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 1.8 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="7" | 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="7" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="7" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="7" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 25{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78954 G1830] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|12|1}} |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $ |
| $52 |
||
| 2.0 |
|||
| 3.1 |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78955 G1820] |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | $42 |
|||
| $454 |
|||
| 1.5 |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>5000]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80801 G1840T] |
|||
| 2.5 GHz |
|||
| $454 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 2.8 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 35 W |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| {{Start date|2014|05|11}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|Iris<br>5100]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 28{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 23{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78956 G1820T] |
|||
| 2.4 GHz |
|||
| July 20, 2014 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{Start date|2013|12|1}} |
|||
| {{dunno}} |
|||
| 3.0 |
|||
| 3.5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76616/intel-core-i74600u-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4600U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $398 |
|||
| 2.1 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4400]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75114/intel-core-i74650u-processor-4m-cache-up-to-3-30-ghz.html 4650U] |
|||
| $454 |
|||
| 1.7 |
|||
| 3.3 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>5000]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78957 G1820TE] |
|||
| 2.2 GHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
{{efn|name="16GB RAM" | Up to 16{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
==== Haswell-Y (Extreme low power) ==== |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Release date |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Price <br/> (USD){{efn|name="RCP"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU core|Cores]] <br> ([[Thread (computing)|threads]]) |
|||
! colspan="2" | CPU clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
! colspan="2" | [[Intel HD and Iris Graphics|GPU]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[CPU Cache|L3 <br/> Cache]] |
|||
! rowspan="3" | Socket |
|||
! colspan="2" | Memory<br>support{{efn|name="16GB RAM"}} |
|||
! rowspan="3" | [[Thermal design power|TDP]] |
|||
! colspan="3" rowspan="2" | Configurable TDP |
|||
|- |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Base |
|||
! rowspan="2" | [[Intel Turbo Boost|Turbo <br> Boost]] <br> 2.0 |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Model |
|||
! rowspan="2" | Max GPU <br> clock rate <br> (GHz) |
|||
|- |
|||
! [[DDR3 SDRAM|DDR3]] |
|||
! {{abbr|ECC|Error correction code memory}} |
|||
! {{abbr|SDP|Scenaro Design Power}} |
|||
! Down |
|||
! Up |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59C4F0; color:#fff;" | Celeron |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78943/intel-celeron-processor-2961y-2m-cache-1-10-ghz.html 2961Y] |
|||
| December 2013 |
|||
| {{resize|OEM}} |
|||
| 2 (2) |
|||
| 1.1 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| 0.85 |
|||
| 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| BGA 1168 |
|||
| DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| {{no}} |
|||
| 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#59C4F0; color:#fff;" | Pentium |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76622/intel-pentium-processor-3560y-2m-cache-1-20-ghz.html 3560Y] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{resize|OEM}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2 (2) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.2 |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>Graphics]] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 0.85 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/78946/intel-pentium-processor-3561y-2m-cache-1-20-ghz.html 3561Y] |
|||
| December 2013 |
|||
| $161 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#00A4E6; color:#fff;" | Core i3 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75988/intel-core-i34010y-processor-3m-cache-1-30-ghz.html 4010Y] |
|||
| June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $304 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 1.3 |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4200]] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 0.85 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="4" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="4" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="4" {{NA}} |
|||
| 9.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76608/intel-core-i34012y-processor-3m-cache-1-50-ghz.html 4012Y] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $304 |
|||
| 1.5 |
|||
| 4.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76609/intel-core-i34020y-processor-3m-cache-1-50-ghz.html 4020Y] |
|||
| $304 |
|||
| 1.5 |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 9.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/81021/intel-core-i34030y-processor-3m-cache-1-60-ghz.html 4030Y] |
|||
| April 14, 2014 |
|||
| $281 |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#1E83CB; color:#fff;" | Core i5 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/75802/intel-core-i54200y-processor-3m-cache-up-to-1-90-ghz.html 4200Y] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | June 2, 2013 |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 2 (4) |
|||
| 1.4 |
|||
| 1.9 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4200]] |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 0.85 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 3{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| rowspan="6" | BGA 1168 |
|||
| rowspan="6" | DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{no}} |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 9.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76610/intel-core-i54202y-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-00-ghz.html 4202Y] |
|||
| $304 |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
| 4.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76611/intel-core-i54210y-processor-3m-cache-up-to-1-90-ghz.html 4210Y] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | September 1, 2013 |
|||
| {{dunno}} |
|||
| 1.5 |
|||
| 1.9 |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/81020/intel-core-i54220y-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-00-ghz.html 4220Y] |
|||
| $304 |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 2.0 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76612/intel-core-i54300y-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-30-ghz.html 4300Y] |
|||
| $287 |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76613/intel-core-i54302y-processor-3m-cache-up-to-2-30-ghz.html 4302Y] |
|||
| {{dunno}} |
|||
| 1.6 |
|||
| 2.3 |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
| 4.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan="16" style="text-align:left; background-color:#0964C7; color:#fff;" | Core i7 |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="text-align: left" | [https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/76618/intel-core-i74610y-processor-4m-cache-up-to-2-90-ghz.html 4610Y] |
|||
| September 1, 2013 |
|||
| $393 |
|||
| 2 (4) |
|||
| 1.7 |
|||
| 2.9 |
|||
| [[Intel Graphics Technology#Haswell|HD<br>4200]] |
|||
| 0.85 |
|||
| 4{{nbsp}}MB |
|||
| BGA 1168 |
|||
| DDR3L-1600 <br/> LPDDR3-1600<br/><small>[[Multi-channel memory architecture#Dual-channel architecture|dual-channel]]</small> |
|||
| {{no}} |
|||
| 11.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 6{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| 9.5{{nbsp}}W |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
{{notelist|refs= |
|||
{{efn|name="RCP" | Price reflects Recommended Customer Price (RCP) rather than MSRP. RCP is the cost per unit, in bulk sales of 1000 units or more, to OEMs, ODMs, and retail outlets when purchasing from Intel. Actual MSRP is higher than RCP}} |
|||
{{efn|name="16GB RAM" | Up to 16{{nbsp}}GB RAM supported}} |
|||
}} |
|||
:{{Note label|PCIeChipsetDependence|a}} Some of these configurations could be disabled by the chipset. For example, H-series chipsets disable all PCIe 3.0 lane configurations except 1×16. |
|||
:{{Note label|VTdChipsetDependence|b}} This feature also requires a chipset that supports VT-d like the Q87 chipset or the X99 chipset. |
|||
:{{Note label|Anniversary|c}} This is called ''20th Anniversary Edition'' and has an unlocked multiplier. |
|||
SKU suffixes to denote: |
|||
* K{{snd}} unlocked <span style="color: #969696">(adjustable CPU multiplier up to 63x)</span> |
|||
**The Pentium G3258 CPU is unlocked despite not having the K-suffix. |
|||
* S{{snd}} performance-optimized lifestyle <span style="color: #969696">(low power with 65 W TDP)</span> |
|||
* T{{snd}} power-optimized lifestyle <span style="color: #969696">(ultra low power with 35–45 W TDP)</span> |
|||
* R{{snd}} BGA packaging / High-performance GPU <span style="color: #969696">(currently Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e))</span> |
|||
* X{{snd}} extreme edition <span style="color: #969696">(adjustable CPU ratio with no ratio limit)</span> |
|||
=== |
==={{Anchor|SERVER-CPUS|HASWELL-WS}}Server processors=== |
||
{{Multiple image |
{{Multiple image |
||
| align = right |
| align = right |
||
| Line 2,751: | Line 1,551: | ||
SKU suffixes to denote: |
SKU suffixes to denote: |
||
* L{{snd}} low power |
* L{{snd}} low power |
||
==={{Anchor|MOBILE}}Mobile processors=== |
|||
* All models support: ''[[MMX (instruction set)|MMX]], [[Streaming SIMD Extensions|SSE]], [[SSE2]], [[SSE3]], [[SSSE3]], [[SSE4.1]], [[SSE4.2]], F16C, Enhanced Intel [[SpeedStep]] Technology (EIST), [[Intel VT-x]], [[Intel 64]], XD bit (an [[NX bit]] implementation)'', and ''Smart Cache.'' |
|||
** Core i3, i5 and i7 support ''[[Advanced Vector Extensions|AVX]], [[Advanced Vector Extensions 2|AVX2]], BMI1, BMI2, [[FMA3]]'', and ''[[hyper-threading]] (HT)''. |
|||
** Core i3, i5 and i7 except the Core i3-4000M support ''[[AES instruction set|AES-NI]]''.<ref>[https://ark.intel.com/products/75104/Intel-Core-i3-4000M-Processor-3M-Cache-2_40-GHz Intel® Core™ i3-4000M Processor (3M Cache, 2.40 GHz) Product Specifications]</ref> |
|||
** Core i5 and i7 except the Core i5-4410E, i5-4402EC, i7-4700EC, and i7-4702EC support ''[[Turbo Boost]] 2.0.'' |
|||
* Platform Controller Hub (PCH) integrated into the CPU package, slightly reducing the amount of space used on motherboards.<ref>{{cite web |
|||
| url = https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/06/the-u-is-for-ultrabook-intels-low-power-dual-core-haswell-cpus-unveiled/ |
|||
| title = The U is for Ultrabook: Intel's low-power, dual-core Haswell CPUs unveiled |
|||
| date = 2013-06-04 | access-date = 2013-10-22 |
|||
| author = Andrew Cunningham | publisher = arstechnica.com |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
* Transistors: 1.3 billion<ref name="techarp">{{cite web | url = http://www.techarp.com/showarticle.aspx?artno=347&pgno=6 | title = Tech ARP - Mobile CPU Comparison Guide Rev. 11.9 | date = 2015-04-09 | access-date = 2015-04-09 | website = techarp.com }}</ref> |
|||
* Die size: 181 mm<sup>2</sup><ref name="techarp" /> |
|||
The following table lists available mobile processors. |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
|||
|- |
|||
! rowspan=2 | Target<br />segment |
|||
! rowspan=2 | Cores<br />(threads) |
|||
! colspan=2 rowspan="2" | Processor<br />branding and model |
|||
! rowspan=2 | GPU model |
|||
! colspan="4" | [[Programmable TDP]]<ref name="intel-mh-lines">{{cite web |
|||
| url = http://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/datasheets/4th-gen-core-family-mobile-m-h-processor-lines-vol-1-datasheet.pdf |
|||
| title = 4th Generation Intel Core processor based on Mobile M-Processor and H-Processor Lines Datasheet, Volume 1 of 2 |
|||
|date=December 2013 | access-date = 2013-12-22 |
|||
| website = Intel.com | quote = Configurable TDP (cTDP) and Low-Power Mode (LPM) form a design vector where the processor behavior and package TDP are dynamically adjusted to a desired system performance and power envelope. [...] With cTDP, the processor is now capable of altering the maximum sustained power with an alternate guaranteed frequency. Configurable TDP allows operation in situations where extra cooling is available or situations where a cooler and quieter mode of operation is desired.}}</ref>{{rp|69–72}} |
|||
! rowspan=2 | CPU Turbo<br />(single core) |
|||
! colspan=2 data-sort-type="number" | Graphics [[clock rate]] |
|||
! rowspan=2 data-sort-type="number" | [[L3 cache|L3<br />cache]] |
|||
! rowspan=2 data-sort-type="number" | [[GPU]]<br />[[eDRAM]] |
|||
! rowspan=2 data-sort-type="text" | Release<br />date |
|||
! rowspan=2 | Release<br />price<br />(USD) |
|||
|- |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | [[Scenario Design Power|SDP]]<ref>{{cite web |
|||
| url = https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2013/01/the-technical-details-behind-intels-7-watt-ivy-bridge-cpus/ |
|||
| title = The technical details behind Intel's 7 Watt Ivy Bridge CPUs |
|||
| date = 2013-01-14 | access-date = 2013-12-22 |
|||
| website = Arstechnica.com |
|||
| quote = If the CPU needs to work hard for an extended period of time and the laptop gets warmer, it will slowly ramp down its speed until it's operating at its stated TDP. [...] There are two OEM-configurable "power level" states that define how quick the CPU can be in these situations: PL2 tells the processor how much power it's allowed to use when it needs a short burst of speed, and PL1 defines how quickly the processor can run under sustained load. [...] This is at the heart of what Intel is doing with the Y-series processors: their maximum TDP has been lowered four watts, from 17 to 13. Intel is also validating them for use at two lower PL1 values: 10 watts and 7 watts. This is where the marketing we discussed earlier comes in—rather than keeping these values under the covers as it has so far been content to do, Intel has taken that lowest value, put it on its product pages, and called it SDP. |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |
|||
| url = http://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/datasheets/4th-gen-core-family-mobile-u-y-processor-lines-vol-1-datasheet.pdf |
|||
| title = 4th Generation Intel Core processor based on Mobile U-Processor and Y-Processor Lines Datasheet, Volume 1 of 2 |
|||
| date = December 2013 | access-date = 2013-12-22 |
|||
| publisher = intel.com }}</ref>{{rp|71}} |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | [[cTDP]] down{{ref label|ctdp-down|a}} |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | [[Nominal TDP]]{{ref label|nominal-tdp|b}} |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | cTDP up{{ref label|ctdp-up|c}} |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | Normal |
|||
! data-sort-type="number" | Turbo |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="30" | Performance |
|||
| rowspan="30" | 4 (8) |
|||
| rowspan="40" | Core i7 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78940 4940MX] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="30" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="29" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 57 W / 3.1 GHz |
|||
| 65 W / 3.8 GHz |
|||
| 4.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.35 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 8 MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21">{{cite web|title=Intel Quietly Launches Ten New Mobile Processors|date=22 January 2014 |url=http://www.tomshardware.com/news/intel-new-haswell-celeron,25815.html|publisher=TomsHardware.com|access-date=11 February 2014}}</ref> |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $1096 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75133 4930MX] |
|||
| 57 W / 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 65 W / 3.7 GHz |
|||
| 3.9 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45">{{cite web|url=http://www.cpu-world.com/CPUs/Core_i7/Intel-Core%20i7-4750HQ%20Mobile%20processor.html |title=Intel Core i7-4750HQ Mobile processor – CL8064701510101 |publisher=Cpu-world.com |access-date=2013-10-12}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83503 4980HQ] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) |
|||
| 47 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| {{n/a}} |
|||
| 4.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 200 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 1.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 6 MB |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 128 MB<ref name="anandtech-i74950hq" /> |
|||
| {{dts|2014|07|21}}<ref name="cpu-world1">{{cite web|url=http://www.cpu-world.com/news_2014/2014072101_Intel_refreshes_Core_i5_i7_and_N-Series_mobile_lineups.html |title=Intel refreshes Core i5, i7 and N-Series mobile lineups |publisher=Cpu-world.com |access-date=2014-07-21}}</ref> |
|||
| rowspan="3" | $623 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76088 4960HQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.6 GHz |
|||
| 3.8 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}}<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cpu-world.com/CPUs/Core_i7/Intel-Core%20i7-4960HQ%20Mobile%20processor.html |title=Intel Core i7-4960HQ Mobile processor – CL8064701511001 |publisher=Cpu-world.com |access-date=2013-10-12}}</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76085 4950HQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.4 GHz |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78939 4910MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| 47 W / 2.9 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.7 GHz |
|||
| 3.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 8 MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| $568 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75131 4900MQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.6 GHz |
|||
| 3.8 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $570 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83504 4870HQ] |
|||
| rowspan="5" | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) |
|||
| 47 W / 2.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{n/a}} |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="21" | 6 MB |
|||
| rowspan="5" | 128 MB |
|||
| {{dts|2014|07|21}}<ref name="cpu-world1"/> |
|||
| $434 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76298 4860EQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 1.8 GHz |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| 750 MHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|08}} |
|||
| $508 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76089 4860HQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.4 GHz |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| $434 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76299 4850EQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| 650 MHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|08}} |
|||
| $466 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76086 4850HQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.3 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.3 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $434 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78937 4810MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| 47 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.6 GHz |
|||
| 3.8 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| $378 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75128 4800MQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.7 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.5 GHz |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $380 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83505 4770HQ] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) |
|||
| 47 W / 2.2 GHz |
|||
| |
|||
| 3.4 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 200 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 128 MB |
|||
| {{dts|2014|07|21}}<ref name="cpu-world1"/> |
|||
| $434 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76090 4760HQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.1 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.1 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| $434 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76087 4750HQ] |
|||
| 47 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| 55 W / 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $440 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78934 4720HQ] |
|||
| rowspan="11" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| 47 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
| {{n/a}} |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 400 MHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="84" {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{dts|2015|01}} |
|||
| rowspan="5" | $378 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78933 4712MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 37 W / 2.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 45 W / 3.1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.15 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78932 4712HQ] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78931 4710MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 47 W / 2.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 55 W / 3.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.5 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78930 4710HQ] |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75119 4702MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 37 W / 2.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 45 W / 2.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 3.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.15 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| rowspan="4" | $383 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75118 4702HQ] |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75117 4700MQ] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 47 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 55 W / 3.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 3.4 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75116 4700HQ] |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76297 4701EQ] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| $415 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75469 4700EQ] |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $378 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75556 4702EC] |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 27 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="11" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 8 MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2014|04}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $459 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75555 4700EC] |
|||
| 43 W / 2.7 GHz |
|||
| {{n/a}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="71" | Mainstream |
|||
| rowspan="58" | 2 (4) |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75114 4650U] |
|||
| HD 5000 (GT3) |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.7 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="11" | 4 MB |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $454 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76618 4610Y] |
|||
| HD 4200 (GT2) |
|||
| 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 9.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.7 GHz |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| 850 MHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| $393 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80345/ 4610M] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="20" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 37 W / 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.3 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $346 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76349/ 4600M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.9 GHz |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76616/ 4600U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 2.1 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
| $398 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83506 4578U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | Iris 5100 (GT3) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 23 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 28 W / 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| {{NA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75992 4558U] |
|||
| 28 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $454 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75112 4550U] |
|||
| HD 5000 (GT3) |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.5 GHz |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81015 4510U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 15 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04}} |
|||
| $393 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75460 4500U] |
|||
| 15 W / 1.8 GHz |
|||
| 25 W / 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $398 |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="30" | Core i5 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75554 4402EC] |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="5" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 27 W / 2.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="27" {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04}} |
|||
| $324 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/79201 4422E] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| 25 W / 1.8 GHz |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 400 MHz |
|||
| 900 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="47" | 3 MB |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | $266 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/79199 4410E] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.9 GHz |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76307 4402E] |
|||
| 25 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| 900 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76292 4400E] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.7 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75034 4360U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 5000 (GT3) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.5 GHz |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 200 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| $315 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75033 4350U] |
|||
| 15 W / 1.4 GHz |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $342 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80344 4340M] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="3" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 37 W / 2.9 GHz |
|||
| 3.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.25 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $266 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76750 4330M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80373 4310M] |
|||
| HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| 37 W / 2.7 GHz |
|||
| 3.4 GHz |
|||
| 400 MHz |
|||
| 1.25 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2014|01|21}}<ref name="new procs 2014-01-21" /> |
|||
| $225 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/80343 4310U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| 3.0 GHz |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
| $281 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76613 4302Y] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4200 (GT2) |
|||
| 4.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 2.3 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 200 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 850 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76612 4300Y] |
|||
| 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 9.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| $304 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76347 4300M] |
|||
| HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="10" {{N/A}} |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
| 37 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| 400 MHz |
|||
| 1.25 GHz |
|||
| $225 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76308 4300U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.9 GHz |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
| $287 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75991 4288U] |
|||
| rowspan="3" | Iris 5100 (GT3) |
|||
| rowspan="3" | 23 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 28 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $342 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75990 4258U] |
|||
| 28 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
| 2.9 GHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/83507 4308U] |
|||
| 28 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| 3.3 GHz |
|||
| 1.2 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|07|20}}<ref name="CPU World i5-4308U">{{cite web|title=Intel Core i5-4308U Mobile processor — CL8064701954700|url=http://www.cpu-world.com/CPUs/Core_i5/Intel-Core%20i5-4308U%20Mobile%20processor.html|website=CPU World}}</ref> |
|||
| $315 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75030 4260U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 5000 (GT3) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.4 GHz |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| $315 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75028 4250U] |
|||
| 15 W / 1.3 GHz |
|||
| 2.6 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $342 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78929 4210H] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 47 W / 2.9 GHz |
|||
| 3.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.15 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|07|20}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $225 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81012 4210M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
| 3.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81016 4210U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.7 GHz |
|||
| 2.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| $287 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81020 4220Y] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | HD 4200 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 9.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| 2.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 850 MHz |
|||
| $281 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76611 4210Y] |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.5 GHz |
|||
| 1.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| $304 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76610 4202Y] |
|||
| 4.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| 2.0 GHz |
|||
| {{N/A}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75802 4200Y] |
|||
| 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.4 GHz |
|||
| 1.9 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $304 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75459 4200U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="12" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| 25 W / ? |
|||
| 2.6 GHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| $287 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75027 4200H] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="2" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 47 W / 2.8 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="33" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 3.4 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.15 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| $257 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76348 4200M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.5 GHz |
|||
| 3.1 GHz |
|||
| $240 |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="18" | Core i3 |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75989 4158U] |
|||
| Iris 5100 (GT3) |
|||
| 23 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 28 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="31" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $342 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81017 4120U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| $281 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/79198 4112E] |
|||
| rowspan="6" | HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="6" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 25 W / 1.8 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 900 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="6" | $225 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/79197 4110E] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76294 4102E] |
|||
| 25 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76293 4100E] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77483 4110M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76346 4100M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.5 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75110 4100U] |
|||
| HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 15 W / 1.8 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="9" | 200 MHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
| $287 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81021 4030Y] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | HD 4200 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 9.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 850 MHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| $281 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76609 4020Y] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5 W / 1.5 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| rowspan="3" | $304 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76608 4012Y] |
|||
| 4.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| {{n/a}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75988 4010Y] |
|||
| 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 9.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.3 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|06|02}}<ref name="th-45" /> |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81018 4030U] |
|||
| rowspan="4" | HD 4400 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="5" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 11.5 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15 W / 1.9 GHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| $281 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81019 4025U] |
|||
| 950 MHz |
|||
| $275 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75107 4010U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15 W / 1.7 GHz |
|||
| 1 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="3" | {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| $287 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75105 4005U] |
|||
| 950 MHz |
|||
| $281 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75104 4000M] |
|||
| HD 4600 (GT2) |
|||
| rowspan="14" {{N/A}} |
|||
| 37 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
| 400 MHz |
|||
| 1.1 GHz |
|||
| $240 |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="13" | 2 (2) |
|||
| rowspan="6" | Pentium |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78946 3561Y] |
|||
| rowspan="13" | HD Graphics |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 11.5 W / 1.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 200 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 850 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="13" | 2 MB |
|||
| {{dts|2013|12}} |
|||
| $161 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76622 3560Y] |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| OEM |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78945 3558U] |
|||
| rowspan="10" {{N/A}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15 W / 1.7 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|12}} |
|||
| $161 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76621 3556U] |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| OEM |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81013 3560M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.4 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $134 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77404 3550M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.3 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| rowspan="7" | Celeron |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78944 2981U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15 W / 1.6 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 200 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="4" | 1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|12}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $137 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/76620 2980U] |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78942 2957U] |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 15 W / 1.4 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|12}} |
|||
| rowspan="2" | $132 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/75608 2955U] |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/81014 2970M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.2 GHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 400 MHz |
|||
| rowspan="2" | 1.1 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2014|04|14}} |
|||
| $75 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/77403 2950M] |
|||
| 37 W / 2.0 GHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|09|01}} |
|||
| $86 |
|||
|- |
|||
| [https://ark.intel.com/products/78943 2961Y] |
|||
| 6 W / 800 MHz |
|||
| 11.5 W / 1.1 GHz |
|||
| 200 MHz |
|||
| 850 MHz |
|||
| {{dts|2013|12}} |
|||
| OEM |
|||
|} |
|||
<ol type="a"> |
|||
<li>{{note label|ctdp-down}} When a cooler or quieter mode of operation is desired, this mode specifies a lower TDP and lower guaranteed frequency versus the nominal mode.<ref name="intel-mh-lines" />{{rp|71–72}} |
|||
<li>{{note label|nominal-tdp}} This is the processor's rated frequency and TDP.<ref name="intel-mh-lines" />{{rp|71–72}} |
|||
<li>{{note label|ctdp-up}} When extra cooling is available, this mode specifies a higher TDP and higher guaranteed frequency versus the nominal mode.<ref name="intel-mh-lines" />{{rp|71–72}} |
|||
</ol> |
|||
SKU suffixes to denote: |
|||
* M{{snd}} mobile processor ([[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]]) |
|||
* Q{{snd}} quad-core |
|||
* U{{snd}} ultra-low power (BGA1168 packaging) |
|||
* X{{snd}} "extreme" |
|||
* Y{{snd}} extreme low-power (BGA1168 packaging) |
|||
* E / H{{snd}} BGA1364 packaging |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 01:11, 16 December 2022
 | |
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Launched | June 4, 2013 |
| CPUID code | 0306C3h |
| Product code |
|
| Cache | |
| L1 cache | 64 KB per core |
| L2 cache | 256 KB per core |
| L3 cache | 2–45 MB (shared) |
| L4 cache | 128 MB of eDRAM (Iris Pro models only) |
| Architecture and classification | |
| Technology node | 22 nm (Tri-Gate) |
| Microarchitecture | Haswell |
| Instructions | x86, x86-64 |
| Extensions | |
| Physical specifications | |
| Cores |
|
| GPUs |
|
| Sockets |
|
| Products, models, variants | |
| Model |
|
| Brand name |
|
| History | |
| Predecessors | Sandy Bridge (Tock) Ivy Bridge (Tick) |
| Successors | Broadwell (Tick/Process) Skylake (Tock) |
Haswell is the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/tick of the Sandy Bridge microarchitecture).[1] Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013,[2] while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum.[3] With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process,[4] Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix.
Haswell CPUs are used in conjunction with the Intel 8 Series chipsets, Intel 9 Series chipsets, and Intel C220 series chipsets.
At least one Haswell-based processor is still being sold as of 2022, the Pentium G3420.[5][6]
Design
The Haswell architecture is specifically designed[7] to optimize the power savings and performance benefits from the move to FinFET (non-planar, "3D") transistors on the improved 22 nm process node.[8]
Haswell has been launched in three major forms:[9]
- Desktop version (LGA 1150 socket and the LGA 2011-v3 socket): Haswell-DT
- Mobile/Laptop version (PGA socket): Haswell-MB
- BGA version:
- 47 W and 57 W TDP classes: Haswell-H (for "All-in-one" systems, Mini-ITX form factor motherboards, and other small footprint formats)
- 13.5 W and 15 W TDP classes (MCP): Haswell-ULT (for Intel's UltraBook platform)
- 10 W TDP class (SoC): Haswell-ULX (for tablets and certain UltraBook-class implementations)
Notes
- ULT = Ultra Low TDP; ULX = Ultra Low eXtreme TDP
- Only certain quad-core variants and BGA R-series stock keeping units (SKUs) receive GT3e (Intel Iris Pro 5200) integrated graphics. All other models have GT3 (Intel HD 5000 or Intel Iris 5100), GT2 (Intel HD 4200, 4400, 4600, P4600 or P4700) or GT1 (Intel HD Graphics) integrated graphics.[10] See also Intel HD and Iris Graphics for more details.
- Due to the low power requirements of tablet and UltraBook platforms, Haswell-ULT and Haswell-ULX are only available in dual-core configurations. All other versions come as dual- or quad-core variants.
Performance
Compared to Ivy Bridge:
- Approximately 8% faster vector processing[11]
- Up to 5% higher single-threaded performance
- 6% higher multi-threaded performance
- Desktop variants of Haswell draw between 8% and 23% more power under load than Ivy Bridge.[11][12][13]
- A 6% increase in sequential CPU performance (eight execution ports per core versus six)[11]
- Up to 20% performance increase over the integrated HD4000 GPU (Haswell HD4600 vs Ivy Bridge's built-in Intel HD4000)[11]
- Total performance improvement on average is about 3%[11]
- Around 15 °C hotter than Ivy Bridge, while clock frequencies of over 4.6 GHz are achievable[14][15][16][17][18][19]
Technology
Features carried over from Ivy Bridge
- 22 nm manufacturing process[4]
- 3D Tri-Gate FinFET transistors[20]
- Micro-operation cache (Uop Cache) capable of storing 1.5 K micro-operations (approximately 6 KB in size)[21]
- 14- to 19-stage instruction pipeline, depending on the micro-operation cache hit or miss (an approach used in the even earlier Sandy Bridge microarchitecture)[21]
- Improve OoO window from 168 to 192[22]
- Queue Allocation from 28/threads to 56
- Mainstream variants are up to quad-core.[23]
- Native support for dual-channel DDR3/DDR3L memory,[24] with up to 32 GB of RAM on LGA 1150 variants
- 64 KB (32 KB Instruction + 32 KB Data) L1 cache and 256 KB L2 cache per core[25]
- A total of 16 PCI Express 3.0 lanes on LGA 1150 variants[26]
New features
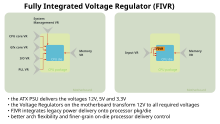
CPU
- Wider core:[27] fourth arithmetic logic unit (ALU), third address generation unit (AGU),[28][29][30] second branch execution unit (BEU), deeper buffers, higher cache bandwidth, improved front-end and memory controller, higher load/store bandwidth.
- New instructions[31] (HNI, includes Advanced Vector Extensions 2 (AVX2), gather, BMI1, BMI2, ABM and FMA3 support).[32]
- The instruction decode queue, which holds instructions after they have been decoded, is no longer statically partitioned between the two threads that each core can service.[21]
- Intel Transactional Synchronization Extensions (TSX) for the Haswell-EX variant. In August 2014 Intel announced that a bug exists in the TSX implementation on the current steppings of Haswell, Haswell-E, Haswell-EP and early Broadwell CPUs, which resulted in disabling the TSX feature on affected CPUs via a microcode update.[33][34][35][36]
- Fully integrated voltage regulator (FIVR), thereby moving some of the components from motherboard onto the CPU.[37][38][39]
- New advanced power-saving system; due to Haswell's new low-power C6 and C7 sleep states, not all power supply units (PSUs) are suitable for computers with Haswell CPUs.[40][41]
- 37, 47, 57 W thermal design power (TDP) mobile processors.[23]
- 35, 45, 65, 84, 88, 95 and 130–140 W (high-end, Haswell-E) TDP desktop processors.[23]
- 15 W or 11.5W TDP processors for the Ultrabook platform (multi-chip package like Westmere)[42] leading to reduced heat, which results in thinner as well as lighter Ultrabooks, but the performance level is slightly lower than the 17 W version.[43]
Translation lookaside buffer sizes[44][45] Cache Page size Name Level 4 KB 2 MB 1 GB DTLB 1st 64 32 4 ITLB 1st 128 8 / logical core none STLB 2nd 1024 none
GPU
- Hardware graphics support for Direct3D 11.1 and OpenGL 4.3.[46][47][48] Intel 10.18.14.5180 driver is the last planned driver release on Windows 7/8.1.[49]
- Four versions of the integrated GPU: GT1, GT2, GT3 and GT3e, where GT3 version has 40 execution units (EUs). Haswell's predecessor, Ivy Bridge, has a maximum of 16 EUs. GT3e version with 40 EUs and on-package 128 MB of embedded DRAM (eDRAM), called Crystalwell, is available only in mobile H-SKUs and desktop (BGA-only) R-SKUs. Effectively, this eDRAM is a Level 4 cache; it is shared dynamically between the on-die GPU and CPU, and serving as a victim cache to the CPU's Level 3 cache.[50][51][52][53][54]
I/O
- New sockets and chipsets:
- DDR4 for enterprise/server segments[58] and for the Enthusiast-Class Desktop Platform Haswell-E[59]
- Variable Base clock (BClk)[60] like LGA 2011.[61]
- Optional support for Thunderbolt technology and Thunderbolt 2.0[62][63]
- Shrink of the Platform Controller Hub (PCH), from 65 nm to 32 nm.[64]
Server processors features
- Haswell-EP variant, released in September 2014, with up to 18 cores and marketed as the Xeon E5-1600 v3 and Xeon E5-2600 v3 series.[65]
- Haswell-EX variant, released in May 2015, with 18 cores and functioning TSX.[35][66][67]
- A new cache design.
- Up to 35 MB total unified cache (last level cache, LLC) for Haswell-EP[68] and up to 40 MB for Haswell-EX.
- LGA 2011-v3 socket replaces LGA 2011 for the Haswell EP; the new socket has the same number of pins, but it is keyed differently due to electrical incompatibility.[69][70][71]
- The already launched Xeon E3 v3 Haswells will get a refresh in spring 2014,[72] together with a refreshed Intel C220 series PCH chipset.[73]
- TDP up to 160 W for Haswell-EP.[74]
- Haswell-EP models with ten and more cores support cluster on die (COD) operation mode,[75] allowing CPU's multiple columns of cores and last level cache (LLC) slices to be logically divided into what is presented as two non-uniform memory access (NUMA) CPUs to the operating system. By keeping data and instructions local to the "partition" of CPU which is processing them, therefore decreasing the LLC access latency, COD brings performance improvements to NUMA-aware operating systems and applications.[76]
Haswell Refresh
Around the middle of 2014, Intel released a refresh of Haswell, simply titled Haswell Refresh. When compared to the original Haswell CPUs lineup, Haswell Refresh CPUs offer a modest increase in clock frequencies, usually of 100 MHz.[77] Haswell Refresh CPUs are supported by Intel's 9 Series chipsets (Z97 and H97, codenamed Wildcat Point), while motherboards with 8 Series chipsets (codenamed Lynx Point) usually require a BIOS update to support Haswell Refresh CPUs.[78]
The CPUs codenamed Devil's Canyon, covering the i5 and i7 K-series SKUs, employ a new and improved thermal interface material (TIM) called next-generation polymer thermal interface material (NGPTIM). This improved TIM reduces the CPU's operating temperatures and improves the overclocking potential, as something that had been problematic since the introduction of Ivy Bridge.[79] Other changes for the Devil's Canyon CPUs include a TDP increase to 88 W, additional decoupling capacitors to help smooth out the outputs from the fully integrated voltage regulator (FIVR), and support for the VT-d that was previously limited to non-K-series SKUs.[80] TSX was another feature brought over from the non-K-series SKUs, until August 2014 when a microcode update disabled TSX due to a bug that was discovered in its implementation.[35][36]
Windows XP and Vista support
While Ivy Bridge is the last Intel processor to fully support all versions of Windows XP, Haswell includes limited driver support for certain XP editions such as POSReady2009. People have modified the graphics driver for these versions to adapt to normal Windows XP to varying degrees of success.
Windows Vista support is also dropped with this processor as well. People who have installed x64 version of Vista have reported various problems such as services not starting automatically. The KB4493471 update (officially intended only for Windows Server 2008, but can be installed on Vista) contains a HAL driver that fixes most of these issues. Windows XP and earlier and x86 version of Vista is unaffected by this bug.
List of Haswell processors
Desktop processors

- All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, F16C, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit implementation), Intel VT-x, and Smart Cache.
- Core i3, i5 and i7 support AVX, AVX2, BMI1, BMI2, FMA3, and AES-NI.[81]
- Core i3 and i7, as well as the Core i5-4570T and i5-4570TE, support Hyper-Threading (HT).[81]
- Core i5 and i7 support Turbo Boost 2.0.[81]
- Although it was initially supported on selected models, since August 2014 desktop variants no longer support TSX due to a bug that was discovered in its implementation; as a workaround, a microcode update disabled the TSX feature.[33][35][36][81]
- SKUs below 45xx as well as R-series and K-series SKUs do not support Trusted Execution Technology or vPro.[81]
- Intel VT-d, which is Intel's IOMMU, is supported on all i5 and i7 SKUs except the i5-4670K and i7-4770K.[81][82][83] Support for VT-d requires the chipset and motherboard to also support VT-d.
- Models i5-4690K and i7-4790K, codenamed Devil's Canyon, have a better internal thermal grease to help heat escape and an improved internal voltage regulator ("FIVR"), to help deliver cleaner power in situations like overclocking.
- Transistors: 1.4 billion[84][85]
- Die size: 177 mm2[84]
- Intel HD and Iris Graphics in following variants:
- R-series desktop processors feature Intel Iris Pro 5200 graphics (GT3e).[86]
- All other currently known i3, i5 and i7 desktop processors include Intel HD 4600 graphics (GT2).[87]
- The exceptions are processors 41xxx, which include HD 4400 graphics (GT2).
- Celeron and Pentium processors contain Intel HD Graphics (GT1).
- Pentium G3258, also known as the Pentium Anniversary Edition, has an unlocked multiplier. Its release marks 20 years of "Pentium" as a brand.[88]
The following table lists available desktop processors.
| Target segment |
Cores (threads) |
Processor branding and model |
GPU model | CPU clock rate | Graphics clock rate | Cache | TDP | PCIe 3.0 lane configurations[a] |
VT-d[b] | Release date |
Release price (USD) |
Motherboard | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Turbo | Normal | Turbo | L3 | L4[a] | Socket | Interface | Memory | ||||||||||
| Enthusiast / High-End | 8 (16) | Core i7 Extreme |
5960X | — | 3.0 GHz | 3.5 GHz | — | — | 20 MB | — | 140 W | 2×16 + 1×8 | Yes | August 29, 2014[89] | $999 | LGA 2011-v3 | DMI 2.0 PCIe 3.0 |
Up to quad channel DDR4-2133 |
| 6 (12) | 5930K | 3.5 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 15 MB | $583 | |||||||||||||
| 5820K | 3.3 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 1×16 + 1×8 + 1×4 | $389 | ||||||||||||||
| Performance | 4 (8) | Core i7 | 4790K | HD 4600 (GT2) |
4.0 GHz | 4.4 GHz | 350 MHz[90] | 1.25 GHz | 8 MB | 88 W | 1×16 2×8 1×8 + 2×4 |
June 2, 2014 | $339 | LGA 1150 |
Up to dual channel DDR3-1600[91] | |||
| 4790 | 3.6 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 1.2 GHz | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $303 | ||||||||||||
| 4790S | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4790T | 2.7 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 45 W | |||||||||||||||
| 4785T | 2.2 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 35 W | |||||||||||||||
| 4771 | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 84 W | September 1, 2013 | $320 | |||||||||||||
| 4770K | 1.25 GHz | No | June 2, 2013[92] | $339 | ||||||||||||||
| 4770 | 3.4 GHz | 1.2 GHz | Yes | $303 | ||||||||||||||
| 4770S | 3.1 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4770R | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) |
3.2 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.3 GHz | 6 MB | 128 MB | $392 | BGA 1364 | ||||||||||
| 4770T | HD 4600 (GT2) |
2.5 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 350 MHz[90] | 1.2 GHz | 8 MB | — | 45 W | $303 | LGA 1150 | ||||||||
| 4770TE | 2.3 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1 GHz | |||||||||||||||
| 4765T | 2.0 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 1.2 GHz | 35 W | ||||||||||||||
| Mainstream | 4 (4) | Core i5 | 4690K | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 6 MB | 88 W | June 2, 2014 | $242 | |||||||||
| 4690 | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $213 | |||||||||||||||
| 4690S | 3.2 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4690T | 2.5 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 45 W | |||||||||||||||
| 4670K | 3.4 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 84 W | No | June 2, 2013 | $242 | ||||||||||||
| 4670 | Yes | $213 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4670S | 3.1 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4670R | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) |
3.0 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.3 GHz | 4 MB | 128 MB | $310 | BGA 1364 | |||||||||
| 4670T | HD 4600 (GT2) |
2.3 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 350 MHz[90] | 1.2 GHz | 6 MB | — | 45 W | $213 | LGA 1150 | ||||||||
| 4590 | 3.3 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 1.15 GHz | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $192 | ||||||||||||
| 4590S | 3.0 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4590T | 2.0 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 35 W | |||||||||||||||
| 4570 | 3.2 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 84 W | June 2, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
| 4570S | 2.9 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4570R | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) |
2.7 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 200 MHz | 4 MB | 128 MB | $288 | BGA 1364 | ||||||||||
| 2 (4) | 4570T | HD 4600 (GT2) |
2.9 GHz | 3.6 GHz | — | 35 W | $192 | LGA 1150 | ||||||||||
| 4570TE | 2.7 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 350 MHz[90] | 1 GHz | ||||||||||||||
| 4 (4) | 4460 | 3.2 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 1.1 GHz | 6 MB | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $182 | ||||||||||
| 4460S | 2.9 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4460T | 1.9 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 35 W | |||||||||||||||
| 4440 | 3.1 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 84 W | September 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
| 4440S | 2.8 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 4430 | 3.0 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 84 W | June 2, 2013[92] | ||||||||||||||
| 4430S | 2.7 GHz | 65 W | ||||||||||||||||
| 2 (4) | Core i3 | 4370 | 3.8 GHz | — | 1.15 GHz | 4 MB | 54 W | No | July 20, 2014 | $149 | ||||||||
| 4360 | 3.7 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4350 | 3.6 GHz | $138 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4340 | September 1, 2013 | $149 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4330 | 3.5 GHz | $138 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4370T | 3.3 GHz | 200 MHz | 35 W | March 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| 4360T | 3.2 GHz | July 20, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4350T | 3.1 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4330T | 3.0 GHz | September 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4340TE | 2.6 GHz | 350 MHz | 1 GHz | May 11, 2014 | $138 | |||||||||||||
| 4330TE | 2.4 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $122 | |||||||||||||||
| 4170 | HD 4400 (GT2) |
3.7 GHz | 1.15 GHz | 3 MB | 54 W | March 30, 2015 | $117 | |||||||||||
| 4160 | 3.6 GHz | July 20, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4150 | 3.5 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4130 | 3.4 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $122 | |||||||||||||||
| 4170T | 3.2 GHz | 200 MHz | 35 W | March 30, 2015 | $117 | |||||||||||||
| 4160T | 3.1 GHz | July 20, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4150T | 3.0 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4130T | 2.9 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $122 | |||||||||||||||
| Budget | 2 (2) | Pentium | G3470 | HD Graphics | 3.6 GHz | 350 MHz | 1.1 GHz | 53 W | March 30, 2015 | $86 | ||||||||
| G3460 | 3.5 GHz | July 20, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3450 | 3.4 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3440 | 3.3 GHz | $75 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3430 | December 1, 2013 | $86 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3420 | 3.2 GHz | $75 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3460T | 3.0 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | 35 W | March 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||
| G3450T | 2.9 GHz | July 20, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3440T | 2.8 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3420T | 2.7 GHz | December 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3320TE | 2.3 GHz | 350 MHz | 1 GHz | Up to dual channel DDR3-1333 | ||||||||||||||
| G3260 | 3.3 GHz | 1.1 GHz | 53 W | March 30, 2015 | $64 | |||||||||||||
| G3258[c] | 3.2 GHz | June 2, 2014 | $72 | |||||||||||||||
| G3250 | July 20, 2014 | $64 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3240 | 3.1 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3220 | 3.0 GHz | December 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3260T | 2.9 GHz | 200 MHz | 35 W | March 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| G3250T | 2.8 GHz | July 20, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3240T | 2.7 GHz | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| G3220T | 2.6 GHz | December 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Celeron | G1850 | 2.9 GHz | 350 MHz | 1.05 GHz | 2 MB | 53 W | May 11, 2014 | $52 | ||||||||||
| G1840 | 2.8 GHz | $42 | ||||||||||||||||
| G1830 | December 1, 2013 | $52 | ||||||||||||||||
| G1820 | 2.7 GHz | $42 | ||||||||||||||||
| G1840T | 2.5 GHz | 200 MHz | 35 W | May 11, 2014 | ||||||||||||||
| G1820T | 2.4 GHz | December 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| G1820TE | 2.2 GHz | 1 GHz | ||||||||||||||||
- a Some of these configurations could be disabled by the chipset. For example, H-series chipsets disable all PCIe 3.0 lane configurations except 1×16.
- b This feature also requires a chipset that supports VT-d like the Q87 chipset or the X99 chipset.
- c This is called 20th Anniversary Edition and has an unlocked multiplier.
SKU suffixes to denote:
- K – unlocked (adjustable CPU multiplier up to 63x)
- The Pentium G3258 CPU is unlocked despite not having the K-suffix.
- S – performance-optimized lifestyle (low power with 65 W TDP)
- T – power-optimized lifestyle (ultra low power with 35–45 W TDP)
- R – BGA packaging / High-performance GPU (currently Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e))
- X – extreme edition (adjustable CPU ratio with no ratio limit)
Server processors
- All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AVX (Advanced Vector Extensions), AVX2, FMA3, F16C, BMI (Bit Manipulation Instructions 1)+BMI2, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit implementation), TXT, Intel vPro, Intel VT-x, Intel VT-d, hyper-threading (except E3-1220 v3 and E3-1225 v3), Turbo Boost 2.0, AES-NI, and Smart Cache.
- Haswell-EX models (E7-48xx/88xx v3) support TSX, while for Haswell-E, Haswell-WS (E3-12xx v3) and Haswell-EP (E5-16xx/26xx v3) models it was disabled via a microcode update in August 2014, due to a bug that was discovered in the TSX implementation.[35][36]
- Transistors: 5.56 billion[93]
- Die size: 661 mm2[93]
The first digit of the model number designates the largest supported multi-socket configuration; thus, E5-26xx v3 models support up to dual-socket configurations, while the E7-48xx v3 and E7-88xx v3 models support up to quad- and eight-socket configurations, respectively. Also, E5-16xx/26xx v3 and E7-48xx/88xx v3 models have no integrated GPU.
Lists of launched server processors are below, split between Haswell E3-12xx v3, E5-16xx/26xx v3 and E7-48xx/88xx v3 models.
| Target segment |
Cores (threads) |
Processor branding and model |
CPU clock rate | L3 cache |
TDP | Release date |
Release price (USD) |
Motherboard | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Turbo | Socket | Interface | Memory | ||||||||
| Server | 4 (8) | Xeon E7 v3 | E7-8893v3 | 3.2 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 45 MB | 140 W | May 2015 | $6,841 | LGA 2011-1 |
QPI (up to 9.6 GT/s[b]) DMI 2.0 PCIe 3.0 |
Up to DDR4-1866 or DDR3-1600 |
| 10 (20) | E7-8891v3 | 2.8 GHz | 165 W | |||||||||
| 18 (36) | E7-8890v3 | 2.5 GHz | 3.3 GHz | $7,174 | ||||||||
| E7-8880v3 | 2.3 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 150 W | $5,895 | ||||||||
| E7-8880Lv3 | 2.0 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 115 W | $6,063 | ||||||||
| E7-8870v3 | 2.1 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 140 W | $4,672 | ||||||||
| 16 (32) | E7-8867v3 | 2.5 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 165 W | ||||||||
| E7-8860v3 | 2.2 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 40 MB | $4,061 | ||||||||
| 14 (28) | E7-4850v3 | 2.8 GHz | 35 MB | 115 W | $3,003 | |||||||
| 12 (24) | E7-4830v3 | 2.1 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 30 MB | $2,170 | |||||||
| 10 (20) | E7-4820v3 | 1.9 GHz | — | 25 MB | $1,502 | |||||||
| 8 (16) | E7-4809v3 | 2.0 GHz | ||||||||||
| Target segment |
Cores (threads) |
Processor branding and model |
CPU clock rate | CPU AVX clock rate[96] |
L3 cache |
TDP | Release date |
Release price (USD) tray / box |
Motherboard | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Turbo | Normal | Turbo | Socket | Interface | Memory | ||||||||
| Server | 18 (36) | Xeon E5 v3 | 2699v3 | 2.3 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 45 MB | 145 W | September 9, 2014 | — | LGA 2011-3 |
QPI (up to 9.6 GT/s[b]) DMI 2.0 PCIe 3.0 |
up to DDR4-2133 |
| 16 (32) | 2698v3 | 40 MB | 135 W | |||||||||||
| 2698Av3[97] | 2.8 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 2.3 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 165 W | November 2014 | OEM | |||||||
| 14 (28) | 2697v3 | 2.6 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 35 MB | 145 W | September 9, 2014 | $2,702 / $2,706 | |||||
| 2695v3 | 2.3 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 120 W | $2,424 / $2,428 | ||||||||
| 12 (24) | 2690v3 | 2.6 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 2.3 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 30 MB | 135 W | $2,090 / $2,094 | ||||||
| 14 (28) | 2683v3 | 2.0 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 1.7 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 35 MB | 120 W | $1,846 / — | ||||||
| 12 (24) | 2680v3 | 2.5 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 2.1 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 30 MB | $1,745 / $1,749 | |||||||
| 2673v3[c] | 2.4 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 105 W | |||||||||||
| 2670v3 | 2.3 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 120 W | $1,589 / $1,593 | ||||||||
| 8 (16) | 2667v3 | 3.2 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 20 MB | 135 W | $2,057 / — | ||||||
| 10 (20) | 2660v3 | 2.6 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 25 MB | 105 W | $1,445 / $1,449 | ||||||
| 12 (24) | 2650Lv3 | 1.8 GHz | 2.5 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.3 GHz | 30 MB | 65 W | $1,329 / — | ||||||
| 2658v3 | 2.2 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 105 W | $1,832 / — | ||||||||
| 10 (20) | 2650v3 | 2.3 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 25 MB | $1,166 / $1,171 | |||||||
| 12 (24) | 2648Lv3 | 1.8 GHz | 2.5 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 30 MB | 75 W | $1,544 / — | ||||||
| 6 (12) | 2643v3 | 3.4 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 20 MB | 135 W | $1,552 / — | ||||||
| 8 (16) | 2640v3 | 2.6 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 20 MB | 90 W | $939 / $944 | up to DDR4-1866 | |||||
| 4 (8) | 2637v3 | 3.5 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 15 MB | 135 W | $996 / — | up to DDR4-2133 | |||||
| 8 (16) | 2630v3 | 2.4 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 2.1 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 20 MB | 85 W | $667 / $671 | up to DDR4-1866 | |||||
| 2630Lv3 | 1.8 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 55 W | $612 / — | ||||||||
| 10 (20) | 2628Lv3 | 2.0 GHz | 2.5 GHz | 1.7 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 25 MB | 75 W | $1,364 / — | ||||||
| 4 (8) | 2623v3 | 3.0 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 10 MB | 105 W | $444 / — | ||||||
| 6 (12) | 2620v3 | 2.4 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 2.1 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 15 MB | 85 W | $417 / $422 | ||||||
| 8 (16) | 2618Lv3 | 2.3 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 20 MB | 75 W | $779 / — | ||||||
| 6 (6) | 2609v3 | 1.9 GHz | — | 1.9 GHz | — | 15 MB | 85 W | $306 / $306 | up to DDR4-1600 | |||||
| 6 (12) | 2608Lv3 | 2.0 GHz | 1.7 GHz | 52 W | $441 / — | up to DDR4-1866 | ||||||||
| 6 (6) | 2603v3 | 1.6 GHz | 1.3 GHz | 85 W | $213 / $217 | up to DDR4-1600 | ||||||||
| Workstation | 10 (20) | 2687Wv3 | 3.1 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 25 MB | 160 W | $2,141 / $2,145 | up to DDR4-2133 | ||||
| 8 (16) | 1680v3 | 3.2 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 20 MB | 140 W | $1,723 / — | DMI 2.0 PCIe 3.0 | |||||
| 1660v3 | 3.0 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 3.5 GHz | $1,080 / — | |||||||||
| 6 (12) | 1650v3 | 3.5 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 15 MB | $583 / $586 | |||||||
| 4 (8) | 1630v3 | 3.7 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 10 MB | $372 / — | |||||||
| 1620v3 | 3.5 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 3.5 GHz | $294 / $297 | |||||||||
| 4 (4) | 1607v3 | 3.1 GHz | — | 2.8 GHz | — | $255 / — | up to DDR4-1866 | |||||||
| 4 (4) | 1603v3 | 2.8 GHz | 2.5 GHz | $202 / — | ||||||||||
| Target segment |
Cores (threads) |
Processor branding and model |
GPU model | CPU clock rate | Graphics clock rate | L3 cache |
GPU eDRAM |
TDP | Release date |
Release price (USD) tray / box |
Motherboard | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Turbo | Normal | Turbo | Socket | Interface | Memory | ||||||||||
| Server | 4 (8) | Xeon E3 v3 | 1286v3 | HD P4700 (GT2) | 3.7 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 350 MHz | 1.3 GHz | 8 MB | — | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $662 / — | LGA 1150 |
DMI 2.0 PCIe 3.0 |
up to dual channel DDR3-1600 with ECC |
| 1286Lv3 | 3.2 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 1.25 GHz | 65 W | $774 / — | |||||||||||
| 1285v3 | 3.6 GHz | 1.3 GHz | 84 W | June 2, 2013 | $662 / — | |||||||||||
| 1285Lv3 | 3.1 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 1.25 GHz | 65 W | $774 / — | |||||||||||
| 1284Lv3 | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) | 1.8 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 750 MHz | 1 GHz | 6 MB | 128 MB | 47 W | February 18, 2014 | OEM | BGA 1364 | |||||
| 1281v3 | — | 3.7 GHz | 4.1 GHz | — | 8 MB | — | 82 W | May 11, 2014 | $612 / — | LGA 1150 | ||||||
| 1280v3 | 3.6 GHz | 4.0 GHz | June 2, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 1276v3 | HD P4600 (GT2) | 350 MHz | 1.25 GHz | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $339 / $350 | ||||||||||
| 1275v3 | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | June 2, 2013 | $339 / $350 | ||||||||||||
| 1275Lv3 | HD (GT1) | 2.7 GHz | 1.2 GHz | 45 W | May 11, 2014 | $328 / — | ||||||||||
| 1271v3 | — | 3.6 GHz | 4.0 GHz | — | 80 W | $328 / $339 | ||||||||||
| 1270v3 | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | June 2, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 1268Lv3 | HD P4600 (GT2) | 2.3 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 350 MHz | 1 GHz | 45 W | $310 / — | |||||||||
| 1265Lv3 | HD (GT1) | 2.5 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 1.2 GHz | $294 / — | |||||||||||
| 1246v3 | HD P4600 (GT2) | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $276 / $287 | ||||||||||
| 1245v3 | 3.4 GHz | 3.8 GHz | June 2, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 1241v3 | — | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | — | 80 W | May 11, 2014 | $262 / $273 | |||||||||
| 1240v3 | 3.4 GHz | 3.8 GHz | June 2, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 1240Lv3 | 2.0 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 25 W | May 11, 2014 | $278 / — | |||||||||||
| 1231v3 | 3.4 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 80 W | $240 / $250 | ||||||||||||
| 1230v3 | 3.3 GHz | 3.7 GHz | June 2, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 1230Lv3 | 1.8 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 25 W | $250 / — | ||||||||||||
| 4 (4) | 1226v3 | HD P4600 (GT2) | 3.3 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 350 MHz | 1.2 GHz | 84 W | May 11, 2014 | $213 / $224 | |||||||
| 1225v3 | 3.2 GHz | 3.6 GHz | June 2, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 1220v3 | — | 3.1 GHz | 3.5 GHz | — | 80 W | $193 / $203 | ||||||||||
| 2 (4) | 1220Lv3 | 1.1 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 4 MB | 13 W | September 1, 2013 | $193 / — | |||||||||
SKU suffixes to denote:
- L – low power
Mobile processors
- All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, F16C, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel VT-x, Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit implementation), and Smart Cache.
- Core i3, i5 and i7 support AVX, AVX2, BMI1, BMI2, FMA3, and hyper-threading (HT).
- Core i3, i5 and i7 except the Core i3-4000M support AES-NI.[98]
- Core i5 and i7 except the Core i5-4410E, i5-4402EC, i7-4700EC, and i7-4702EC support Turbo Boost 2.0.
- Platform Controller Hub (PCH) integrated into the CPU package, slightly reducing the amount of space used on motherboards.[99]
- Transistors: 1.3 billion[100]
- Die size: 181 mm2[100]
The following table lists available mobile processors.
| Target segment |
Cores (threads) |
Processor branding and model |
GPU model | Programmable TDP[101]: 69–72 | CPU Turbo (single core) |
Graphics clock rate | L3 cache |
GPU eDRAM |
Release date |
Release price (USD) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDP[102][103]: 71 | cTDP down[a] | Nominal TDP[b] | cTDP up[c] | Normal | Turbo | ||||||||||
| Performance | 4 (8) | Core i7 | 4940MX | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | — | 57 W / 3.1 GHz | 65 W / 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.35 GHz | 8 MB | — | January 21, 2014[104] | $1096 |
| 4930MX | 57 W / 3.0 GHz | 65 W / 3.7 GHz | 3.9 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | |||||||||||
| 4980HQ | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) | 47 W / 2.8 GHz | — | 4.0 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.3 GHz | 6 MB | 128 MB[51] | July 21, 2014[106] | $623 | |||||
| 4960HQ | 47 W / 2.6 GHz | 55 W / 3.6 GHz | 3.8 GHz | September 1, 2013[107] | |||||||||||
| 4950HQ | 47 W / 2.4 GHz | 55 W / 3.4 GHz | 3.6 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | |||||||||||
| 4910MQ | HD 4600 (GT2) | 47 W / 2.9 GHz | 55 W / 3.7 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 400 MHz | 8 MB | — | January 21, 2014[104] | $568 | ||||||
| 4900MQ | 47 W / 2.8 GHz | 55 W / 3.6 GHz | 3.8 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $570 | ||||||||||
| 4870HQ | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) | 47 W / 2.5 GHz | — | 3.7 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.2 GHz | 6 MB | 128 MB | July 21, 2014[106] | $434 | |||||
| 4860EQ | 47 W / 1.8 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 750 MHz | 1 GHz | August 2013 | $508 | |||||||||
| 4860HQ | 47 W / 2.4 GHz | 55 W / 3.4 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.2 GHz | January 21, 2014[104] | $434 | ||||||||
| 4850EQ | 47 W / 1.6 GHz | — | 3.2 GHz | 650 MHz | 1 GHz | August 2013 | $466 | ||||||||
| 4850HQ | 47 W / 2.3 GHz | 55 W / 3.3 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.2 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $434 | ||||||||
| 4810MQ | HD 4600 (GT2) | 47 W / 2.8 GHz | 55 W / 3.6 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.3 GHz | — | January 21, 2014[104] | $378 | ||||||
| 4800MQ | 47 W / 2.7 GHz | 55 W / 3.5 GHz | 3.7 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $380 | ||||||||||
| 4770HQ | Iris Pro 5200 (GT3e) | 47 W / 2.2 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.2 GHz | 128 MB | July 21, 2014[106] | $434 | |||||||
| 4760HQ | 47 W / 2.1 GHz | 55 W / 3.1 GHz | 3.3 GHz | April 14, 2014 | $434 | ||||||||||
| 4750HQ | 47 W / 2.0 GHz | 55 W / 3.0 GHz | 3.2 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $440 | ||||||||||
| 4720HQ | HD 4600 (GT2) | 47 W / 2.6 GHz | — | 3.6 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.2 GHz | — | January 2015 | $378 | ||||||
| 4712MQ | 37 W / 2.3 GHz | 45 W / 3.1 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1.15 GHz | April 14, 2014 | ||||||||||
| 4712HQ | |||||||||||||||
| 4710MQ | 47 W / 2.5 GHz | 55 W / 3.3 GHz | 3.5 GHz | ||||||||||||
| 4710HQ | 1.2 GHz | ||||||||||||||
| 4702MQ | 37 W / 2.2 GHz | 45 W / 2.9 GHz | 3.2 GHz | 1.15 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $383 | |||||||||
| 4702HQ | |||||||||||||||
| 4700MQ | 47 W / 2.4 GHz | 55 W / 3.2 GHz | 3.4 GHz | ||||||||||||
| 4700HQ | 1.2 GHz | ||||||||||||||
| 4701EQ | 1 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $415 | ||||||||||||
| 4700EQ | June 2, 2013[105] | $378 | |||||||||||||
| 4702EC | — | 27 W / 2.0 GHz | — | — | — | — | 8 MB | April 2014 | $459 | ||||||
| 4700EC | 43 W / 2.7 GHz | — | |||||||||||||
| Mainstream | 2 (4) | 4650U | HD 5000 (GT3) | — | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.7 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | 4 MB | June 2, 2013[105] | $454 | |||
| 4610Y | HD 4200 (GT2) | 6 W / 800 MHz | 9.5 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.7 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 850 MHz | September 1, 2013 | $393 | |||||||
| 4610M | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | — | 37 W / 3.0 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.3 GHz | January 21, 2014[104] | $346 | ||||||
| 4600M | 37 W / 2.9 GHz | 3.6 GHz | September 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||
| 4600U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 2.1 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | $398 | ||||||||
| 4578U | Iris 5100 (GT3) | 23 W / 800 MHz | 28 W / 3.0 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 1.2 GHz | July 20, 2014 | — | ||||||||
| 4558U | 28 W / 2.8 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1.2 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $454 | ||||||||||
| 4550U | HD 5000 (GT3) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.5 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 1.1 GHz | ||||||||||
| 4510U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 15 W / 2.0 GHz | 3.1 GHz | April 2014 | $393 | ||||||||||
| 4500U | 15 W / 1.8 GHz | 25 W / 3.0 GHz | 3.0 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $398 | ||||||||||
| Core i5 | 4402EC | — | — | 27 W / 2.5 GHz | — | — | — | — | April 2014 | $324 | |||||
| 4422E | HD 4600 (GT2) | 25 W / 1.8 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 400 MHz | 900 MHz | 3 MB | April 14, 2014 | $266 | |||||||
| 4410E | 37 W / 2.9 GHz | — | 1 GHz | ||||||||||||
| 4402E | 25 W / 1.6 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 900 MHz | September 1, 2013 | |||||||||||
| 4400E | 37 W / 2.7 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1 GHz | ||||||||||||
| 4360U | HD 5000 (GT3) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.5 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | January 21, 2014[104] | $315 | |||||||
| 4350U | 15 W / 1.4 GHz | 2.9 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $342 | |||||||||||
| 4340M | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | 37 W / 2.9 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.25 GHz | January 21, 2014[104] | $266 | |||||||
| 4330M | 37 W / 2.8 GHz | 3.5 GHz | September 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||
| 4310M | HD 4600 (GT2) | 37 W / 2.7 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.25 GHz | January 21, 2014[104] | $225 | ||||||||
| 4310U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 2.0 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | $281 | ||||||||
| 4302Y | HD 4200 (GT2) | 4.5 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz | 2.3 GHz | 200 MHz | 850 MHz | September 1, 2013 | — | |||||||
| 4300Y | 6 W / 800 MHz | 9.5 W / 800 MHz | $304 | ||||||||||||
| 4300M | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | — | 37 W / 2.6 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.25 GHz | $225 | |||||||
| 4300U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.9 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | $287 | ||||||||
| 4288U | Iris 5100 (GT3) | 23 W / 800 MHz | 28 W / 2.6 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 1.2 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $342 | ||||||||
| 4258U | 28 W / 2.4 GHz | 2.9 GHz | 1.1 GHz | ||||||||||||
| 4308U | 28 W / 2.8 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 1.2 GHz | July 20, 2014[108] | $315 | ||||||||||
| 4260U | HD 5000 (GT3) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.4 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 1 GHz | April 14, 2014 | $315 | ||||||||
| 4250U | 15 W / 1.3 GHz | 2.6 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $342 | |||||||||||
| 4210H | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | 47 W / 2.9 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.15 GHz | July 20, 2014 | $225 | |||||||
| 4210M | 37 W / 2.6 GHz | 3.2 GHz | April 14, 2014 | ||||||||||||
| 4210U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.7 GHz | 2.7 GHz | 200 MHz | 1 GHz | $287 | ||||||||
| 4220Y | HD 4200 (GT2) | 6 W / 800 MHz | 9.5 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 850 MHz | $281 | ||||||||
| 4210Y | 11.5 W / 1.5 GHz | 1.9 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $304 | |||||||||||
| 4202Y | 4.5 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz | 2.0 GHz | — | |||||||||||
| 4200Y | 6 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.4 GHz | 1.9 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $304 | ||||||||||
| 4200U | HD 4400 (GT2) | — | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.6 GHz | 25 W / ? | 2.6 GHz | 1 GHz | $287 | |||||||
| 4200H | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | 47 W / 2.8 GHz | — | 3.4 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.15 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $257 | ||||||
| 4200M | 37 W / 2.5 GHz | 3.1 GHz | $240 | ||||||||||||
| Core i3 | 4158U | Iris 5100 (GT3) | 23 W / 800 MHz | 28 W / 2.0 GHz | — | 200 MHz | 1.1 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $342 | ||||||
| 4120U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 2.0 GHz | 1 GHz | April 14, 2014 | $281 | |||||||||
| 4112E | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | 25 W / 1.8 GHz | 400 MHz | 900 MHz | $225 | |||||||||
| 4110E | 37 W / 2.6 GHz | ||||||||||||||
| 4102E | 25 W / 1.6 GHz | September 1, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 4100E | 37 W / 2.4 GHz | ||||||||||||||
| 4110M | 37 W / 2.6 GHz | 1.1 GHz | April 14, 2014 | ||||||||||||
| 4100M | 37 W / 2.5 GHz | September 1, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| 4100U | HD 4400 (GT2) | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.8 GHz | 200 MHz | 1 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | $287 | ||||||||
| 4030Y | HD 4200 (GT2) | 6 W / 800 MHz | 9.5 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.6 GHz | 850 MHz | April 14, 2014 | $281 | ||||||||
| 4020Y | 11.5 W / 1.5 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $304 | ||||||||||||
| 4012Y | 4.5 W / 800 MHz | — | |||||||||||||
| 4010Y | 6 W / 800 MHz | 9.5 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.3 GHz | June 2, 2013[105] | |||||||||||
| 4030U | HD 4400 (GT2) | — | 11.5 W / 800 MHz | 15 W / 1.9 GHz | 1 GHz | April 14, 2014 | $281 | ||||||||
| 4025U | 950 MHz | $275 | |||||||||||||
| 4010U | 15 W / 1.7 GHz | 1 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $287 | |||||||||||
| 4005U | 950 MHz | $281 | |||||||||||||
| 4000M | HD 4600 (GT2) | — | 37 W / 2.4 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.1 GHz | $240 | |||||||||
| 2 (2) | Pentium | 3561Y | HD Graphics | 6 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.2 GHz | 200 MHz | 850 MHz | 2 MB | December 2013 | $161 | |||||
| 3560Y | September 1, 2013 | OEM | |||||||||||||
| 3558U | — | 15 W / 1.7 GHz | 1 GHz | December 2013 | $161 | ||||||||||
| 3556U | September 1, 2013 | OEM | |||||||||||||
| 3560M | 37 W / 2.4 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.1 GHz | April 14, 2014 | $134 | ||||||||||
| 3550M | 37 W / 2.3 GHz | September 1, 2013 | |||||||||||||
| Celeron | 2981U | 15 W / 1.6 GHz | 200 MHz | 1 GHz | December 2013 | $137 | |||||||||
| 2980U | September 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
| 2957U | 15 W / 1.4 GHz | December 2013 | $132 | ||||||||||||
| 2955U | September 1, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
| 2970M | 37 W / 2.2 GHz | 400 MHz | 1.1 GHz | April 14, 2014 | $75 | ||||||||||
| 2950M | 37 W / 2.0 GHz | September 1, 2013 | $86 | ||||||||||||
| 2961Y | 6 W / 800 MHz | 11.5 W / 1.1 GHz | 200 MHz | 850 MHz | December 2013 | OEM | |||||||||
- When a cooler or quieter mode of operation is desired, this mode specifies a lower TDP and lower guaranteed frequency versus the nominal mode.[101]: 71–72
- This is the processor's rated frequency and TDP.[101]: 71–72
- When extra cooling is available, this mode specifies a higher TDP and higher guaranteed frequency versus the nominal mode.[101]: 71–72
SKU suffixes to denote:
- M – mobile processor (Socket G3)
- Q – quad-core
- U – ultra-low power (BGA1168 packaging)
- X – "extreme"
- Y – extreme low-power (BGA1168 packaging)
- E / H – BGA1364 packaging
See also
Notes
References
- ^ "Intel Developer Forum". Intel.com. Intel. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ Moorhead, Patrick (4 June 2013). "Intel's Newest Core Processors: All About Graphics And Low Power". Forbes.
- ^ Crothers, Brooke (2011-09-14). "Haswell chip completes Ultrabook 'revolution'". News.cnet.com. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ a b "IDF 2008 Shanghai : Compte-rendu Processeur : de Nehalem à Haswell". x86 Secret. Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ "Haswell is back: Intel reverses decision to discontinue 22nm Pentium CPUs". TechSpot. Retrieved 2021-04-12.
- ^ Shilov, Anton. "Intel Un-Discontinues Pentium G3420 'Haswell' CPU". www.anandtech.com. Retrieved 2021-04-12.
- ^ Shrout, Ryan (11 September 2012). "IDF 2012: Intel Haswell Architecture Revealed". PC Perspective.
- ^ "IDF: Intel says Haswell won't use Ivy Bridge transistors". The Inquirer. 2012-09-17. Archived from the original on September 20, 2012. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "Intel Haswell and Broadwell Silicon Variants Detailed". techPowerUp. 2012-12-26. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ Anand Lal Shimpi (2013-05-01). "Intel Iris & Iris Pro Graphics: Haswell GT3/GT3e Gets a Brand". AnandTech. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ^ a b c d e Shvets, Gennadiy (9 July 2013). "Intel Core i5-3570K vs i5-4670K". Retrieved 23 July 2013.
- ^ "Intel Core i7-4770K CPU Review. Intel Haswell for Desktops: Ruin of Our Hopes?. Page 11". X-bit labs. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Google Translate". Translate.Google.com. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- ^ "Intel Haswell hotter and slower than expected". PC Pro. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Haswell heat surprises system builders". bit-tech. Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "Retail Versions of Intel Core i "Haswell" Are "Hotter and Slower" Than Expected – Report". Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "Intel Core i7-4770K CPU Review. Intel Haswell for Desktops: Ruin of Our Hopes?. Page 12". Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ Koen Crijns (2013-10-21). "Workshop: How to overclock Haswell processors — In practice". Us.hardware.info. Retrieved 2014-04-02.
- ^ "Overclocking Haswell on ASUS' 8-Series Motherboards [video]". AnandTech. 2013-06-12. Retrieved 2014-04-02.
- ^ "Haswell: 4th Gen Intel HD Graphics - All's Well for the new IGP?". Hardware Zone. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- ^ a b c Anand Lal Shimpi (2012-10-05). "Intel's Haswell Architecture Analyzed". AnandTech. Retrieved 2013-10-20.
- ^ "Haswell - Microarchitectures - Intel - WikiChip". en.wikichip.org. Retrieved 2021-01-19.
- ^ a b c "Intel 2013 Haswell CPUs Get Detailed in Series of Leaked Slides". Softpedia. 9 November 2011. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ "Haswell". Intel. Archived from the original (slide) on 2012-09-15. Retrieved 2012-02-15.
- ^ "Intel Haswell Architecture Disclosure: Live Blog" (blog).
01:58PM – Same sizes L1/L2 caches as SNB/IVB
- ^ Edwards, Nathan. "Theoretical vs. Actual Bandwidth: PCI Express and Thunderbolt". Tested. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- ^ "Intel's Haswell Architecture Analyzed: Building a New PC and a New Intel".
- ^ Kanter, David (2012-11-13). "Intel's Haswell CPU Microarchitecture". Real World Technologies. Retrieved 2017-04-07.
- ^ Jain, Tarush; Agrawal, Tanmay (2013). "The Haswell Microarchitecture - 4th Generation Processor" (PDF). International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies. 4 (3): 477–480. ISSN 0975-9646.
- ^ Per Hammarlund (August 2013). "Fourth-Generation Intel Core Processor, codenamed Haswell" (PDF). hotchips.org. p. 25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-07-05. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ^ "Haswell New Instruction Descriptions Now Available! | Intel Developer Zone". Software.intel.com. 2011-06-13. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Haswell new instruction descriptions now available". Intel. 2011-06-13. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ a b Ian Cutress (2014-08-12). "Intel Disables TSX Instructions: Erratum Found in Haswell, Haswell-E/EP, Broadwell-Y". AnandTech. Retrieved 2014-08-30.
- ^ "Transactional Synchronization in Haswell". Intel. 2012-02-07. Retrieved 2012-02-07.
- ^ a b c d e Wasson, Scott (2014-08-12). "Errata prompts Intel to disable TSX in Haswell, early Broadwell CPUs". The Tech Report. Retrieved 2014-08-12.
- ^ a b c d "Desktop 4th Generation Intel Core Processor Family, Desktop Intel Pentium Processor Family, and Desktop Intel Celeron Processor Family: Specification Update (Revision 014)" (PDF). Intel. June 2014. p. 46. Retrieved 2014-08-13.
Under a complex set of internal timing conditions and system events, software using the Intel TSX (Transactional Synchronization Extensions) instructions may observe unpredictable system behavior.
- ^ "Intel Haswell". File connect. Archived from the original (JPEG) on 2012-04-25.
- ^ "The Haswell Review: Intel Core i7-4770K & i5-4670K Tested". AnandTech. 2013-06-01. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ "Intel's Haswell Takes A Major Step Forward, Integrates Voltage Regulator". hothardware.com. 2013-05-13. Archived from the original on 2013-10-20. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
- ^ "Few PSUs support Haswell's C6/C7 low-power states". The Tech Report. 2013-04-30. Retrieved 2014-04-02.
- ^ "The big Haswell PSU compatibility list". The Tech Report. 2013-06-04. Retrieved 2014-04-02.
- ^ Sean Hollister (2012-09-05). "Intel's power-efficient Haswell processor targets thinner laptops with new 10-watt TDP". The Verge. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ Intel's power-efficient Haswell processor targets thinner laptops with new 10-watt TDP, 5 September 2012
- ^ "Intel's Haswell CPU Microarchitecture". Realworldtech.com. 2012-11-13. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ Myslewski, Rik (2012-09-20). "Deep, deep dive inside Intel's next-generation processor". The Register. Archived from the original on 2015-01-23. Retrieved 2017-04-07.
- ^ "The Compute Architecture of Intel Processor Graphics Gen7.5". Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "Intel Haswell Architecture Slides – IDF 2012". AnandTech. 2012-09-11.
- ^ "Release Notes Driver version: 15.40.48.5171" (PDF). 2021-02-05. Retrieved 2021-02-05.
- ^ "Download Intel® Graphics Driver for Windows 7*/8.1* [15.36]". Intel Drivers & Support. 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2021-04-14.
This is the last of version 15.36 driver to support 4th generation on Windows 7* and Windows 8.1*. No further drivers are to be expected for this generation on these operating systems.
- ^ "Haswell GT3e Pictured, Coming to Desktops (R-SKU) & Notebooks". AnandTech. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- ^ a b "Intel Iris Pro 5200 Graphics Review: Core i7-4950HQ Tested". AnandTech. 2013-06-01. Retrieved 2013-09-16.
- ^ "Products (Formerly Crystal Well)". Intel. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- ^ "The Intel Ivy Bridge (Core i7 3770K) Review". AnandTech. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Intel's Haswell Architecture Analyzed: Building a New PC and a New Intel". AnandTech. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Mainstream desktop CPUs future evolution — more performance or just more integration? by". VR Zone. 2011-11-06. Archived from the original on 2012-01-12. Retrieved 2012-01-04.
- ^ Nathan Kirsch (2013-06-13). "Intel Desktop Processor and Chipset Roadmap Leaked For 2013 and 2014". legitreviews.com. Retrieved 2013-11-20.
- ^ Kirsch, Nathan (2013-06-15). "Intel Haswell-E Halo Platform Will Have 8-Cores, DDR4, X99 Chipset and More". Legit Reviews. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Haswell" (slide). Intel. Retrieved 2012-02-15.
- ^ "Intel roadmap shows Haswell-E, Haswell Refresh and Skylake". Guru3d.com. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Intel to Officially Enable Better Overclocking in Haswell". News.softpedia.com. 2012-09-20. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ Intel Haswell Processors to Further Improve Overclocking (2012-09-20). "Intel Haswell Processors to Further Improve Overclocking". Xbitlabs.com. Archived from the original on 2013-10-14. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Intel's Thunderbolt 2: Everything You Need to Know". AnandTech. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- ^ "Intel Roadmap Slides Leak Haswell Z87 Chipset Motherboards". Wccftech.com. 2013-06-02. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- ^ "Intel migrates to desktop Multi-Chip Modules (MCMs) with 14nm Broadwell". Fudzilla.com. 2012-04-15. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ Johan De Gelas (2014-09-08). "Intel Xeon E5 Version 3: Up to 18 Haswell EP Cores". AnandTech. Retrieved 2014-09-09.
- ^ Shilov, Anton. "Intel to release 18-core Xeon E7 v3 'Haswell-EX' processors in Q2 2015". kitguru. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ Mujtaba, Hassan (2015-05-06). "Intel Unleashes Haswell-EX Xeon E7 V3 Processors - Up to 18 Cores, 45 MB L3 Cache, 12 TB DDR4 Memory Support and 5.7 Billion Transistors". Wccftech. Retrieved 2017-12-18.
- ^ "Intel's Haswell-X Xeon EP Processor Surfaces in Malaysia". Tom's Hardware. 2013-07-14. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ^ Nath, Preetam (2014-01-10). "[EXCLUSIVE] Intel 2014 Haswell-E to pack 8 cores, DDR4, X99 PCH and more – Page 3 of 3". Vr-zone.com. Archived from the original on 2014-02-01. Retrieved 2014-01-21.
- ^ "Futurology: Haswell-EP will have 14 cores and 35MB L3". Tech News Pedia. 2012-06-21. Archived from the original on 2013-10-14. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ Charlie Demerjian (2012-07-09). "Haswell-EP to use the same socket, just totally different". SemiAccurate. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Launch schedule of Intel Xeon server processors". Cpu-world.com. Retrieved 2014-01-21.
- ^ "Intel public roadmap, 2H2013" (PDF). Retrieved 13 September 2014.
- ^ "Intel Haswell-EP Xeon E5 V3 Processor Pictured – Only Compatible With LGA2011-3 Socket". Wccftech.com. 20 February 2014. Retrieved 2014-02-21.
- ^ "Intel Xeon Processor E5 v3 Product Families: Specification Update" (PDF). Intel. January 2015. pp. 7–8. Retrieved 2015-02-03.
- ^ Johan De Gelas (2014-09-08). "Intel Xeon E5 Version 3 – Up to 18 Haswell EP Cores: The Magic Inside the Uncore". AnandTech. Retrieved 2014-09-09.
- ^ Ian Cutress (2014-05-11). "The Intel Haswell Refresh Review: Core i7-4790, i5-4690 and i3-4360 Tested". AnandTech. Retrieved 2014-07-30.
- ^ "Motherboards — Z87-DELUXE". ASUS. Retrieved 2014-07-26.
- ^ Kirsch, Nathan (2014-06-10). "Intel Core i7-4790K Devil's Canyon Processor Review – Intel Core i7-4790K CPU Temp Testing". legitreviews.com. Retrieved 2014-07-30.
- ^ Cutress, Ian (July 11, 2014). "Devil's Canyon Review: Intel Core i7-4790K and i5-4690K". AnandTech. p. 1. Retrieved August 26, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f "Intel Comparison Table of Haswell Celeron, Pentium, i3, i5, and i7 models". Intel.com. Retrieved 2013-09-02.
- ^ "ARK | Intel Core i7-4790K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz)". Intel. Retrieved 2014-07-15.
- ^ "ARK | Intel Core i5-4690K Processor (6M Cache, up to 3.90 GHz)". Intel. Retrieved 2014-07-18.
- ^ a b Shimpi, Lal. "The Haswell Review: Intel Core i7-4770K & i5-4670K Tested". anandtech. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ Smith, Tony. "Inside Intel's Haswell: What do 1.4 BEELLION transistors get you?". theregister.co.uk. Retrieved 20 November 2014.
- ^ "Intel Haswell R-series CPU Lineup Leaked". VR Zone. 5 April 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-04-07. Retrieved 2013-04-05.
- ^ "Intel Haswell CPU Lineup Leaked, Core i7-4770K Flagship Fourth Generation Processor". wccftech.com. 12 December 2012. Retrieved 2013-04-01.
- ^ "Intel to renew commitment to desktop PCs with a slew of new CPUs". The Tech Report. techreport.com. 2014-03-19. Retrieved 2014-03-25.
- ^ Chris.L (2014-06-20). "確定 9 月 14 日解禁,Intel Haswell-E 與 X99 平台已在路上 - VR-Zone 中文版". Vr-Zone 中文版 (in Chinese). Chinese.vr-zone.com. Archived from the original on 2014-06-25. Retrieved 2014-06-26.
- ^ a b c d "4th Generation Intel® Core™ i5 Processors (Desktop)". Retrieved 2013-06-02.
- ^ "Intel® Core™ i7-4790K Processor (8M Cache, up to 4.40 GHz)". Ark.intel.com. Retrieved 2014-08-20.
- ^ a b "Intel Core i5, i7 Haswell Processors to be Released in June". 22 January 2013. Retrieved 2013-02-05.
- ^ a b "Intel Xeon E5-2600 v3 Processor Overview: Haswell-EP Up to 18 Cores". pcper. 8 September 2014. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- ^ Anthony Shvets (2015-05-07). "Intel launches Xeon E7 v3 server processors". cpu-world.com. Retrieved 2015-05-16.
- ^ Johan De Gelas (2015-05-08). "The Intel Xeon E7-8800 v3 Review: The POWER8 Killer?". AnandTech. Retrieved 2015-05-16.
- ^ "Intel Xeon Processor E5 v3 Product Families: Specification Update" (PDF). Intel. October 2014. pp. 10–11. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- ^ "Lenovo Showcases High-Performance Computing Innovations at Supercomputing 2014". news.lenovo.com. November 18, 2014. Archived from the original on January 7, 2015. Retrieved April 10, 2015.
- ^ Intel® Core™ i3-4000M Processor (3M Cache, 2.40 GHz) Product Specifications
- ^ Andrew Cunningham (2013-06-04). "The U is for Ultrabook: Intel's low-power, dual-core Haswell CPUs unveiled". arstechnica.com. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ^ a b "Tech ARP - Mobile CPU Comparison Guide Rev. 11.9". techarp.com. 2015-04-09. Retrieved 2015-04-09.
- ^ a b c d "4th Generation Intel Core processor based on Mobile M-Processor and H-Processor Lines Datasheet, Volume 1 of 2" (PDF). Intel.com. December 2013. Retrieved 2013-12-22.
Configurable TDP (cTDP) and Low-Power Mode (LPM) form a design vector where the processor behavior and package TDP are dynamically adjusted to a desired system performance and power envelope. [...] With cTDP, the processor is now capable of altering the maximum sustained power with an alternate guaranteed frequency. Configurable TDP allows operation in situations where extra cooling is available or situations where a cooler and quieter mode of operation is desired.
- ^ "The technical details behind Intel's 7 Watt Ivy Bridge CPUs". Arstechnica.com. 2013-01-14. Retrieved 2013-12-22.
If the CPU needs to work hard for an extended period of time and the laptop gets warmer, it will slowly ramp down its speed until it's operating at its stated TDP. [...] There are two OEM-configurable "power level" states that define how quick the CPU can be in these situations: PL2 tells the processor how much power it's allowed to use when it needs a short burst of speed, and PL1 defines how quickly the processor can run under sustained load. [...] This is at the heart of what Intel is doing with the Y-series processors: their maximum TDP has been lowered four watts, from 17 to 13. Intel is also validating them for use at two lower PL1 values: 10 watts and 7 watts. This is where the marketing we discussed earlier comes in—rather than keeping these values under the covers as it has so far been content to do, Intel has taken that lowest value, put it on its product pages, and called it SDP.
- ^ "4th Generation Intel Core processor based on Mobile U-Processor and Y-Processor Lines Datasheet, Volume 1 of 2" (PDF). intel.com. December 2013. Retrieved 2013-12-22.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Intel Quietly Launches Ten New Mobile Processors". TomsHardware.com. 22 January 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "Intel Core i7-4750HQ Mobile processor – CL8064701510101". Cpu-world.com. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ a b c "Intel refreshes Core i5, i7 and N-Series mobile lineups". Cpu-world.com. Retrieved 2014-07-21.
- ^ "Intel Core i7-4960HQ Mobile processor – CL8064701511001". Cpu-world.com. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
- ^ "Intel Core i5-4308U Mobile processor — CL8064701954700". CPU World.
External links
- "Intel Haswell Architecture Disclosure: Live Blog". AnandTech. September 11, 2012.
- "4th Generation of Core Microarchitecture: Intel Haswell". X-bit labs. September 12, 2012. Archived from the original on January 3, 2017. Retrieved September 17, 2012.
- "Intel Core "Haswell" Desktop Processor Box Pricing Compiled". TechPowerUp. April 23, 2013.
- "XtremeSystems OC Examples". Charles Wirth. June 1, 2013.
- "Intel Core i7-4770K CPU Review. Intel Haswell for Desktops: Ruin of Our Hopes?". X-bit labs. June 1, 2013. Archived from the original on January 3, 2017. Retrieved June 19, 2013.
- "Overview of Power Management for 3rd generation Ultrabook Platform, Haswell". AnandTech Forums. 2013-10-15. Archived from the original on 2014-12-05. Retrieved 2013-10-15.


