Languages of Europe: Difference between revisions
Archives908 (talk | contribs) |
Oh my science! Come on, at least try to cite a source for Wikipedia's sake |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
Dots indicate areas where [[multilingualism]] is common.]] |
Dots indicate areas where [[multilingualism]] is common.]] |
||
The [[Germanic languages]] make up the predominant language family in Western, [[Northern Europe|Northern]] and [[Central Europe]]. An estimated 210 million Europeans are native speakers of Germanic languages, the largest groups being [[German-speaking Europe|German]] ({{circa}} 95 million), [[English language in Europe|English]] ({{circa}} 70 million), [[Dutch language|Dutch]] ({{circa}} 24 million), [[Swedish language|Swedish]] ({{circa}} 10 million), [[Danish language|Danish]] ({{circa}} 6 million), and [[Norwegian language|Norwegian]] ({{circa}} 5 million). |
The [[Germanic languages]] make up the predominant language family in Western, [[Northern Europe|Northern]] and [[Central Europe]]. An estimated 210 million Europeans are native speakers of Germanic languages, the largest groups being [[German-speaking Europe|German]] ({{circa}} 95 million), [[English language in Europe|English]] ({{circa}} 70 million), [[Dutch language|Dutch]] ({{circa}} 24 million), [[Swedish language|Swedish]] ({{circa}} 10 million), [[Danish language|Danish]] ({{circa}} 6 million), and [[Norwegian language|Norwegian]] ({{circa}} 5 million).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
There are two extant major sub-divisions: ''[[West Germanic languages|West Germanic]]'' and ''[[North Germanic languages|North Germanic]]''. A third group, [[East Germanic languages|East Germanic]], is now extinct; the only known surviving East Germanic texts are written in the [[Gothic language]]. West Germanic is divided into [[Anglo-Frisian languages|Anglo-Frisian]] (including [[English language|English]]), [[Low German]], [[Low Franconian languages|Low Franconian]] (including [[Dutch language|Dutch]]) and [[High German]] (including [[Standard German]]). |
There are two extant major sub-divisions: ''[[West Germanic languages|West Germanic]]'' and ''[[North Germanic languages|North Germanic]]''. A third group, [[East Germanic languages|East Germanic]], is now extinct; the only known surviving East Germanic texts are written in the [[Gothic language]]. West Germanic is divided into [[Anglo-Frisian languages|Anglo-Frisian]] (including [[English language|English]]), [[Low German]], [[Low Franconian languages|Low Franconian]] (including [[Dutch language|Dutch]]) and [[High German]] (including [[Standard German]]).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
====Anglo-Frisian==== |
====Anglo-Frisian==== |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
The [[Anglo-Frisian languages|Anglo-Frisian language family]] is now mostly represented by [[Anglic languages|English (Anglic)]], descended from the [[Old English language]] spoken by the [[Anglo-Saxons]]: |
The [[Anglo-Frisian languages|Anglo-Frisian language family]] is now mostly represented by [[Anglic languages|English (Anglic)]], descended from the [[Old English language]] spoken by the [[Anglo-Saxons]]: |
||
* [[English language|English]], the main language of the [[United Kingdom]] and the most widespread language in the [[Republic of Ireland]], also spoken as a [[European English|second or third language by many Europeans]]. |
* [[English language|English]], the main language of the [[United Kingdom]] and the most widespread language in the [[Republic of Ireland]], also spoken as a [[European English|second or third language by many Europeans]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Scots language|Scots]], spoken in [[Scotland]] and [[Ulster]], recognized by some as a language and by others as a dialect of English. |
* [[Scots language|Scots]], spoken in [[Scotland]] and [[Ulster]], recognized by some as a language and by others as a dialect of English.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The [[Frisian languages]] are spoken by about 500,000 [[Frisians]], who live on the southern coast of the [[North Sea]] in the [[Netherlands]] and [[Germany]]. These languages include [[West Frisian language|West Frisian]], [[East Frisian language|East Frisian]] (only surviving dialect of it is [[Saterlandic]]) and [[North Frisian language|North Frisian]]. |
The [[Frisian languages]] are spoken by about 500,000 [[Frisians]], who live on the southern coast of the [[North Sea]] in the [[Netherlands]] and [[Germany]]. These languages include [[West Frisian language|West Frisian]], [[East Frisian language|East Frisian]] (only surviving dialect of it is [[Saterlandic]]) and [[North Frisian language|North Frisian]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
====Dutch==== |
====Dutch==== |
||
{{Main|Dutch language#Europe{{!}}Dutch-speaking Europe|Dutch language|Low Franconian}} |
{{Main|Dutch language#Europe{{!}}Dutch-speaking Europe|Dutch language|Low Franconian}} |
||
[[Dutch language|Dutch]] is spoken throughout the [[Netherlands]], the northern half of [[Belgium]], as well as the [[Nord-Pas de Calais]] region of [[France]]. The traditional dialects of the [[Lower Rhine region|Lower Rhine]] region of Germany, are linguistically more closely related to Dutch than to modern German. In Belgian and French contexts, Dutch is sometimes referred to as [[Flemish]]. [[Dutch dialects]] are varied and cut across national borders. |
[[Dutch language|Dutch]] is spoken throughout the [[Netherlands]], the northern half of [[Belgium]], as well as the [[Nord-Pas de Calais]] region of [[France]]. The traditional dialects of the [[Lower Rhine region|Lower Rhine]] region of Germany, are linguistically more closely related to Dutch than to modern German. In Belgian and French contexts, Dutch is sometimes referred to as [[Flemish]]. [[Dutch dialects]] are varied and cut across national borders.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
====German==== |
====German==== |
||
{{Main|German language|Geographical distribution of German speakers}} |
{{Main|German language|Geographical distribution of German speakers}} |
||
[[German language|German]] is spoken throughout [[Germany]], [[Austria]], [[Liechtenstein]], much of [[Switzerland]] (including the northeast areas bordering on Germany and Austria), northern [[Italy]] ([[South Tyrol]]), [[Luxembourg]], the [[East Cantons of Belgium]] and the [[Alsace]] and [[Lorraine]] regions of [[France]]. |
[[German language|German]] is spoken throughout [[Germany]], [[Austria]], [[Liechtenstein]], much of [[Switzerland]] (including the northeast areas bordering on Germany and Austria), northern [[Italy]] ([[South Tyrol]]), [[Luxembourg]], the [[East Cantons of Belgium]] and the [[Alsace]] and [[Lorraine]] regions of [[France]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
There are several groups of German dialects: |
There are several groups of German dialects: |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
** [[Upper German]], including [[Bavarian language|Bavarian]] and [[Swiss German]] |
** [[Upper German]], including [[Bavarian language|Bavarian]] and [[Swiss German]] |
||
** [[Yiddish]] is a [[Jewish languages|Jewish language]] developed in Germany and shares many features of High German dialects and [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]]. |
** [[Yiddish]] is a [[Jewish languages|Jewish language]] developed in Germany and shares many features of High German dialects and [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]]. |
||
* [[Low German]] (or Low Saxon) is spoken in various regions throughout Northern Germany and the northern and eastern parts of the Netherlands. It is an official language in Germany. It may be separated into [[West Low German]] and [[East Low German]]. |
* [[Low German]] (or Low Saxon) is spoken in various regions throughout Northern Germany and the northern and eastern parts of the Netherlands. It is an official language in Germany. It may be separated into [[West Low German]] and [[East Low German]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
====North Germanic (Scandinavian)==== |
====North Germanic (Scandinavian)==== |
||
The ''[[North Germanic languages]]'' are spoken in [[Scandinavia|Scandinavian countries]] and include [[Danish language|Danish]] ([[Denmark]]), [[Norwegian language|Norwegian]] ([[Norway]]), [[Swedish language|Swedish]] ([[Sweden]] and parts of [[Finland]]), or [[Elfdalian]] (in a small part of central Sweden), [[Faroese language|Faroese]] ([[Faroe Islands]]), and [[Icelandic language|Icelandic]] ([[Iceland]]). |
The ''[[North Germanic languages]]'' are spoken in [[Scandinavia|Scandinavian countries]] and include [[Danish language|Danish]] ([[Denmark]]), [[Norwegian language|Norwegian]] ([[Norway]]), [[Swedish language|Swedish]] ([[Sweden]] and parts of [[Finland]]), or [[Elfdalian]] (in a small part of central Sweden), [[Faroese language|Faroese]] ([[Faroe Islands]]), and [[Icelandic language|Icelandic]] ([[Iceland]]).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
English has a long history of contact with Scandinavian languages, given the immigration of Scandinavians early in the history of Britain, and shares various features with the Scandinavian languages.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/11/121127094111.htm|title=Linguist makes sensational claim: English is a Scandinavian language|website=ScienceDaily|access-date=2016-03-06}}</ref> Even so, especially Swedish, but also Danish and Norwegian, have strong vocabulary connections to the [[German language]]. |
English has a long history of contact with Scandinavian languages, given the immigration of Scandinavians early in the history of Britain, and shares various features with the Scandinavian languages.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/11/121127094111.htm|title=Linguist makes sensational claim: English is a Scandinavian language|website=ScienceDaily|access-date=2016-03-06}}</ref> Even so, especially Swedish, but also Danish and Norwegian, have strong vocabulary connections to the [[German language]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Romance === |
=== Romance === |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
[[File:Romance 20c en.png|thumb|300px|Romance languages, 20th century.]] |
[[File:Romance 20c en.png|thumb|300px|Romance languages, 20th century.]] |
||
Roughly 215 million Europeans (primarily in [[Southern Europe|Southern]] and [[Western Europe|Western]] Europe) are native speakers of [[Romance languages]], the largest groups including: |
Roughly 215 million Europeans (primarily in [[Southern Europe|Southern]] and [[Western Europe|Western]] Europe) are native speakers of [[Romance languages]], the largest groups including:{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
[[French language|French]] ({{circa}} 72 million), |
[[French language|French]] ({{circa}} 72 million), |
||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
[[Occitan language|Occitan]] ({{circa}} 500,000), besides numerous smaller communities. |
[[Occitan language|Occitan]] ({{circa}} 500,000), besides numerous smaller communities. |
||
The Romance languages evolved from varieties of [[Vulgar Latin]] spoken in the various parts of the [[Roman Empire]] in [[Late Antiquity]]. [[Latin]] was itself part of the (otherwise extinct) [[Italic languages|Italic]] branch of Indo-European. |
The Romance languages evolved from varieties of [[Vulgar Latin]] spoken in the various parts of the [[Roman Empire]] in [[Late Antiquity]]. [[Latin]] was itself part of the (otherwise extinct) [[Italic languages|Italic]] branch of Indo-European.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
Romance languages are divided phylogenetically into ''[[Italo-Western]]'', ''[[Eastern Romance]]'' (including [[Romanian language|Romanian]]) and ''[[Sardinian language|Sardinian]]''. The Romance-speaking area of Europe is occasionally referred to as ''[[Latin Europe]]''.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Friedman |first1=Lawrence |last2=Perez-Perdomo |first2=Rogelio |date=2003 |title=Legal Culture in the Age of Globalization: Latin America and Latin Europe |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wEMUKyPTE9AC&q=%22latin+europe%22 |publisher=Stanford University Press |page=1 |isbn=0-8047-6695-9 |author-link1=Lawrence M. Friedman }}</ref> |
Romance languages are divided phylogenetically into ''[[Italo-Western]]'', ''[[Eastern Romance]]'' (including [[Romanian language|Romanian]]) and ''[[Sardinian language|Sardinian]]''. The Romance-speaking area of Europe is occasionally referred to as ''[[Latin Europe]]''.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Friedman |first1=Lawrence |last2=Perez-Perdomo |first2=Rogelio |date=2003 |title=Legal Culture in the Age of Globalization: Latin America and Latin Europe |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wEMUKyPTE9AC&q=%22latin+europe%22 |publisher=Stanford University Press |page=1 |isbn=0-8047-6695-9 |author-link1=Lawrence M. Friedman }}</ref> |
||
We can further break down Italo-Western into the ''[[Italo-Dalmatian languages]]'' (sometimes grouped with Eastern Romance), including the Tuscan-derived [[Italian language|Italian]] and numerous [[Languages of Italy|local Romance languages in Italy]] as well as [[Dalmatian language|Dalmatian]], and the ''[[Western Romance languages]]''. The Western Romance languages in turn separate into the [[Gallo-Romance languages]], including [[French language|French]] and its varieties ([[Langues d'oïl]]), the [[Rhaeto-Romance languages]] and the [[Gallo-Italic languages]]; the [[Occitano-Romance languages]], grouped with either Gallo-Romance or East Iberian, including [[Occitan language|Occitan]], [[Catalan language|Catalan]] and [[Aragonese language|Aragonese]]; and finally the [[West Iberian languages]] (Spanish-Portuguese), including the [[Astur-Leonese languages]], [[Galician-Portuguese]], and [[Castilian languages|Castilian]]. |
We can further break down Italo-Western into the ''[[Italo-Dalmatian languages]]'' (sometimes grouped with Eastern Romance), including the Tuscan-derived [[Italian language|Italian]] and numerous [[Languages of Italy|local Romance languages in Italy]] as well as [[Dalmatian language|Dalmatian]], and the ''[[Western Romance languages]]''. The Western Romance languages in turn separate into the [[Gallo-Romance languages]], including [[French language|French]] and its varieties ([[Langues d'oïl]]), the [[Rhaeto-Romance languages]] and the [[Gallo-Italic languages]]; the [[Occitano-Romance languages]], grouped with either Gallo-Romance or East Iberian, including [[Occitan language|Occitan]], [[Catalan language|Catalan]] and [[Aragonese language|Aragonese]]; and finally the [[West Iberian languages]] (Spanish-Portuguese), including the [[Astur-Leonese languages]], [[Galician-Portuguese]], and [[Castilian languages|Castilian]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Slavic === |
=== Slavic === |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
{{legend|#004040|South Slavic languages}}]] |
{{legend|#004040|South Slavic languages}}]] |
||
[[Slavic languages]] are spoken in large areas of Southern, Central and [[Eastern Europe]]. An estimated 250 million Europeans are native speakers of Slavic languages, the largest groups being |
[[Slavic languages]] are spoken in large areas of Southern, Central and [[Eastern Europe]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} An estimated 250 million Europeans are native speakers of Slavic languages,{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} the largest groups being |
||
[[Russian language|Russian]] ({{circa}} 110 million in [[European Russia]] and adjacent parts of Eastern Europe, Russian forming the largest linguistic community in Europe), |
[[Russian language|Russian]] ({{circa}} 110 million in [[European Russia]] and adjacent parts of Eastern Europe, Russian forming the largest linguistic community in Europe), |
||
[[Polish language|Polish]] ({{circa}} 45 million), |
[[Polish language|Polish]] ({{circa}} 45 million), |
||
[[Ukrainian language|Ukrainian]] ({{circa}} 40 million), |
[[Ukrainian language|Ukrainian]] ({{circa}} 40 million), |
||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
[[Slovak language|Slovak]] ({{circa}} 5 million) |
[[Slovak language|Slovak]] ({{circa}} 5 million) |
||
[[Belarusian language|Belarusian]] and [[Slovene language|Slovene]] ({{circa}} 3 million each) |
[[Belarusian language|Belarusian]] and [[Slovene language|Slovene]] ({{circa}} 3 million each) |
||
and [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]] ({{circa}} 2 million). |
and [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]] ({{circa}} 2 million).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
Phylogenetically, Slavic is divided into three subgroups: |
Phylogenetically, Slavic is divided into three subgroups: |
||
* ''[[West Slavic languages|West Slavic]]'' includes [[Polish language|Polish]], [[Czech language|Czech]], [[Slovak language|Slovak]], [[Lower Sorbian language|Lower Sorbian]], [[Upper Sorbian language|Upper Sorbian]], [[Silesian language|Silesian]] and [[Kashubian language|Kashubian]]. |
* ''[[West Slavic languages|West Slavic]]'' includes [[Polish language|Polish]], [[Czech language|Czech]], [[Slovak language|Slovak]], [[Lower Sorbian language|Lower Sorbian]], [[Upper Sorbian language|Upper Sorbian]], [[Silesian language|Silesian]] and [[Kashubian language|Kashubian]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* ''[[East Slavic languages|East Slavic]]'' includes [[Russian language|Russian]], [[Ukrainian language|Ukrainian]], [[Belarusian language|Belarusian]], and [[Rusyn language|Rusyn]]. |
* ''[[East Slavic languages|East Slavic]]'' includes [[Russian language|Russian]], [[Ukrainian language|Ukrainian]], [[Belarusian language|Belarusian]], and [[Rusyn language|Rusyn]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* ''[[South Slavic languages|South Slavic]]'' includes [[Slovene language|Slovene]] and [[Serbo-Croatian]] in the southwest and [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]], [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]] and [[Church Slavonic]] (a [[liturgical language]]) in the southeast, each with numerous distinctive dialects. South Slavic languages constitute a [[Dialect continuum#South Slavic continuum|dialect continuum]] where standard Slovene, Macedonian and Bulgarian are each based on a distinct dialect, whereas [[pluricentric language|pluricentric]] Serbo-Croatian boasts four [[mutual intelligibility|mutually intelligible]] [[Comparison of standard Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian|national standard varieties]] all based on a single dialect, [[Shtokavian dialect|Shtokavian]]. |
* ''[[South Slavic languages|South Slavic]]'' includes [[Slovene language|Slovene]] and [[Serbo-Croatian]] in the southwest and [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]], [[Macedonian language|Macedonian]] and [[Church Slavonic]] (a [[liturgical language]]) in the southeast, each with numerous distinctive dialects. South Slavic languages constitute a [[Dialect continuum#South Slavic continuum|dialect continuum]] where standard Slovene, Macedonian and Bulgarian are each based on a distinct dialect, whereas [[pluricentric language|pluricentric]] Serbo-Croatian boasts four [[mutual intelligibility|mutually intelligible]] [[Comparison of standard Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian|national standard varieties]] all based on a single dialect, [[Shtokavian dialect|Shtokavian]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Others === |
=== Others === |
||
* [[Greek language|Greek]] ({{circa}} 13 million) is the official language of [[Greece]] and [[Cyprus]], and there are Greek-speaking enclaves in [[Albania]], [[Bulgaria]], [[Italy]], [[North Macedonia]], [[Romania]], [[Georgia (country)|Georgia]], [[Ukraine]], [[Lebanon]], [[Egypt]], [[Israel]], [[Jordan]], and [[Turkey]], and in [[Greek diaspora|Greek communities]] around the world. Dialects of modern Greek that originate from [[Attic Greek]] (through [[Koine Greek|Koine]] and then [[Medieval Greek]]) are [[Cappadocian Greek|Cappadocian]], [[Pontic Greek|Pontic]], [[Cretan Greek|Cretan]], [[Cypriot Greek|Cypriot]], [[Katharevousa]], and [[Yevanic]]. |
* [[Greek language|Greek]] ({{circa}} 13 million) is the official language of [[Greece]] and [[Cyprus]], and there are Greek-speaking enclaves in [[Albania]], [[Bulgaria]], [[Italy]], [[North Macedonia]], [[Romania]], [[Georgia (country)|Georgia]], [[Ukraine]], [[Lebanon]], [[Egypt]], [[Israel]], [[Jordan]], and [[Turkey]], and in [[Greek diaspora|Greek communities]] around the world. Dialects of modern Greek that originate from [[Attic Greek]] (through [[Koine Greek|Koine]] and then [[Medieval Greek]]) are [[Cappadocian Greek|Cappadocian]], [[Pontic Greek|Pontic]], [[Cretan Greek|Cretan]], [[Cypriot Greek|Cypriot]], [[Katharevousa]], and [[Yevanic]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
** [[Greek-Bovesian|Italiot Greek]] is, debatably, a [[Doric Greek|Doric]] dialect of Greek. It is spoken in southern Italy only, in the [[Province of Reggio Calabria|southern Calabria]] region (as [[Greek-Bovesian|Grecanic]])<ref>F. Violi, ''Lessico Grecanico-Italiano-Grecanico'', Apodiafàzzi, [[Reggio Calabria]], 1997.</ref><ref>Paolo Martino, ''L'isola grecanica dell'Aspromonte. Aspetti sociolinguistici'', 1980. Risultati di un'inchiesta del 1977</ref><ref>Filippo Violi, ''Storia degli studi e della letteratura popolare grecanica'', C.S.E. Bova ([[Province of Reggio Calabria|RC]]), 1992</ref><ref>Filippo Condemi, ''Grammatica Grecanica'', Coop. Contezza, [[Reggio Calabria]], 1987;</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.treccani.it/magazine/lingua_italiana/speciali/minoranze/Romano.html|title=In Salento e Calabria le voci della minoranza linguistica greca|website=Treccani, l'Enciclopedia italiana}}</ref> and in the [[Salento]] region (as [[Griko]]). It was studied by the German linguist [[Gerhard Rohlfs]] during the 1930s and 1950s. |
** [[Greek-Bovesian|Italiot Greek]] is, debatably, a [[Doric Greek|Doric]] dialect of Greek. It is spoken in southern Italy only, in the [[Province of Reggio Calabria|southern Calabria]] region (as [[Greek-Bovesian|Grecanic]])<ref>F. Violi, ''Lessico Grecanico-Italiano-Grecanico'', Apodiafàzzi, [[Reggio Calabria]], 1997.</ref><ref>Paolo Martino, ''L'isola grecanica dell'Aspromonte. Aspetti sociolinguistici'', 1980. Risultati di un'inchiesta del 1977</ref><ref>Filippo Violi, ''Storia degli studi e della letteratura popolare grecanica'', C.S.E. Bova ([[Province of Reggio Calabria|RC]]), 1992</ref><ref>Filippo Condemi, ''Grammatica Grecanica'', Coop. Contezza, [[Reggio Calabria]], 1987;</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.treccani.it/magazine/lingua_italiana/speciali/minoranze/Romano.html|title=In Salento e Calabria le voci della minoranza linguistica greca|website=Treccani, l'Enciclopedia italiana}}</ref> and in the [[Salento]] region (as [[Griko]]). It was studied by the German linguist [[Gerhard Rohlfs]] during the 1930s and 1950s.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
** [[Tsakonian language|Tsakonian]] is a Doric dialect of the Greek language spoken in the lower [[Arcadia (regional unit)|Arcadia]] region of the [[Peloponnese]] around the village of [[Leonidio]] |
** [[Tsakonian language|Tsakonian]] is a Doric dialect of the Greek language spoken in the lower [[Arcadia (regional unit)|Arcadia]] region of the [[Peloponnese]] around the village of [[Leonidio]]{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
[[File:Baltic languages.png|thumb|200px|Historic distribution of the Baltic languages in the Baltic (simplified).]] |
[[File:Baltic languages.png|thumb|200px|Historic distribution of the Baltic languages in the Baltic (simplified).]] |
||
* The [[Baltic languages]] are spoken in [[Lithuania]] ([[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]] ({{circa}} 3 million), [[Samogitian language|Samogitian]]) and [[Latvia]] ([[Latvian language|Latvian]] ({{circa}} 2 million), [[Latgalian language|Latgalian]]). Samogitian and Latgalian are usually considered to be dialects of Lithuanian and Latvian respectively. |
* The [[Baltic languages]] are spoken in [[Lithuania]] ([[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]] ({{circa}} 3 million), [[Samogitian language|Samogitian]]) and [[Latvia]] ([[Latvian language|Latvian]] ({{circa}} 2 million), [[Latgalian language|Latgalian]]). Samogitian and Latgalian are usually considered to be dialects of Lithuanian and Latvian respectively.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
** There are also several extinct Baltic languages, including: [[Galindian language|Galindian]], [[Curonian language|Curonian]], [[Old Prussian language|Old Prussian]], [[Selonian language|Selonian]], [[Semigallian language|Semigallian]] and [[Sudovian language|Sudovian]]. |
** There are also several extinct Baltic languages, including: [[Galindian language|Galindian]], [[Curonian language|Curonian]], [[Old Prussian language|Old Prussian]], [[Selonian language|Selonian]], [[Semigallian language|Semigallian]] and [[Sudovian language|Sudovian]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Albanian language|Albanian]] ({{circa}} 5 million) has two major dialects, [[Tosk Albanian]] and [[Gheg Albanian]]. It is spoken in [[Albania]] and [[Kosovo]], neighboring [[North Macedonia]], [[Serbia]], [[Greece]], [[Italy]], and [[Montenegro]]. It is also widely spoken in the [[Albanian diaspora]]. |
* [[Albanian language|Albanian]] ({{circa}} 5 million) has two major dialects, [[Tosk Albanian]] and [[Gheg Albanian]]. It is spoken in [[Albania]] and [[Kosovo]], neighboring [[North Macedonia]], [[Serbia]], [[Greece]], [[Italy]], and [[Montenegro]]. It is also widely spoken in the [[Albanian diaspora]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Armenian language|Armenian]] ({{circa}} 7 million) has two major forms, [[Western Armenian]] and [[Eastern Armenian]]. It is spoken in [[Armenia]], [[Republic of Artsakh|Artsakh]] and [[Georgia (country)|Georgia]] ([[Samtskhe-Javakheti]]), also [[Russia]], [[France]], [[Italy]], [[Turkey]], [[Greece]], and [[Cyprus]]. It is also widely spoken in the [[Armenian Diaspora]]. |
* [[Armenian language|Armenian]] ({{circa}} 7 million) has two major forms, [[Western Armenian]] and [[Eastern Armenian]]. It is spoken in [[Armenia]], [[Republic of Artsakh|Artsakh]] and [[Georgia (country)|Georgia]] ([[Samtskhe-Javakheti]]), also [[Russia]], [[France]], [[Italy]], [[Turkey]], [[Greece]], and [[Cyprus]]. It is also widely spoken in the [[Armenian Diaspora]]. {{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* There are six living [[Celtic languages]], spoken in areas of northwestern Europe dubbed the "[[Celtic nations]]". All six are members of the [[Insular Celtic languages|Insular Celtic]] family, which in turn is divided into: |
* There are six living [[Celtic languages]], spoken in areas of northwestern Europe dubbed the "[[Celtic nations]]". All six are members of the [[Insular Celtic languages|Insular Celtic]] family, which in turn is divided into: |
||
** [[Brittonic languages|Brittonic family]]: [[Welsh language|Welsh]] ([[Wales]], {{circa}} 700,000), [[Cornish language|Cornish]] ([[Cornwall]], {{circa}} 500) and [[Breton language|Breton]] ([[Brittany]], {{circa}} 200,000) |
** [[Brittonic languages|Brittonic family]]: [[Welsh language|Welsh]] ([[Wales]], {{circa}} 700,000), [[Cornish language|Cornish]] ([[Cornwall]], {{circa}} 500) and [[Breton language|Breton]] ([[Brittany]], {{circa}} 200,000) |
||
** [[Goidelic languages|Goidelic family]]: [[Irish language|Irish]] ([[Ireland]], {{circa}} 2,000,000), [[Scottish Gaelic language|Scottish Gaelic]] ([[Scotland]], {{circa}} 50,000), and [[Manx language|Manx]] ([[Isle of Man]], 1,800) |
** [[Goidelic languages|Goidelic family]]: [[Irish language|Irish]] ([[Ireland]], {{circa}} 2,000,000), [[Scottish Gaelic language|Scottish Gaelic]] ([[Scotland]], {{circa}} 50,000), and [[Manx language|Manx]] ([[Isle of Man]], 1,800){{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
: [[Continental Celtic languages]] had previously been spoken across Europe from Iberia and Gaul to Asia Minor, but became extinct in the first millennium AD. |
: [[Continental Celtic languages]] had previously been spoken across Europe from Iberia and Gaul to Asia Minor, but became extinct in the first millennium AD.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* The [[Indo-Aryan languages]] have one major representation: [[Romani language|Romani]] ({{circa}} 1.5 million speakers), introduced in Europe during the late medieval period. Lacking a nation state, Romani is spoken as a minority language throughout Europe. |
* The [[Indo-Aryan languages]] have one major representation: [[Romani language|Romani]] ({{circa}} 1.5 million speakers), introduced in Europe during the late medieval period. Lacking a nation state, Romani is spoken as a minority language throughout Europe.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* The [[Iranian languages]] in Europe are natively represented in the North Caucasus, notably with [[Ossetic language|Ossetian]] ({{circa}} 600,000). |
* The [[Iranian languages]] in Europe are natively represented in the North Caucasus, notably with [[Ossetic language|Ossetian]] ({{circa}} 600,000).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
== Non-Indo-European languages == |
== Non-Indo-European languages == |
||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
[[File:Carte peuples turcs.png|thumb|right|340px|Distribution of Turkic languages in Eurasia]] |
[[File:Carte peuples turcs.png|thumb|right|340px|Distribution of Turkic languages in Eurasia]] |
||
* [[Oghuz languages]] in Europe include [[Turkish language|Turkish]], spoken in [[East Thrace]] and by immigrant communities; [[Azerbaijani language|Azerbaijani]] is spoken in [[Azerbaijan|Northeast Azerbaijan]] and parts of [[Southern Russia]] and [[Gagauz language|Gagauz]] is spoken in [[Gagauzia]]. |
* [[Oghuz languages]] in Europe include [[Turkish language|Turkish]], spoken in [[East Thrace]] and by immigrant communities; [[Azerbaijani language|Azerbaijani]] is spoken in [[Azerbaijan|Northeast Azerbaijan]] and parts of [[Southern Russia]] and [[Gagauz language|Gagauz]] is spoken in [[Gagauzia]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Kipchak languages]] in Europe include [[Karaim language|Karaim]], [[Crimean Tatar language|Crimean Tatar]] and [[Krymchak language|Krymchak]], which is spoken in mainly [[Crimea]]; [[Tatar language|Tatar]], which is spoken in [[Tatarstan]]; [[Bashkir language|Bashkir]], which is spoken in [[Bashkortostan]]; [[Karachay-Balkar language|Karachay-Balkar]], which is spoken in the [[North Caucasus]], and [[Kazakh language|Kazakh]], which is spoken in [[Kazakhstan|Northwest Kazakhstan]]. |
* [[Kipchak languages]] in Europe include [[Karaim language|Karaim]], [[Crimean Tatar language|Crimean Tatar]] and [[Krymchak language|Krymchak]], which is spoken in mainly [[Crimea]]; [[Tatar language|Tatar]], which is spoken in [[Tatarstan]]; [[Bashkir language|Bashkir]], which is spoken in [[Bashkortostan]]; [[Karachay-Balkar language|Karachay-Balkar]], which is spoken in the [[North Caucasus]], and [[Kazakh language|Kazakh]], which is spoken in [[Kazakhstan|Northwest Kazakhstan]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Oghur languages]] were historically indigenous to much of Eastern Europe; however, most of them are extinct today, with the exception of [[Chuvash language|Chuvash]], which is spoken in [[Chuvashia]]. |
* [[Oghur languages]] were historically indigenous to much of Eastern Europe; however, most of them are extinct today, with the exception of [[Chuvash language|Chuvash]], which is spoken in [[Chuvashia]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Uralic === |
=== Uralic === |
||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
[[File:Oeraals verspreiding-af.svg|thumb|right|340px|Distribution of Uralic languages in Eurasia]] |
[[File:Oeraals verspreiding-af.svg|thumb|right|340px|Distribution of Uralic languages in Eurasia]] |
||
Uralic is native to northern Eurasia. [[Finno-Ugric languages|Finno-Ugric]] groups the Uralic languages other than [[Samoyedic languages|Samoyedic]]. |
Uralic is native to northern Eurasia. [[Finno-Ugric languages|Finno-Ugric]] groups the Uralic languages other than [[Samoyedic languages|Samoyedic]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
[[Finnic languages]] include [[Finnish language|Finnish]] ({{circa}} 5 million), [[Estonian language|Estonian]] ({{circa}} 1 million) and [[Mari language|Mari]] (c. 400,000). The [[Sami languages]] ({{circa}} 30,000) are closely related to Finnic. |
[[Finnic languages]] include [[Finnish language|Finnish]] ({{circa}} 5 million), [[Estonian language|Estonian]] ({{circa}} 1 million) and [[Mari language|Mari]] (c. 400,000). The [[Sami languages]] ({{circa}} 30,000) are closely related to Finnic.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The [[Ugric languages]] are represented in Europe with the [[Hungarian language]] ({{circa}} 13 million), historically introduced with the [[Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin]] of the 9th century. |
The [[Ugric languages]] are represented in Europe with the [[Hungarian language]] ({{circa}} 13 million), historically introduced with the [[Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin]] of the 9th century.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Others === |
=== Others === |
||
* The [[Basque language]] (or ''Euskara'', {{circa}} 750,000) is a [[language isolate]] and the ancestral language of the [[Basque people]] who inhabit the [[Basque Country (greater region)|Basque Country]], a region in the western [[Pyrenees]] mountains mostly in northeastern [[Spain]] and partly in southwestern [[France]] of about 3 million inhabitants, where it is spoken fluently by about 750,000 and understood by more than 1.5 million people. Basque is directly related to [[Aquitanian language|ancient Aquitanian]], and it is likely that an early form of the Basque language was present in Western Europe before the arrival of the Indo-European languages in the area in the [[Bronze Age Europe|Bronze Age]]. |
* The [[Basque language]] (or ''Euskara'', {{circa}} 750,000) is a [[language isolate]] and the ancestral language of the [[Basque people]] who inhabit the [[Basque Country (greater region)|Basque Country]], a region in the western [[Pyrenees]] mountains mostly in northeastern [[Spain]] and partly in southwestern [[France]] of about 3 million inhabitants, where it is spoken fluently by about 750,000 and understood by more than 1.5 million people. Basque is directly related to [[Aquitanian language|ancient Aquitanian]], and it is likely that an early form of the Basque language was present in Western Europe before the arrival of the Indo-European languages in the area in the [[Bronze Age Europe|Bronze Age]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[North Caucasian languages]] is a geographical blanket term for two unrelated [[Language family|language families]] spoken chiefly in the north [[Caucasus]] and [[Turkey]]—the [[Northwest Caucasian languages|Northwest Caucasian]] family (including [[Abkhaz language|Abkhaz]] and [[Adyghe language|Circassian]]) and the [[Northeast Caucasian languages|Northeast Caucasian]] family, spoken mainly in the border area of the southern [[Russian Federation]] (including [[Dagestan]], [[Chechnya]], and [[Ingushetia]]). |
* [[North Caucasian languages]] is a geographical blanket term for two unrelated [[Language family|language families]] spoken chiefly in the north [[Caucasus]] and [[Turkey]]—the [[Northwest Caucasian languages|Northwest Caucasian]] family (including [[Abkhaz language|Abkhaz]] and [[Adyghe language|Circassian]]) and the [[Northeast Caucasian languages|Northeast Caucasian]] family, spoken mainly in the border area of the southern [[Russian Federation]] (including [[Dagestan]], [[Chechnya]], and [[Ingushetia]]).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Kalmyk language|Kalmyk]] is a [[Mongolic languages|Mongolic language]], spoken in the [[Republic of Kalmykia]], part of the [[Russian Federation]]. Its speakers entered the Volga region in the early 17th century. |
* [[Kalmyk language|Kalmyk]] is a [[Mongolic languages|Mongolic language]], spoken in the [[Republic of Kalmykia]], part of the [[Russian Federation]]. Its speakers entered the Volga region in the early 17th century.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Kartvelian languages]] (also known as [[Southwest Caucasian languages]]), the most common of which is [[Georgian language|Georgian]] ({{circa}} 3.5 million), others being [[Mingrelian language|Mingrelian]] and [[Svan language|Svan]], spoken mainly in the Caucasus and Anatolia. |
* [[Kartvelian languages]] (also known as [[Southwest Caucasian languages]]), the most common of which is [[Georgian language|Georgian]] ({{circa}} 3.5 million), others being [[Mingrelian language|Mingrelian]] and [[Svan language|Svan]], spoken mainly in the Caucasus and Anatolia.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Maltese language|Maltese]] ({{circa}} 500,000) is a [[Semitic language]] with [[Romance language|Romance]] and [[Germanic language|Germanic]] influences, spoken in [[Malta]].<ref>{{cite web |last=Alexander |first=Marie |title=2nd International Conference of Maltese Linguistics: Saturday, September 19 – Monday, September 21, 2009 |url=http://www.fb10.uni-bremen.de/maltese/abstracts.aspx |year=2009 |publisher=International Association of Maltese Linguistics |access-date=2 November 2009|display-authors=etal}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |first=J. |last=Aquilina |title=Maltese as a Mixed Language |journal=Journal of Semitic Studies |year=1958 |volume=3 |number=1 |pages=58–79 |doi=10.1093/jss/3.1.58}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=The Structure of Maltese |first=Joseph |last=Aquilina |journal=Journal of the American Oriental Society |volume=80 |number=3 |date=July–September 1960 |pages=267–68 |doi=10.2307/596187|jstor=596187 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Europe's New Arabic Connection |first1=Louis |last1=Werner |first2=Alan |last2=Calleja |url=http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200406/europe.s.new.arabic.connection.htm |journal=Saudi Aramco World |date=November–December 2004 |access-date=2016-02-05 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120929195459/http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200406/europe.s.new.arabic.connection.htm |archive-date=2012-09-29 |url-status=dead }}</ref> It is based on [[Sicilian Arabic]], with influences from [[Sicilian language|Sicilian]], [[Italian language|Italian]], [[French language|French]] and, more recently, [[English language|English]]. It is unique in that it is the only Semitic language whose [[standard language|standard form]] is written in [[Latin script]]. It is also the second smallest official language of the [[European Union|EU]] in terms of speakers (after Irish), and the only official Semitic language within the EU. |
* [[Maltese language|Maltese]] ({{circa}} 500,000) is a [[Semitic language]] with [[Romance language|Romance]] and [[Germanic language|Germanic]] influences, spoken in [[Malta]].<ref>{{cite web |last=Alexander |first=Marie |title=2nd International Conference of Maltese Linguistics: Saturday, September 19 – Monday, September 21, 2009 |url=http://www.fb10.uni-bremen.de/maltese/abstracts.aspx |year=2009 |publisher=International Association of Maltese Linguistics |access-date=2 November 2009|display-authors=etal}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |first=J. |last=Aquilina |title=Maltese as a Mixed Language |journal=Journal of Semitic Studies |year=1958 |volume=3 |number=1 |pages=58–79 |doi=10.1093/jss/3.1.58}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=The Structure of Maltese |first=Joseph |last=Aquilina |journal=Journal of the American Oriental Society |volume=80 |number=3 |date=July–September 1960 |pages=267–68 |doi=10.2307/596187|jstor=596187 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Europe's New Arabic Connection |first1=Louis |last1=Werner |first2=Alan |last2=Calleja |url=http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200406/europe.s.new.arabic.connection.htm |journal=Saudi Aramco World |date=November–December 2004 |access-date=2016-02-05 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120929195459/http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200406/europe.s.new.arabic.connection.htm |archive-date=2012-09-29 |url-status=dead }}</ref> It is based on [[Sicilian Arabic]], with influences from [[Sicilian language|Sicilian]], [[Italian language|Italian]], [[French language|French]] and, more recently, [[English language|English]]. It is unique in that it is the only Semitic language whose [[standard language|standard form]] is written in [[Latin script]]. It is also the second smallest official language of the [[European Union|EU]] in terms of speakers (after Irish), and the only official Semitic language within the EU.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Cypriot Maronite Arabic]] (also known as Cypriot Arabic) is a [[varieties of Arabic|variety of Arabic]] spoken by [[Maronite]]s in [[Cyprus]]. Most speakers live in [[Nicosia]], but others are in the communities of [[Kormakiti]] and [[Limassol|Lemesos]]. Brought to the island by Maronites fleeing [[Lebanon]] over 700 years ago, this variety of Arabic has been influenced by [[Greek language|Greek]] in both [[phonology]] and [[vocabulary]], while retaining certain unusually archaic features in other respects. Dialects of [[Eastern Aramaic]] are spoken by [[Assyrian people|Assyrian]] communities in the Caucasus and southern Russia who fled the Assyrian Genocide during World War I. |
* [[Cypriot Maronite Arabic]] (also known as Cypriot Arabic) is a [[varieties of Arabic|variety of Arabic]] spoken by [[Maronite]]s in [[Cyprus]]. Most speakers live in [[Nicosia]], but others are in the communities of [[Kormakiti]] and [[Limassol|Lemesos]]. Brought to the island by Maronites fleeing [[Lebanon]] over 700 years ago, this variety of Arabic has been influenced by [[Greek language|Greek]] in both [[phonology]] and [[vocabulary]], while retaining certain unusually archaic features in other respects. Dialects of [[Eastern Aramaic]] are spoken by [[Assyrian people|Assyrian]] communities in the Caucasus and southern Russia who fled the Assyrian Genocide during World War I.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
===Sign languages=== |
===Sign languages=== |
||
{{Main|List of sign languages#Europe}} |
{{Main|List of sign languages#Europe}} |
||
Several dozen manual languages exist across Europe, with the most widespread sign language family being the [[French Sign Language family|Francosign languages]], with its languages found in countries from [[Iberian Peninsula|Iberia]] to the [[Balkans]] and the [[Baltics]]. Accurate historical information of sign and tactile languages is difficult to come by, with folk histories noting the existence signing communities across Europe hundreds of years ago. [[British Sign Language|British Sign Language (BSL)]] and [[French Sign Language|French Sign Language (LSF)]] are probably the oldest confirmed, continuously spoken sign languages. Alongside [[German Sign Language|German Sign Language (DGS)]] according to [[Ethnologue]], these three have the most numbers of signers, though very few institutions take appropriate statistics on contemporary signing populations, making legitimate data hard to find. |
Several dozen manual languages exist across Europe, with the most widespread sign language family being the [[French Sign Language family|Francosign languages]], with its languages found in countries from [[Iberian Peninsula|Iberia]] to the [[Balkans]] and the [[Baltics]]. Accurate historical information of sign and tactile languages is difficult to come by, with folk histories noting the existence signing communities across Europe hundreds of years ago. [[British Sign Language|British Sign Language (BSL)]] and [[French Sign Language|French Sign Language (LSF)]] are probably the oldest confirmed, continuously spoken sign languages. Alongside [[German Sign Language|German Sign Language (DGS)]] according to [[Ethnologue]], these three have the most numbers of signers, though very few institutions take appropriate statistics on contemporary signing populations, making legitimate data hard to find.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
Notably, few European sign languages have overt connections with the local majority/oral languages, aside from standard [[language contact]] and [[borrowing (linguistics)|borrowing]], meaning grammatically the sign languages and the oral languages of Europe are quite distinct from one another. Due to (visual/aural) modality differences, most sign languages are named for the larger ethnic nation in which they are spoken, plus the words "sign language", rendering what is spoken across much of [[France]], [[Wallonia]] and [[Romandy]] as [[French Sign Language]] or [[French Sign Language|LSF]] for: '''''l'''angue des '''s'''ignes '''f'''rançaise''. |
Notably, few European sign languages have overt connections with the local majority/oral languages, aside from standard [[language contact]] and [[borrowing (linguistics)|borrowing]], meaning grammatically the sign languages and the oral languages of Europe are quite distinct from one another. Due to (visual/aural) modality differences, most sign languages are named for the larger ethnic nation in which they are spoken, plus the words "sign language", rendering what is spoken across much of [[France]], [[Wallonia]] and [[Romandy]] as [[French Sign Language]] or [[French Sign Language|LSF]] for: '''''l'''angue des '''s'''ignes '''f'''rançaise''.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
Recognition of non-oral languages varies widely from region to region.<ref>{{Cite book|doi=10.1002/9781405198431.wbeal1417|chapter=Language Policy for Sign Languages|title=The Encyclopedia of Applied Linguistics|year=2014|last1=Reagan|first1=Timothy|pages=1–6|isbn=9781405194730}}</ref> Some countries afford legal recognition, even to official on a state level, whereas others continue to be actively suppressed.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Murray |first1=Joseph J. |title=Linguistic Human Rights Discourse in Deaf Community Activism |journal=Sign Language Studies |date=2015 |volume=15 |issue=4 |pages=379–410 |pmid=26190995 |url= |doi=10.1353/sls.2015.0012 |jstor=26190995 |pmc=4490244 }}</ref> |
Recognition of non-oral languages varies widely from region to region.<ref>{{Cite book|doi=10.1002/9781405198431.wbeal1417|chapter=Language Policy for Sign Languages|title=The Encyclopedia of Applied Linguistics|year=2014|last1=Reagan|first1=Timothy|pages=1–6|isbn=9781405194730}}</ref> Some countries afford legal recognition, even to official on a state level, whereas others continue to be actively suppressed.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Murray |first1=Joseph J. |title=Linguistic Human Rights Discourse in Deaf Community Activism |journal=Sign Language Studies |date=2015 |volume=15 |issue=4 |pages=379–410 |pmid=26190995 |url= |doi=10.1353/sls.2015.0012 |jstor=26190995 |pmc=4490244 }}</ref> |
||
The major sign linguistic families are: |
The major sign linguistic families are:{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[French Sign Language family|Francosign]] languages, such as [[French Sign Language|LSF]], [[Irish Sign Language|Irish SL]], [[Austrian Sign Language|Austrian Sign Language (ÖGS)]], [[Estonian Sign Language|Eesti Viipekeel]], and probably both [[Catalan Sign Language|Catalan]] and [[Valencian Sign Language]]s. |
* [[French Sign Language family|Francosign]] languages, such as [[French Sign Language|LSF]], [[Irish Sign Language|Irish SL]], [[Austrian Sign Language|Austrian Sign Language (ÖGS)]], [[Estonian Sign Language|Eesti Viipekeel]], and probably both [[Catalan Sign Language|Catalan]] and [[Valencian Sign Language]]s.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
** [[Danish Sign Language family|Danish Sign]] languages, such as [[Danish Sign Language|DTS]], [[Icelandic Sign Language|Icelandic Taknmal]], Faroese Taknmal, and [[Norwegian Sign Language|NTS]]. |
** [[Danish Sign Language family|Danish Sign]] languages, such as [[Danish Sign Language|DTS]], [[Icelandic Sign Language|Icelandic Taknmal]], Faroese Taknmal, and [[Norwegian Sign Language|NTS]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
** [[Austrian Sign Language|Austro]]-[[Hungarian Sign Language|Hungarian Sign]] descendants, including the sub-families descended from both (separately) the [[Yugoslav Sign Language]] and [[Russian Sign Language]], such as [[Macedonian Sign Language]] and [[Croatian Sign Language|HZJ]], or [[Lithuanian Sign Language|LGK]] and [[Ukrainian Sign Language|Ukrainian Sign Language (USL)]]. |
** [[Austrian Sign Language|Austro]]-[[Hungarian Sign Language|Hungarian Sign]] descendants, including the sub-families descended from both (separately) the [[Yugoslav Sign Language]] and [[Russian Sign Language]], such as [[Macedonian Sign Language]] and [[Croatian Sign Language|HZJ]], or [[Lithuanian Sign Language|LGK]] and [[Ukrainian Sign Language|Ukrainian Sign Language (USL)]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[BANZSL|Banzsl]] languages, such as [[British Sign Language|BSL]] and [[Northern Ireland Sign Language|Northern Ireland Sign Language (NISL)]]. |
* [[BANZSL|Banzsl]] languages, such as [[British Sign Language|BSL]] and [[Northern Ireland Sign Language|Northern Ireland Sign Language (NISL)]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
** [[Swedish Sign Language family|Swedish Sign]] family, such as [[Swedish Sign Language|SSL]], [[Finnish Sign Language|Viittomakieli]], [[Finland-Swedish Sign Language|FinnSSL]], and [[Portuguese Sign Language|Portuguese Sign Language (LGP)]], all of which ''may'' be descended from [[British Sign Language#History|Old BSL]]. |
** [[Swedish Sign Language family|Swedish Sign]] family, such as [[Swedish Sign Language|SSL]], [[Finnish Sign Language|Viittomakieli]], [[Finland-Swedish Sign Language|FinnSSL]], and [[Portuguese Sign Language|Portuguese Sign Language (LGP)]], all of which ''may'' be descended from [[British Sign Language#History|Old BSL]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[German Sign Language family|Germanosign]] languages, such as [[German Sign Language|DGS]] and [[Polish Sign Language|Polish Sign Language (PJM)]]. |
* [[German Sign Language family|Germanosign]] languages, such as [[German Sign Language|DGS]] and [[Polish Sign Language|Polish Sign Language (PJM)]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* Isolate languages, such as [[Albanian Sign Language]], [[Armenian Sign Language]], [[Caucasian Sign Language]], [[Spanish Sign Language|Spanish Sign Language (LSE)]], [[Turkish Sign Language|Turkish Sign Language (TİD)]], and perhaps [[Ghardaia Sign Language]]. |
* Isolate languages, such as [[Albanian Sign Language]], [[Armenian Sign Language]], [[Caucasian Sign Language]], [[Spanish Sign Language|Spanish Sign Language (LSE)]], [[Turkish Sign Language|Turkish Sign Language (TİD)]], and perhaps [[Ghardaia Sign Language]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
== History of standardization == |
== History of standardization == |
||
| Line 191: | Line 190: | ||
=== Language and identity, standardization processes === |
=== Language and identity, standardization processes === |
||
In the Middle Ages the two most important defining elements of Europe were ''Christianitas'' and ''Latinitas''. |
In the Middle Ages the two most important defining elements of Europe were ''Christianitas'' and ''Latinitas''.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The earliest dictionaries were glossaries: more or less structured lists of lexical pairs (in alphabetical order or according to conceptual fields). The Latin-German (Latin-Bavarian) ''[[Abrogans]]'' was among the first. A new wave of [[lexicography]] can be seen from the late 15th century onwards (after the introduction of the printing press, with the growing interest in standardisation of languages). |
The earliest dictionaries were glossaries: more or less structured lists of lexical pairs (in alphabetical order or according to conceptual fields). The Latin-German (Latin-Bavarian) ''[[Abrogans]]'' was among the first. A new wave of [[lexicography]] can be seen from the late 15th century onwards (after the introduction of the printing press, with the growing interest in standardisation of languages).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The concept of the [[nation state]] began to emerge in the [[early modern period]]. Nations adopted particular dialects as their national language. This, together with improved communications, led to official efforts to standardise the [[national language]], and a number of language academies were established: 1582 ''[[Accademia della Crusca]]'' in Florence, 1617 ''[[Fruchtbringende Gesellschaft]]'' in Weimar, 1635 ''[[Académie française]]'' in Paris, 1713 ''[[Real Academia Española]]'' in Madrid. Language became increasingly linked to nation as opposed to culture, and was also used to promote religious and ethnic identity: e.g. different [[Bible translations]] in the same language for Catholics and Protestants. |
The concept of the [[nation state]] began to emerge in the [[early modern period]]. Nations adopted particular dialects as their national language. This, together with improved communications, led to official efforts to standardise the [[national language]], and a number of language academies were established: 1582 ''[[Accademia della Crusca]]'' in Florence, 1617 ''[[Fruchtbringende Gesellschaft]]'' in Weimar, 1635 ''[[Académie française]]'' in Paris, 1713 ''[[Real Academia Española]]'' in Madrid. Language became increasingly linked to nation as opposed to culture, and was also used to promote religious and ethnic identity: e.g. different [[Bible translations]] in the same language for Catholics and Protestants.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The first languages whose standardisation was promoted included Italian (''questione della lingua'': Modern Tuscan/Florentine vs. Old Tuscan/Florentine vs. Venetian → Modern Florentine + archaic Tuscan + Upper Italian), French (the standard is based on Parisian), English (the standard is based on the London dialect) and (High) German (based on the dialects of the chancellery of Meissen in Saxony, Middle German, and the chancellery of Prague in Bohemia ("Common German")). But several other nations also began to develop a standard variety in the 16th century. |
The first languages whose standardisation was promoted included Italian (''questione della lingua'': Modern Tuscan/Florentine vs. Old Tuscan/Florentine vs. Venetian → Modern Florentine + archaic Tuscan + Upper Italian), French (the standard is based on Parisian), English (the standard is based on the London dialect) and (High) German (based on the dialects of the chancellery of Meissen in Saxony, Middle German, and the chancellery of Prague in Bohemia ("Common German")). But several other nations also began to develop a standard variety in the 16th century.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Lingua franca === |
=== Lingua franca === |
||
| Line 204: | Line 203: | ||
* [[Ancient Greek language|Classical Greek]] and then [[Koine Greek]] in the [[Mediterranean Sea|Mediterranean Basin]] from the [[Athenian Empire]] to the [[Eastern Roman Empire]], being replaced by [[Modern Greek]]. |
* [[Ancient Greek language|Classical Greek]] and then [[Koine Greek]] in the [[Mediterranean Sea|Mediterranean Basin]] from the [[Athenian Empire]] to the [[Eastern Roman Empire]], being replaced by [[Modern Greek]]. |
||
* [[Koine Greek]] and [[Modern Greek]], in the [[Byzantine Empire|Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire]] and other parts of the Balkans south of the [[Jireček Line]].<ref>{{cite journal |title=Review [untitled] of Ariadna Camariano-Cioran, Les Academies Princieres de Bucarest et de Jassy et leur Professeurs |journal=Church History |volume=45 |number=1 |date = March 1976|pages=115–116 |quote=...Greek, the ''lingua franca'' of commerce and religion, provided a cultural unity to the Balkans...Greek penetrated Moldavian and Wallachian territories as early as the fourteenth century.... The heavy influence of Greek culture upon the intellectual and academic life of Bucharest and [[Iaşi|Jassy]] was longer termed than historians once believed. |first=James Steve |last=Counelis |doi=10.2307/3164593|jstor=3164593 |s2cid=162293323 }}</ref> |
* [[Koine Greek]] and [[Modern Greek]], in the [[Byzantine Empire|Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire]] and other parts of the Balkans south of the [[Jireček Line]].<ref>{{cite journal |title=Review [untitled] of Ariadna Camariano-Cioran, Les Academies Princieres de Bucarest et de Jassy et leur Professeurs |journal=Church History |volume=45 |number=1 |date = March 1976|pages=115–116 |quote=...Greek, the ''lingua franca'' of commerce and religion, provided a cultural unity to the Balkans...Greek penetrated Moldavian and Wallachian territories as early as the fourteenth century.... The heavy influence of Greek culture upon the intellectual and academic life of Bucharest and [[Iaşi|Jassy]] was longer termed than historians once believed. |first=James Steve |last=Counelis |doi=10.2307/3164593|jstor=3164593 |s2cid=162293323 }}</ref> |
||
* [[Vulgar Latin]] and [[Late Latin]] among the uneducated and educated populations respectively of the [[Roman Empire]] and the states that followed it in the same range no later than 900 AD; [[Medieval Latin]] and [[Renaissance Latin]] among the educated populations of western, northern, central and part of eastern Europe until the rise of the national languages in that range, beginning with the first language academy in Italy in 1582/83; [[new Latin]] written only in scholarly and scientific contexts by a small minority of the educated population at scattered locations over all of Europe; [[ecclesiastical Latin]], in spoken and written contexts of liturgy and church administration only, over the range of the [[Roman Catholic Church]]. |
* [[Vulgar Latin]] and [[Late Latin]] among the uneducated and educated populations respectively of the [[Roman Empire]] and the states that followed it in the same range no later than 900 AD; [[Medieval Latin]] and [[Renaissance Latin]] among the educated populations of western, northern, central and part of eastern Europe until the rise of the national languages in that range, beginning with the first language academy in Italy in 1582/83; [[new Latin]] written only in scholarly and scientific contexts by a small minority of the educated population at scattered locations over all of Europe; [[ecclesiastical Latin]], in spoken and written contexts of liturgy and church administration only, over the range of the [[Roman Catholic Church]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Mediterranean Lingua Franca|Lingua Franca]] or Sabir, the original of the name, an Italian-based [[pidgin]] language of mixed origins used by maritime commercial interests around the Mediterranean in the Middle Ages and early Modern Age.<ref>{{cite book |title=Lingua Franca in the Mediterranean |first=John E. |last=Wansbrough |chapter=Chapter 3: Lingua Franca |year=1996 |publisher=Routledge}}</ref> |
* [[Mediterranean Lingua Franca|Lingua Franca]] or Sabir, the original of the name, an Italian-based [[pidgin]] language of mixed origins used by maritime commercial interests around the Mediterranean in the Middle Ages and early Modern Age.<ref>{{cite book |title=Lingua Franca in the Mediterranean |first=John E. |last=Wansbrough |chapter=Chapter 3: Lingua Franca |year=1996 |publisher=Routledge}}</ref> |
||
* [[Old French]] in continental western European countries and in the [[Crusader states]].<ref name=calvet175-176>{{cite book |title=Language wars and linguistic politics |first=Louis Jean |last=Calvet |location=Oxford [England]; New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1998 |pages=175–76}}</ref> |
* [[Old French]] in continental western European countries and in the [[Crusader states]].<ref name=calvet175-176>{{cite book |title=Language wars and linguistic politics |first=Louis Jean |last=Calvet |location=Oxford [England]; New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1998 |pages=175–76}}</ref> |
||
* [[Czech language|Czech]], mainly during the reign of [[Holy Roman Empire|Holy Roman Emperor]] [[Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor|Charles IV]] (14th century) but also during other periods of Bohemian control over the Holy Roman Empire. |
* [[Czech language|Czech]], mainly during the reign of [[Holy Roman Empire|Holy Roman Emperor]] [[Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor|Charles IV]] (14th century) but also during other periods of Bohemian control over the Holy Roman Empire.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Middle Low German]], around the 14th–16th century, during the heyday of the [[Hanseatic League]], mainly in Northeastern Europe across the Baltic Sea. |
* [[Middle Low German]], around the 14th–16th century, during the heyday of the [[Hanseatic League]], mainly in Northeastern Europe across the Baltic Sea. |
||
* [[Spanish language|Spanish]] as Castilian in Spain and [[New Spain]] from the times of [[the Catholic Monarchs]] and [[Christopher Columbus|Columbus]], c. 1492; that is, after the [[Reconquista]], until established as a national language in the times of [[Louis XIV]], c. 1648; subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the [[Spanish Empire]].<ref>{{cite book |page=[https://archive.org/details/decolonizinginte00jone/page/n55 98] |title=Decolonizing international relations |url=https://archive.org/details/decolonizinginte00jone |url-access=limited |first=Branwen Gruffydd |last=Jones |location=Lanham, MD|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2006}}</ref> |
* [[Spanish language|Spanish]] as Castilian in Spain and [[New Spain]] from the times of [[the Catholic Monarchs]] and [[Christopher Columbus|Columbus]], c. 1492; that is, after the [[Reconquista]], until established as a national language in the times of [[Louis XIV]], c. 1648; subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the [[Spanish Empire]].<ref>{{cite book |page=[https://archive.org/details/decolonizinginte00jone/page/n55 98] |title=Decolonizing international relations |url=https://archive.org/details/decolonizinginte00jone |url-access=limited |first=Branwen Gruffydd |last=Jones |location=Lanham, MD|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2006}}</ref> |
||
* [[Polish language|Polish]], due to the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] (16th–18th centuries). |
* [[Polish language|Polish]], due to the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] (16th–18th centuries).{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Italian language|Italian]] due to the [[Renaissance]], the [[opera]], the [[Italian Empire]], the [[Italian fashion|fashion industry]] and the influence of the [[Roman Catholic church]].<ref>{{harvnb|Kahane|1986|p=495}}</ref> |
* [[Italian language|Italian]] due to the [[Renaissance]], the [[opera]], the [[Italian Empire]], the [[Italian fashion|fashion industry]] and the influence of the [[Roman Catholic church]].<ref>{{harvnb|Kahane|1986|p=495}}</ref> |
||
* [[French language|French]] from the golden age under [[Cardinal Richelieu]] and [[Louis XIV]] c. 1648; i.e., after the [[Thirty Years' War]], in France and the [[French colonial empire]], until established as the national language during the [[French Revolution]] of 1789 and subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the various [[French colonial empire|French Empires]].<ref name=calvet175-176/> |
* [[French language|French]] from the golden age under [[Cardinal Richelieu]] and [[Louis XIV]] c. 1648; i.e., after the [[Thirty Years' War]], in France and the [[French colonial empire]], until established as the national language during the [[French Revolution]] of 1789 and subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the various [[French colonial empire|French Empires]].<ref name=calvet175-176/> |
||
* [[German language|German]] in Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe.<ref>{{cite journal |first1=Jeroen |last1=Darquennes |first2=Peter |last2=Nelde |title=German as a Lingua Franca |journal=Annual Review of Applied Linguistics |volume=26 |pages=61–77 |year=2006 |doi=10.1017/s0267190506000043|s2cid=61449212 }}</ref> |
* [[German language|German]] in Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe.<ref>{{cite journal |first1=Jeroen |last1=Darquennes |first2=Peter |last2=Nelde |title=German as a Lingua Franca |journal=Annual Review of Applied Linguistics |volume=26 |pages=61–77 |year=2006 |doi=10.1017/s0267190506000043|s2cid=61449212 }}</ref> |
||
* [[English language|English]] in [[Great Britain]] until its consolidation as a national language in the [[Renaissance]] and the rise of [[Modern English]]; subsequently internationally under the various states in or formerly in the [[British Empire]]; globally since the victories of the predominantly English speaking countries ([[United States]], [[United Kingdom]], [[Canada]], [[Australia]], [[New Zealand]], and others) and their allies in the two world wars ending in 1918 ([[World War I]]) and 1945 ([[World War II]]) and the subsequent rise of the United States as a [[superpower]] and major [[United States#Culture|cultural influence]]. |
* [[English language|English]] in [[Great Britain]] until its consolidation as a national language in the [[Renaissance]] and the rise of [[Modern English]]; subsequently internationally under the various states in or formerly in the [[British Empire]]; globally since the victories of the predominantly English speaking countries ([[United States]], [[United Kingdom]], [[Canada]], [[Australia]], [[New Zealand]], and others) and their allies in the two world wars ending in 1918 ([[World War I]]) and 1945 ([[World War II]]) and the subsequent rise of the United States as a [[superpower]] and major [[United States#Culture|cultural influence]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
* [[Russian language|Russian]] in the former [[Soviet Union]] and [[Russian Empire]] including [[Northern Asia|Northern]] and [[Central Asia]]. |
* [[Russian language|Russian]] in the former [[Soviet Union]] and [[Russian Empire]] including [[Northern Asia|Northern]] and [[Central Asia]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Linguistic minorities === |
=== Linguistic minorities === |
||
Historical attitudes towards linguistic diversity are illustrated by two French laws: the [[Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts|Ordonnance de Villers-Cotterêts]] (1539), which said that every document in France should be written in French (neither in Latin nor in Occitan) and the [[Toubon Law|Loi Toubon]] (1994), which aimed to eliminate anglicisms from official documents. States and populations within a state have often resorted to war to settle their differences. There have been attempts to prevent such hostilities: two such initiatives were promoted by the [[Council of Europe]], founded in 1949, which affirms the right of minority language speakers to use their language fully and freely.<ref>{{cite web|title=European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages: Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992|url=http://conventions.coe.int/treaty/en/Treaties/Html/148.htm|publisher=Council of Europe|year=1992}}</ref> The Council of Europe is committed to protecting linguistic diversity. Currently all European countries except [[France]], [[Andorra]] and [[Turkey]] have signed the [[Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities]], while [[Greece]], [[Iceland]] and [[Luxembourg]] have signed it, but have not ratified it; this framework entered into force in 1998. Another European treaty, the [[European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages]], was adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the [[Council of Europe]]: it entered into force in 1998, and while it is legally binding for 24 countries, [[France]], [[Iceland]], [[Italy]], [[North Macedonia]], [[Moldova]] and [[Russia]] have chosen to sign without ratifying the convention. |
Historical attitudes towards linguistic diversity are illustrated by two French laws: the [[Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts|Ordonnance de Villers-Cotterêts]] (1539), which said that every document in France should be written in French (neither in Latin nor in Occitan) and the [[Toubon Law|Loi Toubon]] (1994), which aimed to eliminate anglicisms from official documents. States and populations within a state have often resorted to war to settle their differences. There have been attempts to prevent such hostilities: two such initiatives were promoted by the [[Council of Europe]], founded in 1949, which affirms the right of minority language speakers to use their language fully and freely.<ref>{{cite web|title=European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages: Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992|url=http://conventions.coe.int/treaty/en/Treaties/Html/148.htm|publisher=Council of Europe|year=1992}}</ref> The Council of Europe is committed to protecting linguistic diversity. Currently all European countries except [[France]], [[Andorra]] and [[Turkey]] have signed the [[Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities]], while [[Greece]], [[Iceland]] and [[Luxembourg]] have signed it, but have not ratified it; this framework entered into force in 1998. Another European treaty, the [[European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages]], was adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the [[Council of Europe]]: it entered into force in 1998, and while it is legally binding for 24 countries, [[France]], [[Iceland]], [[Italy]], [[North Macedonia]], [[Moldova]] and [[Russia]] have chosen to sign without ratifying the convention.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== Scripts === |
=== Scripts === |
||
| Line 238: | Line 237: | ||
]]--> |
]]--> |
||
The main scripts used in Europe today are the [[Latin script|Latin]] and [[Cyrillic script|Cyrillic]]. |
The main scripts used in Europe today are the [[Latin script|Latin]] and [[Cyrillic script|Cyrillic]].{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The [[Greek alphabet]] was derived from the [[Phoenician alphabet]], and Latin was derived from the Greek via the [[Old Italic alphabet]]. In the Early Middle Ages, [[Ogham]] was used in Ireland and [[runes]] (derived from Old Italic script) in Scandinavia. Both were replaced in general use by the Latin alphabet by the Late Middle Ages. The Cyrillic script was derived from the Greek with the first texts appearing around 940 AD. |
The [[Greek alphabet]] was derived from the [[Phoenician alphabet]], and Latin was derived from the Greek via the [[Old Italic alphabet]]. In the Early Middle Ages, [[Ogham]] was used in Ireland and [[runes]] (derived from Old Italic script) in Scandinavia. Both were replaced in general use by the Latin alphabet by the Late Middle Ages. The Cyrillic script was derived from the Greek with the first texts appearing around 940 AD.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
{{See also|Antiqua–Fraktur dispute}} |
{{See also|Antiqua–Fraktur dispute}} |
||
Around 1900 there were mainly two typeface variants of the [[Latin alphabet]] used in Europe: [[Antiqua (typeface class)|Antiqua]] and [[Fraktur]]. Fraktur was used most for German, Estonian, Latvian, Norwegian and Danish whereas Antiqua was used for Italian, Spanish, French, Polish, Portuguese, English, Romanian, Swedish and Finnish. The Fraktur variant was banned by [[Hitler]] in 1941, having been described as "[[Schwabacher]] Jewish letters".<ref>[http://www.ligaturix.de/bormann.htm Facsimile of Bormann's Memorandum (in German)]<br /> |
Around 1900 there were mainly two typeface variants of the [[Latin alphabet]] used in Europe: [[Antiqua (typeface class)|Antiqua]] and [[Fraktur]]. Fraktur was used most for German, Estonian, Latvian, Norwegian and Danish whereas Antiqua was used for Italian, Spanish, French, Polish, Portuguese, English, Romanian, Swedish and Finnish. The Fraktur variant was banned by [[Hitler]] in 1941, having been described as "[[Schwabacher]] Jewish letters".<ref>[http://www.ligaturix.de/bormann.htm Facsimile of Bormann's Memorandum (in German)]<br /> |
||
The memorandum itself is typed in Antiqua, but the [[NSDAP]] [[letterhead]] is printed in Fraktur.<br />"For general attention, on behalf of the Führer, I make the following announcement:<br />It is wrong to regard or to describe the so‑called Gothic script as a German script. In reality, the so‑called Gothic script consists of Schwabach Jew letters. Just as they later took control of the newspapers, upon the introduction of printing the Jews residing in Germany took control of the printing presses and thus in Germany the Schwabach Jew letters were forcefully introduced.<br />Today the Führer, talking with Herr Reichsleiter Amann and Herr Book Publisher Adolf Müller, has decided that in the future the Antiqua script is to be described as normal script. All printed materials are to be gradually converted to this normal script. As soon as is feasible in terms of textbooks, only the normal script will be taught in village and state schools.<br />The use of the Schwabach Jew letters by officials will in future cease; appointment certifications for functionaries, street signs, and so forth will in future be produced only in normal script.<br />On behalf of the Führer, Herr Reichsleiter Amann will in future convert those newspapers and periodicals that already have foreign distribution, or whose foreign distribution is desired, to normal script".</ref> Other scripts have historically been in use in Europe, including Phoenician, from which modern Latin letters descend, Ancient [[Egyptian hieroglyphs]] on Egyptian artefacts traded during Antiquity, various runic systems used in Northern Europe preceding Christianisation, and Arabic during the era of the Ottoman Empire. |
The memorandum itself is typed in Antiqua, but the [[NSDAP]] [[letterhead]] is printed in Fraktur.<br />"For general attention, on behalf of the Führer, I make the following announcement:<br />It is wrong to regard or to describe the so‑called Gothic script as a German script. In reality, the so‑called Gothic script consists of Schwabach Jew letters. Just as they later took control of the newspapers, upon the introduction of printing the Jews residing in Germany took control of the printing presses and thus in Germany the Schwabach Jew letters were forcefully introduced.<br />Today the Führer, talking with Herr Reichsleiter Amann and Herr Book Publisher Adolf Müller, has decided that in the future the Antiqua script is to be described as normal script. All printed materials are to be gradually converted to this normal script. As soon as is feasible in terms of textbooks, only the normal script will be taught in village and state schools.<br />The use of the Schwabach Jew letters by officials will in future cease; appointment certifications for functionaries, street signs, and so forth will in future be produced only in normal script.<br />On behalf of the Führer, Herr Reichsleiter Amann will in future convert those newspapers and periodicals that already have foreign distribution, or whose foreign distribution is desired, to normal script".</ref> Other scripts have historically been in use in Europe, including Phoenician, from which modern Latin letters descend, Ancient [[Egyptian hieroglyphs]] on Egyptian artefacts traded during Antiquity, various runic systems used in Northern Europe preceding Christianisation, and Arabic during the era of the Ottoman Empire.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
[[Old Hungarian alphabet|Hungarian rovás]] was used by the Hungarian people in the early Middle Ages, but it was gradually replaced with the Latin-based Hungarian alphabet when Hungary became a kingdom, though it was revived in the 20th century and has certain marginal, but growing area of usage since then. |
[[Old Hungarian alphabet|Hungarian rovás]] was used by the Hungarian people in the early Middle Ages, but it was gradually replaced with the Latin-based Hungarian alphabet when Hungary became a kingdom, though it was revived in the 20th century and has certain marginal, but growing area of usage since then.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
=== European Union === |
=== European Union === |
||
{{main|Languages of the European Union}} |
{{main|Languages of the European Union}} |
||
The [[European Union]] (as of 2021) had 27 member states accounting for a population of 447 million, or about 60% of the population of Europe. |
The [[European Union]] (as of 2021) had 27 member states accounting for a population of 447 million, or about 60% of the population of Europe.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The European Union has designated by agreement with the member states 24 languages as "official and working": Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Irish, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish and Swedish.<ref>{{cite web|title=Languages Policy: Linguistic diversity: Official languages of the EU|url=http://ec.europa.eu/languages/policy/linguistic-diversity/official-languages-eu_en.htm|publisher=European Commission, European Union|date=4 June 2009|access-date= 9 August 2015}}</ref> This designation provides member states with two "entitlements": the member state may communicate with the EU in any of the designated languages, and view "EU regulations and other legislative documents" in that language.<ref>{{cite web|title=Languages of Europe: Official EU languages |url=http://ec.europa.eu/education/languages/languages-of-europe/doc135_en.htm |publisher=European Commission, European Union |year=2009 |access-date=5 November 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090202112407/http://ec.europa.eu/education/languages/languages-of-europe/doc135_en.htm |archive-date=2 February 2009 }}</ref> |
The European Union has designated by agreement with the member states 24 languages as "official and working": Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Irish, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish and Swedish.<ref>{{cite web|title=Languages Policy: Linguistic diversity: Official languages of the EU|url=http://ec.europa.eu/languages/policy/linguistic-diversity/official-languages-eu_en.htm|publisher=European Commission, European Union|date=4 June 2009|access-date= 9 August 2015}}</ref> This designation provides member states with two "entitlements": the member state may communicate with the EU in any of the designated languages, and view "EU regulations and other legislative documents" in that language.<ref>{{cite web|title=Languages of Europe: Official EU languages |url=http://ec.europa.eu/education/languages/languages-of-europe/doc135_en.htm |publisher=European Commission, European Union |year=2009 |access-date=5 November 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090202112407/http://ec.europa.eu/education/languages/languages-of-europe/doc135_en.htm |archive-date=2 February 2009 }}</ref> |
||
| Line 260: | Line 259: | ||
{{See|List of endangered languages in Europe|List of extinct languages of Europe|List of languages of Russia}} |
{{See|List of endangered languages in Europe|List of extinct languages of Europe|List of languages of Russia}} |
||
The following is a table of European languages. The number of speakers as a first or second language (L1 and L2 speakers) listed are speakers in Europe only;{{refn|"Europe" is taken as a geographical term, [[Definition of Europe|defined]] by the conventional [[Europe-Asia boundary]] along the Caucasus and the Urals. Estimates for populations geographically in Europe are given for [[transcontinental countries]].|group=nb}} see [[list of languages by number of native speakers]] and [[list of languages by total number of speakers]] for global estimates on numbers of speakers. |
The following is a table of European languages. The number of speakers as a first or second language (L1 and L2 speakers) listed are speakers in Europe only;{{refn|"Europe" is taken as a geographical term, [[Definition of Europe|defined]] by the conventional [[Europe-Asia boundary]] along the Caucasus and the Urals. Estimates for populations geographically in Europe are given for [[transcontinental countries]].|group=nb}} see [[list of languages by number of native speakers]] and [[list of languages by total number of speakers]] for global estimates on numbers of speakers.{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
The list is intended to include any language variety with an [[ISO 639]] code. However, it omits sign languages. Because the ISO-639-2 and ISO-639-3 codes have different definitions, this means that some communities of speakers may be listed more than once. For instance, speakers of [[Bavarian language|Bavarian]] are listed both under "Bavarian" (ISO-639-3 code ''bar'') as well as under "German" (ISO-639-2 code ''de''). |
The list is intended to include any language variety with an [[ISO 639]] code. However, it omits sign languages. Because the ISO-639-2 and ISO-639-3 codes have different definitions, this means that some communities of speakers may be listed more than once. For instance, speakers of [[Bavarian language|Bavarian]] are listed both under "Bavarian" (ISO-639-3 code ''bar'') as well as under "German" (ISO-639-2 code ''de'').{{Citation needed|date=August 2022}} |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
||
Revision as of 21:28, 16 August 2022
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2019) |
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language; within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic with more than 200 million speakers each, between them accounting for close to 90% of Europeans. Smaller phyla of Indo-European found in Europe include Hellenic (Greek, c. 13 million), Baltic (c. 7 million), Albanian (c. 5 million), Celtic (c. 4 million), Armenian (c. 4 million) and Indo-Aryan (Romani, c. 1.5 million).
Of the approximately 45 million Europeans speaking non-Indo-European languages, most speak languages within either the Uralic or Turkic families. Still smaller groups (such as Basque, Semitic languages, and various languages of the Caucasus) account for less than 1% of the European population between them. Immigration has added sizeable communities of speakers of African and Asian languages, amounting to about 4% of the population,[1] with Arabic being the most widely spoken of them.
Five languages have more than 50 million native speakers in Europe: Russian, French, Italian, German, and English. Russian is the most spoken native language in Europe; and English has the largest number of speakers in total, including some 200 million speakers of English as a second or foreign language. (See English language in Europe.)
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European language family is descended from Proto-Indo-European, which is believed to have been spoken thousands of years ago. Early speakers of Indo-European daughter languages most likely expanded into Europe with the incipient Bronze Age, around 4,000 years ago (Bell-Beaker culture).
Germanic
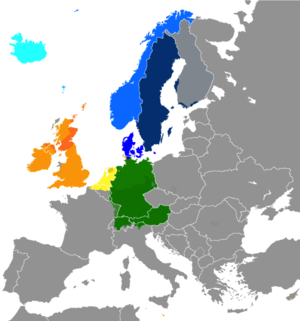
The Germanic languages make up the predominant language family in Western, Northern and Central Europe. An estimated 210 million Europeans are native speakers of Germanic languages, the largest groups being German (c. 95 million), English (c. 70 million), Dutch (c. 24 million), Swedish (c. 10 million), Danish (c. 6 million), and Norwegian (c. 5 million).[citation needed]
There are two extant major sub-divisions: West Germanic and North Germanic. A third group, East Germanic, is now extinct; the only known surviving East Germanic texts are written in the Gothic language. West Germanic is divided into Anglo-Frisian (including English), Low German, Low Franconian (including Dutch) and High German (including Standard German).[citation needed]
Anglo-Frisian
The Anglo-Frisian language family is now mostly represented by English (Anglic), descended from the Old English language spoken by the Anglo-Saxons:
- English, the main language of the United Kingdom and the most widespread language in the Republic of Ireland, also spoken as a second or third language by many Europeans.[citation needed]
- Scots, spoken in Scotland and Ulster, recognized by some as a language and by others as a dialect of English.[citation needed]
The Frisian languages are spoken by about 500,000 Frisians, who live on the southern coast of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. These languages include West Frisian, East Frisian (only surviving dialect of it is Saterlandic) and North Frisian.[citation needed]
Dutch
Dutch is spoken throughout the Netherlands, the northern half of Belgium, as well as the Nord-Pas de Calais region of France. The traditional dialects of the Lower Rhine region of Germany, are linguistically more closely related to Dutch than to modern German. In Belgian and French contexts, Dutch is sometimes referred to as Flemish. Dutch dialects are varied and cut across national borders.[citation needed]
German
German is spoken throughout Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, much of Switzerland (including the northeast areas bordering on Germany and Austria), northern Italy (South Tyrol), Luxembourg, the East Cantons of Belgium and the Alsace and Lorraine regions of France.[citation needed]
There are several groups of German dialects:
- High German includes several dialect families:
- Standard German
- Central German dialects, spoken in central Germany and including Luxembourgish
- High Franconian, a family of transitional dialects between Central and Upper High German
- Upper German, including Bavarian and Swiss German
- Yiddish is a Jewish language developed in Germany and shares many features of High German dialects and Hebrew.
- Low German (or Low Saxon) is spoken in various regions throughout Northern Germany and the northern and eastern parts of the Netherlands. It is an official language in Germany. It may be separated into West Low German and East Low German.[citation needed]
North Germanic (Scandinavian)
The North Germanic languages are spoken in Scandinavian countries and include Danish (Denmark), Norwegian (Norway), Swedish (Sweden and parts of Finland), or Elfdalian (in a small part of central Sweden), Faroese (Faroe Islands), and Icelandic (Iceland).[citation needed]
English has a long history of contact with Scandinavian languages, given the immigration of Scandinavians early in the history of Britain, and shares various features with the Scandinavian languages.[2] Even so, especially Swedish, but also Danish and Norwegian, have strong vocabulary connections to the German language.[citation needed]
Romance

Roughly 215 million Europeans (primarily in Southern and Western Europe) are native speakers of Romance languages, the largest groups including:[citation needed]
French (c. 72 million), Italian (c. 65 million), Spanish (c. 40 million), Romanian (c. 24 million), Portuguese (c. 10 million), Catalan (c. 7 million), Sicilian (c. 5 million, also subsumed under Italian), Venetian (c. 4 million), Galician (c. 2 million), Sardinian (c. 1 million), Occitan (c. 500,000), besides numerous smaller communities.
The Romance languages evolved from varieties of Vulgar Latin spoken in the various parts of the Roman Empire in Late Antiquity. Latin was itself part of the (otherwise extinct) Italic branch of Indo-European.[citation needed] Romance languages are divided phylogenetically into Italo-Western, Eastern Romance (including Romanian) and Sardinian. The Romance-speaking area of Europe is occasionally referred to as Latin Europe.[3]
We can further break down Italo-Western into the Italo-Dalmatian languages (sometimes grouped with Eastern Romance), including the Tuscan-derived Italian and numerous local Romance languages in Italy as well as Dalmatian, and the Western Romance languages. The Western Romance languages in turn separate into the Gallo-Romance languages, including French and its varieties (Langues d'oïl), the Rhaeto-Romance languages and the Gallo-Italic languages; the Occitano-Romance languages, grouped with either Gallo-Romance or East Iberian, including Occitan, Catalan and Aragonese; and finally the West Iberian languages (Spanish-Portuguese), including the Astur-Leonese languages, Galician-Portuguese, and Castilian.[citation needed]
Slavic

Slavic languages are spoken in large areas of Southern, Central and Eastern Europe.[citation needed] An estimated 250 million Europeans are native speakers of Slavic languages,[citation needed] the largest groups being Russian (c. 110 million in European Russia and adjacent parts of Eastern Europe, Russian forming the largest linguistic community in Europe), Polish (c. 45 million), Ukrainian (c. 40 million), Serbo-Croatian (c. 21 million), Czech (c. 11 million), Bulgarian (c. 9 million), Slovak (c. 5 million) Belarusian and Slovene (c. 3 million each) and Macedonian (c. 2 million).[citation needed]
Phylogenetically, Slavic is divided into three subgroups:
- West Slavic includes Polish, Czech, Slovak, Lower Sorbian, Upper Sorbian, Silesian and Kashubian.[citation needed]
- East Slavic includes Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, and Rusyn.[citation needed]
- South Slavic includes Slovene and Serbo-Croatian in the southwest and Bulgarian, Macedonian and Church Slavonic (a liturgical language) in the southeast, each with numerous distinctive dialects. South Slavic languages constitute a dialect continuum where standard Slovene, Macedonian and Bulgarian are each based on a distinct dialect, whereas pluricentric Serbo-Croatian boasts four mutually intelligible national standard varieties all based on a single dialect, Shtokavian.[citation needed]
Others
- Greek (c. 13 million) is the official language of Greece and Cyprus, and there are Greek-speaking enclaves in Albania, Bulgaria, Italy, North Macedonia, Romania, Georgia, Ukraine, Lebanon, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Turkey, and in Greek communities around the world. Dialects of modern Greek that originate from Attic Greek (through Koine and then Medieval Greek) are Cappadocian, Pontic, Cretan, Cypriot, Katharevousa, and Yevanic.[citation needed]
- Italiot Greek is, debatably, a Doric dialect of Greek. It is spoken in southern Italy only, in the southern Calabria region (as Grecanic)[4][5][6][7][8] and in the Salento region (as Griko). It was studied by the German linguist Gerhard Rohlfs during the 1930s and 1950s.[citation needed]
- Tsakonian is a Doric dialect of the Greek language spoken in the lower Arcadia region of the Peloponnese around the village of Leonidio[citation needed]
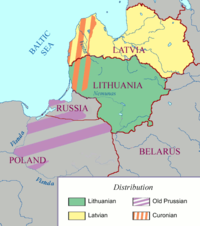
- The Baltic languages are spoken in Lithuania (Lithuanian (c. 3 million), Samogitian) and Latvia (Latvian (c. 2 million), Latgalian). Samogitian and Latgalian are usually considered to be dialects of Lithuanian and Latvian respectively.[citation needed]
- There are also several extinct Baltic languages, including: Galindian, Curonian, Old Prussian, Selonian, Semigallian and Sudovian.[citation needed]
- Albanian (c. 5 million) has two major dialects, Tosk Albanian and Gheg Albanian. It is spoken in Albania and Kosovo, neighboring North Macedonia, Serbia, Greece, Italy, and Montenegro. It is also widely spoken in the Albanian diaspora.[citation needed]
- Armenian (c. 7 million) has two major forms, Western Armenian and Eastern Armenian. It is spoken in Armenia, Artsakh and Georgia (Samtskhe-Javakheti), also Russia, France, Italy, Turkey, Greece, and Cyprus. It is also widely spoken in the Armenian Diaspora. [citation needed]
- There are six living Celtic languages, spoken in areas of northwestern Europe dubbed the "Celtic nations". All six are members of the Insular Celtic family, which in turn is divided into:
- Brittonic family: Welsh (Wales, c. 700,000), Cornish (Cornwall, c. 500) and Breton (Brittany, c. 200,000)
- Goidelic family: Irish (Ireland, c. 2,000,000), Scottish Gaelic (Scotland, c. 50,000), and Manx (Isle of Man, 1,800)[citation needed]
- Continental Celtic languages had previously been spoken across Europe from Iberia and Gaul to Asia Minor, but became extinct in the first millennium AD.[citation needed]
- The Indo-Aryan languages have one major representation: Romani (c. 1.5 million speakers), introduced in Europe during the late medieval period. Lacking a nation state, Romani is spoken as a minority language throughout Europe.[citation needed]
- The Iranian languages in Europe are natively represented in the North Caucasus, notably with Ossetian (c. 600,000).[citation needed]
Non-Indo-European languages
Turkic
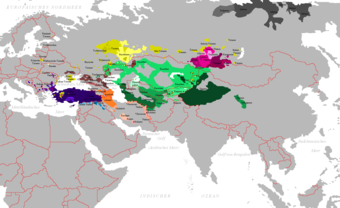
- Oghuz languages in Europe include Turkish, spoken in East Thrace and by immigrant communities; Azerbaijani is spoken in Northeast Azerbaijan and parts of Southern Russia and Gagauz is spoken in Gagauzia.[citation needed]
- Kipchak languages in Europe include Karaim, Crimean Tatar and Krymchak, which is spoken in mainly Crimea; Tatar, which is spoken in Tatarstan; Bashkir, which is spoken in Bashkortostan; Karachay-Balkar, which is spoken in the North Caucasus, and Kazakh, which is spoken in Northwest Kazakhstan.[citation needed]
- Oghur languages were historically indigenous to much of Eastern Europe; however, most of them are extinct today, with the exception of Chuvash, which is spoken in Chuvashia.[citation needed]
Uralic

Uralic is native to northern Eurasia. Finno-Ugric groups the Uralic languages other than Samoyedic.[citation needed] Finnic languages include Finnish (c. 5 million), Estonian (c. 1 million) and Mari (c. 400,000). The Sami languages (c. 30,000) are closely related to Finnic.[citation needed]
The Ugric languages are represented in Europe with the Hungarian language (c. 13 million), historically introduced with the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin of the 9th century.[citation needed] The Samoyedic Nenets language is spoken in Nenets Autonomous Okrug of Russia, located in the far northeastern corner of Europe (as delimited by the Ural Mountains).[citation needed]
Others
- The Basque language (or Euskara, c. 750,000) is a language isolate and the ancestral language of the Basque people who inhabit the Basque Country, a region in the western Pyrenees mountains mostly in northeastern Spain and partly in southwestern France of about 3 million inhabitants, where it is spoken fluently by about 750,000 and understood by more than 1.5 million people. Basque is directly related to ancient Aquitanian, and it is likely that an early form of the Basque language was present in Western Europe before the arrival of the Indo-European languages in the area in the Bronze Age.[citation needed]
- North Caucasian languages is a geographical blanket term for two unrelated language families spoken chiefly in the north Caucasus and Turkey—the Northwest Caucasian family (including Abkhaz and Circassian) and the Northeast Caucasian family, spoken mainly in the border area of the southern Russian Federation (including Dagestan, Chechnya, and Ingushetia).[citation needed]
- Kalmyk is a Mongolic language, spoken in the Republic of Kalmykia, part of the Russian Federation. Its speakers entered the Volga region in the early 17th century.[citation needed]
- Kartvelian languages (also known as Southwest Caucasian languages), the most common of which is Georgian (c. 3.5 million), others being Mingrelian and Svan, spoken mainly in the Caucasus and Anatolia.[citation needed]
- Maltese (c. 500,000) is a Semitic language with Romance and Germanic influences, spoken in Malta.[9][10][11][12] It is based on Sicilian Arabic, with influences from Sicilian, Italian, French and, more recently, English. It is unique in that it is the only Semitic language whose standard form is written in Latin script. It is also the second smallest official language of the EU in terms of speakers (after Irish), and the only official Semitic language within the EU.[citation needed]
- Cypriot Maronite Arabic (also known as Cypriot Arabic) is a variety of Arabic spoken by Maronites in Cyprus. Most speakers live in Nicosia, but others are in the communities of Kormakiti and Lemesos. Brought to the island by Maronites fleeing Lebanon over 700 years ago, this variety of Arabic has been influenced by Greek in both phonology and vocabulary, while retaining certain unusually archaic features in other respects. Dialects of Eastern Aramaic are spoken by Assyrian communities in the Caucasus and southern Russia who fled the Assyrian Genocide during World War I.[citation needed]
Sign languages
Several dozen manual languages exist across Europe, with the most widespread sign language family being the Francosign languages, with its languages found in countries from Iberia to the Balkans and the Baltics. Accurate historical information of sign and tactile languages is difficult to come by, with folk histories noting the existence signing communities across Europe hundreds of years ago. British Sign Language (BSL) and French Sign Language (LSF) are probably the oldest confirmed, continuously spoken sign languages. Alongside German Sign Language (DGS) according to Ethnologue, these three have the most numbers of signers, though very few institutions take appropriate statistics on contemporary signing populations, making legitimate data hard to find.[citation needed]
Notably, few European sign languages have overt connections with the local majority/oral languages, aside from standard language contact and borrowing, meaning grammatically the sign languages and the oral languages of Europe are quite distinct from one another. Due to (visual/aural) modality differences, most sign languages are named for the larger ethnic nation in which they are spoken, plus the words "sign language", rendering what is spoken across much of France, Wallonia and Romandy as French Sign Language or LSF for: langue des signes française.[citation needed]
Recognition of non-oral languages varies widely from region to region.[13] Some countries afford legal recognition, even to official on a state level, whereas others continue to be actively suppressed.[14]
The major sign linguistic families are:[citation needed]
- Francosign languages, such as LSF, Irish SL, Austrian Sign Language (ÖGS), Eesti Viipekeel, and probably both Catalan and Valencian Sign Languages.[citation needed]
- Danish Sign languages, such as DTS, Icelandic Taknmal, Faroese Taknmal, and NTS.[citation needed]
- Austro-Hungarian Sign descendants, including the sub-families descended from both (separately) the Yugoslav Sign Language and Russian Sign Language, such as Macedonian Sign Language and HZJ, or LGK and Ukrainian Sign Language (USL).[citation needed]
- Banzsl languages, such as BSL and Northern Ireland Sign Language (NISL).[citation needed]
- Swedish Sign family, such as SSL, Viittomakieli, FinnSSL, and Portuguese Sign Language (LGP), all of which may be descended from Old BSL.[citation needed]
- Germanosign languages, such as DGS and Polish Sign Language (PJM).[citation needed]
- Isolate languages, such as Albanian Sign Language, Armenian Sign Language, Caucasian Sign Language, Spanish Sign Language (LSE), Turkish Sign Language (TİD), and perhaps Ghardaia Sign Language.[citation needed]
History of standardization
Language and identity, standardization processes
In the Middle Ages the two most important defining elements of Europe were Christianitas and Latinitas.[citation needed]
The earliest dictionaries were glossaries: more or less structured lists of lexical pairs (in alphabetical order or according to conceptual fields). The Latin-German (Latin-Bavarian) Abrogans was among the first. A new wave of lexicography can be seen from the late 15th century onwards (after the introduction of the printing press, with the growing interest in standardisation of languages).[citation needed]
The concept of the nation state began to emerge in the early modern period. Nations adopted particular dialects as their national language. This, together with improved communications, led to official efforts to standardise the national language, and a number of language academies were established: 1582 Accademia della Crusca in Florence, 1617 Fruchtbringende Gesellschaft in Weimar, 1635 Académie française in Paris, 1713 Real Academia Española in Madrid. Language became increasingly linked to nation as opposed to culture, and was also used to promote religious and ethnic identity: e.g. different Bible translations in the same language for Catholics and Protestants.[citation needed]
The first languages whose standardisation was promoted included Italian (questione della lingua: Modern Tuscan/Florentine vs. Old Tuscan/Florentine vs. Venetian → Modern Florentine + archaic Tuscan + Upper Italian), French (the standard is based on Parisian), English (the standard is based on the London dialect) and (High) German (based on the dialects of the chancellery of Meissen in Saxony, Middle German, and the chancellery of Prague in Bohemia ("Common German")). But several other nations also began to develop a standard variety in the 16th century.[citation needed]
Lingua franca
Europe has had a number of languages that were considered linguae francae over some ranges for some periods according to some historians. Typically in the rise of a national language the new language becomes a lingua franca to peoples in the range of the future nation until the consolidation and unification phases. If the nation becomes internationally influential, its language may become a lingua franca among nations that speak their own national languages. Europe has had no lingua franca ranging over its entire territory spoken by all or most of its populations during any historical period. Some linguae francae of past and present over some of its regions for some of its populations are:
- Classical Greek and then Koine Greek in the Mediterranean Basin from the Athenian Empire to the Eastern Roman Empire, being replaced by Modern Greek.
- Koine Greek and Modern Greek, in the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire and other parts of the Balkans south of the Jireček Line.[15]
- Vulgar Latin and Late Latin among the uneducated and educated populations respectively of the Roman Empire and the states that followed it in the same range no later than 900 AD; Medieval Latin and Renaissance Latin among the educated populations of western, northern, central and part of eastern Europe until the rise of the national languages in that range, beginning with the first language academy in Italy in 1582/83; new Latin written only in scholarly and scientific contexts by a small minority of the educated population at scattered locations over all of Europe; ecclesiastical Latin, in spoken and written contexts of liturgy and church administration only, over the range of the Roman Catholic Church.[citation needed]
- Lingua Franca or Sabir, the original of the name, an Italian-based pidgin language of mixed origins used by maritime commercial interests around the Mediterranean in the Middle Ages and early Modern Age.[16]
- Old French in continental western European countries and in the Crusader states.[17]
- Czech, mainly during the reign of Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV (14th century) but also during other periods of Bohemian control over the Holy Roman Empire.[citation needed]
- Middle Low German, around the 14th–16th century, during the heyday of the Hanseatic League, mainly in Northeastern Europe across the Baltic Sea.
- Spanish as Castilian in Spain and New Spain from the times of the Catholic Monarchs and Columbus, c. 1492; that is, after the Reconquista, until established as a national language in the times of Louis XIV, c. 1648; subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the Spanish Empire.[18]
- Polish, due to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (16th–18th centuries).[citation needed]
- Italian due to the Renaissance, the opera, the Italian Empire, the fashion industry and the influence of the Roman Catholic church.[19]
- French from the golden age under Cardinal Richelieu and Louis XIV c. 1648; i.e., after the Thirty Years' War, in France and the French colonial empire, until established as the national language during the French Revolution of 1789 and subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the various French Empires.[17]
- German in Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe.[20]
- English in Great Britain until its consolidation as a national language in the Renaissance and the rise of Modern English; subsequently internationally under the various states in or formerly in the British Empire; globally since the victories of the predominantly English speaking countries (United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and others) and their allies in the two world wars ending in 1918 (World War I) and 1945 (World War II) and the subsequent rise of the United States as a superpower and major cultural influence.[citation needed]
- Russian in the former Soviet Union and Russian Empire including Northern and Central Asia.[citation needed]
Linguistic minorities
Historical attitudes towards linguistic diversity are illustrated by two French laws: the Ordonnance de Villers-Cotterêts (1539), which said that every document in France should be written in French (neither in Latin nor in Occitan) and the Loi Toubon (1994), which aimed to eliminate anglicisms from official documents. States and populations within a state have often resorted to war to settle their differences. There have been attempts to prevent such hostilities: two such initiatives were promoted by the Council of Europe, founded in 1949, which affirms the right of minority language speakers to use their language fully and freely.[21] The Council of Europe is committed to protecting linguistic diversity. Currently all European countries except France, Andorra and Turkey have signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, while Greece, Iceland and Luxembourg have signed it, but have not ratified it; this framework entered into force in 1998. Another European treaty, the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, was adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe: it entered into force in 1998, and while it is legally binding for 24 countries, France, Iceland, Italy, North Macedonia, Moldova and Russia have chosen to sign without ratifying the convention.[citation needed]
Scripts
The main scripts used in Europe today are the Latin and Cyrillic.[citation needed]
The Greek alphabet was derived from the Phoenician alphabet, and Latin was derived from the Greek via the Old Italic alphabet. In the Early Middle Ages, Ogham was used in Ireland and runes (derived from Old Italic script) in Scandinavia. Both were replaced in general use by the Latin alphabet by the Late Middle Ages. The Cyrillic script was derived from the Greek with the first texts appearing around 940 AD.[citation needed]
Around 1900 there were mainly two typeface variants of the Latin alphabet used in Europe: Antiqua and Fraktur. Fraktur was used most for German, Estonian, Latvian, Norwegian and Danish whereas Antiqua was used for Italian, Spanish, French, Polish, Portuguese, English, Romanian, Swedish and Finnish. The Fraktur variant was banned by Hitler in 1941, having been described as "Schwabacher Jewish letters".[22] Other scripts have historically been in use in Europe, including Phoenician, from which modern Latin letters descend, Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs on Egyptian artefacts traded during Antiquity, various runic systems used in Northern Europe preceding Christianisation, and Arabic during the era of the Ottoman Empire.[citation needed]
Hungarian rovás was used by the Hungarian people in the early Middle Ages, but it was gradually replaced with the Latin-based Hungarian alphabet when Hungary became a kingdom, though it was revived in the 20th century and has certain marginal, but growing area of usage since then.[citation needed]
European Union
The European Union (as of 2021) had 27 member states accounting for a population of 447 million, or about 60% of the population of Europe.[citation needed]
The European Union has designated by agreement with the member states 24 languages as "official and working": Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Irish, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish and Swedish.[23] This designation provides member states with two "entitlements": the member state may communicate with the EU in any of the designated languages, and view "EU regulations and other legislative documents" in that language.[24]
The European Union and the Council of Europe have been collaborating in education of member populations in languages for "the promotion of plurilingualism" among EU member states.[25] The joint document, "Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment (CEFR)", is an educational standard defining "the competencies necessary for communication" and related knowledge for the benefit of educators in setting up educational programs. In a 2005 independent survey requested by the EU's Directorate-General for Education and Culture regarding the extent to which major European languages were spoken in member states. The results were published in a 2006 document, "Europeans and Their Languages", or "Eurobarometer 243". In this study, statistically relevant[clarification needed][Do you mean "significant"?] samples of the population in each country were asked to fill out a survey form concerning the languages that they spoke with sufficient competency "to be able to have a conversation".[26]
List of languages
The following is a table of European languages. The number of speakers as a first or second language (L1 and L2 speakers) listed are speakers in Europe only;[nb 1] see list of languages by number of native speakers and list of languages by total number of speakers for global estimates on numbers of speakers.[citation needed]
The list is intended to include any language variety with an ISO 639 code. However, it omits sign languages. Because the ISO-639-2 and ISO-639-3 codes have different definitions, this means that some communities of speakers may be listed more than once. For instance, speakers of Bavarian are listed both under "Bavarian" (ISO-639-3 code bar) as well as under "German" (ISO-639-2 code de).[citation needed]
| Name | ISO- 639 |
Classification | Speakers in Europe | Official status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | Total | National[nb 2] | Regional | |||
| Adyghe | ady | Northwest Caucasian, Circassian | 117,500[27] | Adygea (Russia) | ||
| Albanian (Shqip) Arbëresh Arvanitika |
sq | Indo-European | 5,367,000[28] 5,877,100[29] (Balkans) |
Albania, Kosovo[nb 3], North Macedonia | Italy, Arbëresh dialect: Sicily, Calabria,[30] Apulia, Molise, Basilicata, Abruzzo, Campania, Montenegro (Ulcinj, Tuzi) | |
| Aragonese | an | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 25,000[31] | 55,000[32] | Aragon (Spain)[nb 4] | |
| Aromanian | rup | Indo-European, Romance, Eastern | 114,000[33] | North Macedonia (Kruševo) | ||
| Asturian (Astur-Leonese) | ast | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 351,791[34] | 641,502[34] | Asturias[nb 4] | |
| Avar | av | Northeast Caucasian, Avar–Andic | 760,000 | Dagestan (Russia) | ||
| Azerbaijani | az | Turkic, Oghuz | 500,000[35] | Azerbaijan | Dagestan (Russia) | |
| Bashkir | ba | Turkic, Kipchak | 1,221,000[36] | Bashkortostan (Russia) | ||
| Basque | eu | Basque | 750,000[37] | Basque Country: Basque Autonomous Community (Spain, official), Navarre (Spain, official in the Basque-speaking and mixed parts of the region), French Basque Country (France, not official) | ||
| Bavarian | bar | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Upper, Bavarian | 14,000,000[38] | Austria (as German) | South Tyrol | |
| Belarusian | be | Indo-European, Slavic, East | 3,300,000[39] | Belarus | ||
| Bosnian | bs | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Western, Serbo-Croatian | 2,500,000[40] | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Kosovo[nb 3], Montenegro | |
| Breton | br | Indo-European, Celtic, Brittonic | 206,000[41] | None, de facto status in Brittany (France) | ||
| Bulgarian | bg | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Eastern | 7,800,000[42] | Bulgaria | Mount Athos (Greece) | |
| Catalan | ca | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Occitano-Romance | 4,000,000[43] | 10,000,000[44] | Andorra | Balearic Islands (Spain), Catalonia (Spain), Valencian Community (Spain), Aragon (Spain)[nb 4], Pyrénées-Orientales (France)[nb 4], Alghero (Italy) |
| Chechen | ce | Northeast Caucasian, Nakh | 1,400,000[45] | Chechnya & Dagestan (Russia) | ||
| Chuvash | cv | Turkic, Oghur | 1,100,000[46] | Chuvashia (Russia) | ||
| Cimbrian | cim | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Upper, Bavarian | 400[47] | |||
| Cornish | kw | Indo-European, Celtic, Brittonic | 557[48] | Cornwall (United Kingdom)[nb 4] | ||
| Corsican | co | Indo-European, Romance, Italo-Dalmatian | 30,000[49] | 125,000[49] | Corsica (France), Sardinia (Italy) | |
| Crimean Tatar | crh | Turkic, Kipchak | 480,000[50] | Crimea | ||
| Croatian | hr | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Western, Serbo-Croatian | 5,600,000[51] | Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia | Burgenland (Austria), Vojvodina (Serbia) | |
| Czech | cs | Indo-European, Slavic, West, Czech–Slovak | 10,600,000[52] | Czech Republic | ||
| Danish | da | Indo-European, Germanic, North | 5,500,000[53] | Denmark | Faroe Islands (Denmark), Schleswig-Holstein (Germany)[54] | |
| Dutch | nl | Indo-European, Germanic, West, Low Franconian | 22,000,000[55] | Belgium, Netherlands | ||
| Elfdalian | ovd | Indo-European, Germanic, North | 2000 | |||
| Emilian | egl | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Italic | Emilia (Italy) | |||
| English | en | Indo-European, Germanic, West, Anglo-Frisian, Anglic | 63,000,000[56] | 260,000,000[57] | Ireland, Malta, United Kingdom | |
| Erzya | myv | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Mordvinic | 120,000[58] | Mordovia (Russia) | ||
| Estonian | et | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 1,165,400[59] | Estonia | ||
| Extremaduran | ext | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 200,000[60] | Extremadura (Spain) | ||
| Faroese | fo | Indo-European, Germanic, North | 66,150[61] | Faroe Islands (Denmark) | ||
| Finnish | fi | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 5,400,000[62] | Finland | Karelia (Russia) | |
| Franco-Provençal (Arpitan) | frp | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Romance | 140,000[63] | Aosta Valley (Italy) | ||
| French | fr | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Romance, Oïl | 81,000,000[64] | 210,000,000[57] | Belgium, France, Luxembourg, Monaco, Switzerland | Aosta Valley[65] (Italy), Jersey (United Kingdom), El Pas de la Casa (Andorra) |
| Frisian | fry frr stq |
Indo-European, Germanic, West, Anglo-Frisian | 470,000[66] | Friesland (Netherlands), Schleswig-Holstein (Germany)[67] | ||
| Friulan | fur | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Italic | 600,000[68] | Friuli (Italy) | ||
| Gagauz | gag | Turkic, Oghuz | 140,000[69] | Gagauzia (Moldova) | ||
| Galician | gl | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 2,400,000[70] | Galicia (Spain), Eo-Navia (Asturias)[nb 4], Bierzo (Province of León)[nb 4] and Western Sanabria (Province of Zamora)[nb 4] | ||
| German | de | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German | 97,000,000[71] | 170,000,000[57] | Austria, Belgium, Germany, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Switzerland | South Tyrol,[72] Friuli-Venezia Giulia[73] (Italy) |
| Greek | el | Indo-European, Hellenic | 13,500,000[74] | Cyprus, Greece | Albania (Himara, Finiq, Dervican and other southern townships) | |
| Hungarian | hu | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Ugric | 13,000,000[75] | Hungary | Burgenland (Austria), Vojvodina (Serbia), Romania, Slovakia, Subcarpathia (Ukraine), Mur region, (Slovenia), northern Croatia | |
| Icelandic | is | Indo-European, Germanic, North | 330,000[76] | Iceland | ||
| Ingrian | izh | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 120[77] | |||
| Ingush | inh | Northeast Caucasian, Nakh | 300,000[78] | Ingushetia (Russia) | ||
| Irish | ga | Indo-European, Celtic, Goidelic | 240,000[79] | 2,000,000 | Ireland | Northern Ireland (United Kingdom) |
| Istriot | ist | Indo-European, Romance | 900[80] | |||
| Istro-Romanian | ruo | Indo-European, Romance, Eastern | 1,100[81] | |||
| Italian | it | Indo-European, Romance, Italo-Dalmatian | 65,000,000[82] | 82,000,000[57] | Italy, San Marino, Switzerland, Vatican City | Istria County (Croatia), Slovenian Istria (Slovenia) |
| Italiot Greek | mis | Indo-European, Hellenic, Greek, Attic-Ionic | 20,000 native speakers in 1981[83] | 50,000 | Calabria[84] (Bovesia), Apulia[85] (Salento), (Italy) | |
| Judeo-Italian | itk | Indo-European, Romance, Italo-Dalmatian | 250[86] | |||
| Judaeo-Spanish (Ladino) | lad | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 320,000[87] | few[88] | Bosnia and Herzegovina[nb 4], France[nb 4] | |
| Kabardian | kbd | Northwest Caucasian, Circassian | 530,000[89] | Kabardino-Balkaria & Karachay-Cherkessia (Russia) | ||
| Kalmyk | xal | Mongolic | 80,500[90] | Kalmykia (Russia) | ||
| Karelian | krl | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 36,000[91] | Karelia (Russia) | ||
| Karachay-Balkar | krc | Turkic, Kipchak | 300,000[92] | Kabardino-Balkaria & Karachay-Cherkessia (Russia) | ||
| Kashubian | csb | Indo-European, Slavic, West, Lechitic | 50,000[93] | Poland | ||
| Kazakh | kk | Turkic, Kipchak | 1,000,000[94] | Kazakhstan | Astrakhan Oblast (Russia) | |
| Komi | kv | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Permic | 220,000[95] | Komi Republic (Russia) | ||
| Kven | fkv | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 2000-8000 | Norway | ||
| Kumyk | kum | Turkic, Kipchak | 450,000[96] | Dagestan (Russia) | ||
| Latin | la | Indo-European, Italic, Latino-Faliscan | extinct | few[97] | Vatican City | |
| Latvian | lv | Indo-European, Baltic | 1,750,000[98] | Latvia | ||
| Ligurian | lij | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Italic | 500,000[99] | Monaco (Monégasque dialect is the "national language") | Liguria (Italy), Carloforte and Calasetta (Sardinia, Italy)[100][101] | |
| Limburgish | li lim |
Indo-European, Germanic, West, Low Franconian | 1,300,000 (2001)[102] | Limburg (Belgium), Limburg (Netherlands) | ||
| Lithuanian | lt | Indo-European, Baltic | 3,000,000[103] | Lithuania | ||
| Lombard | lmo | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Italic | 3,600,000[104] | Lombardy (Italy) | ||
| Low German (Low Saxon) | nds wep |
Indo-European, Germanic, West | 1,000,000[105] | 2,600,000[105] | Schleswig-Holstein (Germany)[106] | |
| Luxembourgish | lb | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German | 336,000[107] | 386,000[107] | Luxembourg | Wallonia (Belgium) |
| Macedonian | mk | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Eastern | 1,400,000[108] | North Macedonia | ||
| Mainfränkisch | vmf | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Upper | 4,900,000[109] | Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria & Thuringia (Germany) | ||
| Maltese | mt | Semitic, Arabic | 520,000[110] | Malta | ||
| Manx | gv | Indo-European, Celtic, Goidelic | 230[111] | 2,300[112] | Isle of Man | |
| Mari | chm mhr mrj |
Uralic, Finno-Ugric | 500,000[113] | Mari El (Russia) | ||
| Megleno-Romanian | ruq | Indo-European, Romance, Eastern | 3,000[114] | |||
| Mirandese | mwl | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 15,000[115] | Miranda do Douro (Portugal) | ||
| Moksha | mdf | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Mordvinic | 2,000[116] | Mordovia (Russia) | ||
| Montenegrin | cnr | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Western, Serbo-Croatian | 240,700[117] | Montenegro | ||
| Neapolitan | nap | Indo-European, Romance, Italo-Dalmatian | 5,700,000[118] | Campania (Italy)[119] | ||
| Nenets | yrk | Uralic, Samoyedic | 4,000[120] | Nenets Autonomous Okrug (Russia) | ||
| Norman | nrf | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Romance, Oïl | 50,000[121] | Normandy (France), Jersey (United Kingdom) | ||
| Norwegian | no | Indo-European, Germanic, North | 5,200,000[122] | Norway | ||
| Occitan | oc | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Occitano-Romance | 500,000[123] | Catalonia (Spain)[nb 5] | ||
| Ossetian | os | Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Iranian, Eastern | 450,000[124] | Georgia | North Ossetia-Alania (Russia) | |
| Palatinate German | pfl | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Central | 1,000,000[125] | Germany | ||
| Picard | pcd | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Romance, Oïl | 200,000[126] | Wallonia (Belgium) | ||
| Piedmontese | pms | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Italic | 1,600,000[127] | Piedmont (Italy)[128] | ||
| Polish | pl | Indo-European, Slavic, West, Lechitic | 38,500,000[129] | Poland | ||
| Portuguese | pt | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 10,000,000[130] | Portugal | ||
| Rhaeto-Romance | fur lld roh |
Indo-European, Romance, Western | 370,000[131] | Switzerland | Veneto Belluno, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, South Tyrol,[132] & Trentino (Italy) | |
| Ripuarian (Platt) | ksh | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Central | 900,000[133] | Germany, Netherlands, Wallonia (Belgium) | ||
| Romagnol | rgn | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Italic | Romagna (Italy) | |||
| Romani | rom | Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Indo-Aryan, Western | 1,500,000[134] | Kosovo[nb 3][135] | ||
| Romanian | ro | Indo-European, Romance, Eastern | 24,000,000[136] | 28,000,000[137] | Moldova, Romania | Mount Athos (Greece), Vojvodina (Serbia) |
| Russian | ru | Indo-European, Slavic, East | 106,000,000[138] | 160,000,000[138] | Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia | Mount Athos (Greece), Gagauzia (Moldova), Left Bank of the Dniester (Moldova), Ukraine, Georgia, Armenia, Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania |
| Sami | se | Uralic, Finno-Ugric | 23,000[139] | Norway | Sweden, Finland | |
| Sardinian | sc | Indo-European, Romance | 1,350,000[140] | Sardinia (Italy) | ||
| Scots | sco | Indo-European, Germanic, West, Anglo-Frisian, Anglic | 110,000[141] | Scotland (United Kingdom), Ulster (Republic of Ireland), Northern Ireland (United Kingdom) | ||
| Scottish Gaelic | gd | Indo-European, Celtic, Goidelic | 57,000[142] | Scotland (United Kingdom) | ||
| Serbian | sr | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Western, Serbo-Croatian | 9,000,000[143] | Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo[nb 3], Serbia | Croatia, Mount Athos (Greece), North Macedonia, Montenegro | |
| Sicilian | scn | Indo-European, Romance, Italo-Dalmatian | 4,700,000[144] | Sicily (Italy) | ||
| Silesian | szl | Indo-European, Slavic, West, Lechitic | 522,000[145] | Upper Silesia (Poland, Czech Republic & Germany), Silesia (Poland) | ||
| Silesian German | sli | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Central | 11,000[146] | Upper Silesia (Poland, Czech Republic & Germany), Silesia (Poland) | ||
| Slovak | sk | Indo-European, Slavic, West, Czech–Slovak | 5,200,000[147] | Slovakia | Vojvodina (Serbia), Czech Republic | |
| Slovene | sl | Indo-European, Slavic, South, Western | 2,100,000[148] | Slovenia | Friuli-Venezia Giulia[73] (Italy) | |
| Sorbian (Wendish) | wen | Indo-European, Slavic, West | 20,000[149] | Brandenburg & Sachsen (Germany)[150] | ||
| Spanish | es | Indo-European, Romance, Western, West Iberian | 47,000,000[151] | 76,000,000[57] | Spain | Gibraltar (United Kingdom) |
| Swabian German | swg | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Upper, Alemannic | 820,000[152] | Germany | ||
| Swedish | sv | Indo-European, Germanic, North | 11,100,000[153] | 13,280,000[153] | Finland, Sweden | |
| Swiss German | gsw | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Upper, Alemannic | 5,000,000[154] | Switzerland (as German) | ||
| Tabasaran | tab | Northeast Caucasian, Lezgic | 126,900[155] | Dagestan (Russia) | ||
| Tat | ttt | Indo-European, Iranian, Western | 30,000[156] | Dagestan (Russia) | ||
| Tatar | tt | Turkic, Kipchak | 4,300,000[157] | Tatarstan (Russia) | ||
| Turkish | tr | Turkic, Oghuz | 15,752,673[158] | Turkey, Cyprus | Northern Cyprus | |
| Udmurt | udm | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Permic | 340,000[159] | Udmurtia (Russia) | ||
| Ukrainian | uk | Indo-European, Slavic, East | 32,600,000[160] | Ukraine | Left Bank of the Dniester (Moldova) | |
| Upper Saxon | sxu | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Central | 2,000,000[161] | Sachsen (Germany) | ||
| Vepsian | vep | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 1,640[162] | Karelia (Russia) | ||
| Venetian | vec | Indo-European, Romance, Italo-Dalmatian | 3,800,000[163] | Veneto (Italy)[164] | ||
| Võro | vro | Uralic, Finno-Ugric, Finnic | 87,000[165] | Võru County (Estonia) | ||
| Walloon | wa | Indo-European, Romance, Western, Gallo-Romance, Oïl | 600,000[166] | Wallonia (Belgium) | ||
| Walser German | wae | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German, Upper, Alemannic | 20,000[167] | |||
| Welsh | cy | Indo-European, Celtic, Brittonic | 562,000[168] | 750,000 | Wales (United Kingdom) | |
| Wymysorys | wym | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German | 70[169] | |||
| Yenish | yec | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German | 16,000[170] | Switzerland[nb 4] | ||
| Yiddish | yi | Indo-European, Germanic, West, High German | 600,000[171] | Bosnia and Herzegovina[nb 4], Netherlands[nb 4], Poland[nb 4], Romania[nb 4], Sweden[nb 4], Ukraine[nb 4] | ||
Languages spoken in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, Georgia, and Turkey
There are various definitions of Europe, which may or may not include all or parts of Turkey, Cyprus, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia. For convenience, the languages and associated statistics for all five of these countries are grouped together on this page, as they are usually presented at a national, rather than subnational, level.
| Name | ISO- 639 |
Classification | Speakers in expanded geopolitical Europe | Official status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L1+L2 | National[nb 6] | Regional | |||
| Abkhaz | ab | Northwest Caucasian, Abazgi | Abkhazia/Georgia:[172] 191,000[173] Turkey: 44,000[174] |
Abkhazia | Abkhazia | |
| Adyghe (West Circassian) | ady | Northwest Caucasian, Circassian | Turkey: 316,000[174] | |||
| Albanian | sq | Indo-European, Albanian | Turkey: 66,000 (Tosk)[174] | |||
| Arabic | ar | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic, West | Turkey: 2,437,000 Not counting post-2014 Syrian refugees[174] | |||
| Armenian | hy | Indo-European, Armenian | Armenia: 3 million[175] Artsakh/Azerbaijan:[176] 145,000 [citation needed] Georgia: around 0.2 million ethnic Armenians (Abkhazia: 44,870[177]) Turkey: 61,000[174] Cyprus: 668[178]: 3 |
Armenia Artsakh |
Cyprus | |
| Azerbaijani | az | Turkic, Oghuz | Azerbaijan 9 million[citation needed][179] Turkey: 540,000[174] Georgia 0.2 million |
Azerbaijan | ||
| Batsbi | bbl | Northeast Caucasian, Nakh | Georgia: 500[180][needs update] | |||
| Bulgarian | bg | Indo-European, Slavic, South | Turkey: 351,000[174] | |||
| Crimean | crh | Turkic, Kipchak | Turkey: 100,000[174] | |||
| Georgian | ka | Kartvelian, Karto-Zan | Georgia: 3,224,696[181] Turkey: 151,000[174] Azerbaijan: 9,192 ethnic Georgians[182] |
Georgia | ||
| Greek | el | Indo-European, Hellenic | Cyprus: 679,883[183]: 2.2 Turkey: 3,600[174] |
Cyprus | ||
| Juhuri | jdt | Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Iranian, Southwest | Azerbaijan: 24,000 (1989)[184][needs update] | |||
| Kurdish | kur | Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Iranian, Northwest | Turkey: 15 million[185] Armenia: 33,509[186] Georgia: 14,000 [citation needed] Azerbaijan: 9,000[citation needed] |
Armenia | ||
| Laz | lzz | Kartvelian, Karto-Zan, Zan | Turkey: 20,000[187] Georgia: 2,000[187] |
|||
| Megleno-Romanian | ruq | Indo-European, Italic, Romance, East | Turkey: 4–5,000[188] | |||
| Mingrelian | xmf | Kartvelian, Karto-Zan, Zan | Georgia (including Abkhazia): 344,000[189] | |||
| Pontic Greek | pnt | Indo-European, Hellenic | Turkey: greater than 5,000[190] Armenia: 900 ethnic Caucasus Greeks[191] Georgia: 5,689 Caucasus Greeks[181] |
|||
| Romani language and Domari language | rom, dmt | Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Indic | Turkey: 500,000[174] | |||
| Russian | ru | Indo-European, Balto-Slavic, Slavic | Armenia: 15,000[192] Azerbaijan: 250,000[192] Georgia: 130,000[192] |
Armenia: about 0.9 million[193] Azerbaijan: about 2.6 million[193] Georgia: about 1 million[193] Cyprus: 20,984[194] |
Abkhazia South Ossetia |
Armenia Azerbaijan |
| Svan | sva | Kartvelian, Svan | Georgia (incl. Abkhazia): 30,000[195] | |||
| Tat | ttt | Indo-European, Indo-Aryan, Iranian, Southwest | Azerbaijan: 10,000[196][needs update] | |||
| Turkish | tr | Turkic, Oghuz | Turkey: 66,850,000[174] Cyprus: 1,405[197] + 265,100 in the North[198] |
Turkey Cyprus Northern Cyprus |
||
Immigrant communities
Recent (post–1945) immigration to Europe introduced substantial communities of speakers of non-European languages.[1]
The largest such communities include Arabic speakers (see Arabs in Europe) and Turkish speakers (beyond European Turkey and the historical sphere of influence of the Ottoman Empire, see Turks in Europe).[199] Armenians, Berbers, and Kurds have diaspora communities of c. 1–2,000,000 each. The various languages of Africa and languages of India form numerous smaller diaspora communities.
- List of the largest immigrant languages
| Name | ISO 639 | Classification | Native | Ethnic diaspora |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabic | ar | Afro-Asiatic, Semitic | 5,000,000[200] | 12,000,000[201] |
| Turkish | tr | Turkic, Oghuz | 3,000,000[202] | 7,000,000[203] |
| Armenian | hy | Indo-European | 1,000,000[204] | 3,000,000[205] |
| Kurdish | ku | Indo-European, Iranian, Western | 600,000[206] | 1,000,000[207] |
| Bengali–Assamese | bn as syl | Indo-European, Indo-Aryan | 600,000[208] | 1,000,000[209] |
| Azerbaijani | az | Turkic, Oghuz | 500,000[210] | 700,000[211] |
| Kabyle | kab | Afro-Asiatic, Berber | 500,000[212] | 1,000,000[213] |
| Chinese | zh | Sino-Tibetan, Sinitic | 300,000[214] | 2,000,000[215] |
| Urdu | ur | Indo-European, Indo-Aryan | 300,000[216] | 1,800,000[217] |
| Uzbek | uz | Turkic, Karluk | 300,000[218] | 2,000,000[219] |
| Persian | fa | Indo-European, Iranian, Western | 300,000[220] | 400,000[221] |
| Punjabi | pa | Indo-European, Indo-Aryan | 300,000[222] | 700,000[223] |
| Gujarati | gu | Indo-European, Indo-Aryan | 200,000[224] | 600,000[225] |
| Tamil | ta | Dravidian | 200,000[226] | 500,000[227] |
| Somali | so | Afro-Asiatic, Cushitic | 200,000[228] | 400,000[229] |
See also
- Ethnic groups in Europe
- Eurolinguistics
- European Day of Languages
- Greek East and Latin West
- List of endangered languages in Europe
- List of multilingual countries and regions of Europe
- Standard Average European
- Travellingua
Notes
- ^ "Europe" is taken as a geographical term, defined by the conventional Europe-Asia boundary along the Caucasus and the Urals. Estimates for populations geographically in Europe are given for transcontinental countries.
- ^ Sovereign states, defined as United Nations member states and observer states. 'Recognised minority language' status is not included.
- ^ a b c d The Republic of Kosovo is a partially recognized state (recognized by 111 out of 193 UN member states as of 2017).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Recognized and protected, but not official.
- ^ The Aranese dialect, in Val d'Aran county.
- ^ Sovereign states, defined as United Nations member states and observer states. 'Recognised minority language' status is not included.
References
- ^ a b "International migrant stock: By destination and origin". United Nations.
- ^ "Linguist makes sensational claim: English is a Scandinavian language". ScienceDaily. Retrieved 6 March 2016.
- ^ Friedman, Lawrence; Perez-Perdomo, Rogelio (2003). Legal Culture in the Age of Globalization: Latin America and Latin Europe. Stanford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 0-8047-6695-9.
- ^ F. Violi, Lessico Grecanico-Italiano-Grecanico, Apodiafàzzi, Reggio Calabria, 1997.
- ^ Paolo Martino, L'isola grecanica dell'Aspromonte. Aspetti sociolinguistici, 1980. Risultati di un'inchiesta del 1977
- ^ Filippo Violi, Storia degli studi e della letteratura popolare grecanica, C.S.E. Bova (RC), 1992
- ^ Filippo Condemi, Grammatica Grecanica, Coop. Contezza, Reggio Calabria, 1987;
- ^ "In Salento e Calabria le voci della minoranza linguistica greca". Treccani, l'Enciclopedia italiana.
- ^ Alexander, Marie; et al. (2009). "2nd International Conference of Maltese Linguistics: Saturday, September 19 – Monday, September 21, 2009". International Association of Maltese Linguistics. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
- ^ Aquilina, J. (1958). "Maltese as a Mixed Language". Journal of Semitic Studies. 3 (1): 58–79. doi:10.1093/jss/3.1.58.
- ^ Aquilina, Joseph (July–September 1960). "The Structure of Maltese". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 80 (3): 267–68. doi:10.2307/596187. JSTOR 596187.
- ^ Werner, Louis; Calleja, Alan (November–December 2004). "Europe's New Arabic Connection". Saudi Aramco World. Archived from the original on 29 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2016.
- ^ Reagan, Timothy (2014). "Language Policy for Sign Languages". The Encyclopedia of Applied Linguistics. pp. 1–6. doi:10.1002/9781405198431.wbeal1417. ISBN 9781405194730.
- ^ Murray, Joseph J. (2015). "Linguistic Human Rights Discourse in Deaf Community Activism". Sign Language Studies. 15 (4): 379–410. doi:10.1353/sls.2015.0012. JSTOR 26190995. PMC 4490244. PMID 26190995.
- ^ Counelis, James Steve (March 1976). "Review [untitled] of Ariadna Camariano-Cioran, Les Academies Princieres de Bucarest et de Jassy et leur Professeurs". Church History. 45 (1): 115–116. doi:10.2307/3164593. JSTOR 3164593. S2CID 162293323.
...Greek, the lingua franca of commerce and religion, provided a cultural unity to the Balkans...Greek penetrated Moldavian and Wallachian territories as early as the fourteenth century.... The heavy influence of Greek culture upon the intellectual and academic life of Bucharest and Jassy was longer termed than historians once believed.
- ^ Wansbrough, John E. (1996). "Chapter 3: Lingua Franca". Lingua Franca in the Mediterranean. Routledge.
- ^ a b Calvet, Louis Jean (1998). Language wars and linguistic politics. Oxford [England]; New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 175–76.
- ^ Jones, Branwen Gruffydd (2006). Decolonizing international relations. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 98.
- ^ Kahane 1986, p. 495
- ^ Darquennes, Jeroen; Nelde, Peter (2006). "German as a Lingua Franca". Annual Review of Applied Linguistics. 26: 61–77. doi:10.1017/s0267190506000043. S2CID 61449212.
- ^ "European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages: Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992". Council of Europe. 1992.
- ^ Facsimile of Bormann's Memorandum (in German)
The memorandum itself is typed in Antiqua, but the NSDAP letterhead is printed in Fraktur.
"For general attention, on behalf of the Führer, I make the following announcement:
It is wrong to regard or to describe the so‑called Gothic script as a German script. In reality, the so‑called Gothic script consists of Schwabach Jew letters. Just as they later took control of the newspapers, upon the introduction of printing the Jews residing in Germany took control of the printing presses and thus in Germany the Schwabach Jew letters were forcefully introduced.
Today the Führer, talking with Herr Reichsleiter Amann and Herr Book Publisher Adolf Müller, has decided that in the future the Antiqua script is to be described as normal script. All printed materials are to be gradually converted to this normal script. As soon as is feasible in terms of textbooks, only the normal script will be taught in village and state schools.
The use of the Schwabach Jew letters by officials will in future cease; appointment certifications for functionaries, street signs, and so forth will in future be produced only in normal script.
On behalf of the Führer, Herr Reichsleiter Amann will in future convert those newspapers and periodicals that already have foreign distribution, or whose foreign distribution is desired, to normal script". - ^ "Languages Policy: Linguistic diversity: Official languages of the EU". European Commission, European Union. 4 June 2009. Retrieved 9 August 2015.
- ^ "Languages of Europe: Official EU languages". European Commission, European Union. 2009. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ "Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment (CEFR)". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 30 October 2009. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ "Europeans and Their Languages" (PDF). European Commission. 2006. p. 8. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ Adyghe at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Albanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Albanian". Ethnologue. Retrieved 12 December 2018. Population total of all languages of the Albanian macrolanguage.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 August 2009. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ https://zaguan.unizar.es/record/60448 Report about Census of population 2011 of Aragonese Sociolinguistics Seminar and University of Zaragoza
- ^ "Más de 50.000 personas hablan aragonés". Aragón Digital. Archived from the original on 1 January 2015.
- ^ Aromanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ a b III Sociolinguistic Study of Asturias (2017). Euskobarometro.
- ^ c. 130,000 in Dagestan. In addition, there are about 0.5 million speakers in immigrant communities in Russia, see #Immigrant communities. Azerbaijani at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Bashkort at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ (in French) VI° Enquête Sociolinguistique en Euskal herria (Communauté Autonome d'Euskadi, Navarre et Pays Basque Nord) Archived 21 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine (2016).
- ^ German dialect, Bavarian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Belarusian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Bosnian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Breton at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Bulgarian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Catalan". 19 November 2019.
- ^ "Informe sobre la Situació de la Llengua Catalana | Xarxa CRUSCAT. Coneixements, usos i representacions del català". blogs.iec.cat.
- ^ Chechen at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Chuvash at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ German dialect, Cimbrian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ UK 2011 Census
- ^ a b Corsican at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Crimean Tatar at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Croatian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Czech at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Danish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ recognized as official language in Nordfriesland, Schleswig-Flensburg, Flensburg and Rendsburg-Eckernförde (§ 82b LVwG)
- ^ Dutch at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ English at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ a b c d e Europeans and their Languages Archived 6 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Data for EU27 Archived 29 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine, published in 2012.
- ^ Erzya at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Estonian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Extremaduran at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Faroese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Finnish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Franco-Provençal at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ French at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Le Statut spécial de la Vallée d'Aoste, Article 38, Title VI. Region Vallée d'Aoste. Archived from the original on 4 November 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- ^ Frisian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ recognized as official language in the Nordfriesland district and in Helgoland (§ 82b LVwG).
- ^ e18|fur|Friulan
- ^ Gagauz at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Galician at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ includes: bar Bavarian, cim Cimbrian, ksh Kölsch, sli Lower Silesian, vmf Mainfränkisch, pfl Palatinate German, swg Swabian German, gsw Swiss German, sxu Upper Saxon, wae Walser German, wep Westphalian, wym Wymysorys, yec Yenish, yid Yiddish; see German dialects.
- ^ Statuto Speciale Per Il Trentino-Alto Adige Archived 26 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine (1972), Art. 99–101.
- ^ a b "Official site of the Autonomous Region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia".
- ^ 11 million in Greece, out of 13.4 million in total. Greek at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Hungarian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Icelandic at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Ingrian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Ingush at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Irish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Istriot at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Istro-Romanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Italian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ N. Vincent, Italian, in B. Comrie (ed.) The world's major languages, London, Croom Helm, 1981. pp. 279–302.
- ^ "Consiglio regionale della Calabria". www.consiglioregionale.calabria.it.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 January 2018. Retrieved 21 January 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Judeo-Italian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Judaeo-Spanish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ SIL Ethnologue: "Not the dominant language for most. Formerly the main language of Sephardic Jewry. Used in literary and music contexts." ca. 100k speakers in total, most of them in Israel, small communities in the Balkans, Greece, Turkey and in Spain.
- ^ Kabardian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Oirat at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Karelian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Karachay-Balkar at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Kashubian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ About 10 million in Kazakhstan. Kazakh at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required). Technically, the westernmost portions of Kazakhstan (Atyrau Region, West Kazakhstan Region) are in Europe, with a total population of less than one million.
- ^ 220,000 native speakers out of an ethnic population of 550,000. Combines Komi-Permyak (koi) with 65,000 speakers and Komi-Zyrian (kpv) with 156,000 speakers. Komi at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ 2010 Russian Census
- ^ Contemporary Latin: People fluent in Latin as a second language are probably in the dozens, not hundreds. Reginald Foster (as of 2013) estimated "no more than 100" according to Robin Banerji, Pope resignation: Who speaks Latin these days?, BBC News, 12 February 2013.
- ^ Latvian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Ligurian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Legge Regionale 15 ottobre 1997, n. 26". Regione autonoma della Sardegna – Regione Autònoma de Sardigna.
- ^ "Legge Regionale 3 Luglio 2018, n. 22". Regione autonoma della Sardegna – Regione Autònoma de Sardigna.
- ^ "Redirected". Ethnologue. 19 November 2019. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ Lithuanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Lombard at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ a b 2.6 million cited as estimate of all Germans who speak Platt "well or very well" (including L2; 4.3 million cited as the number of all speakers including those with "moderate" knowledge) in 2009. Heute in Bremen. „Ohne Zweifel gefährdet". Frerk Möller im Interview, taz, 21. Februar 2009. However, Wirrer (1998) described Low German as "moribund".Jan Wirrer: Zum Status des Niederdeutschen. In: Zeitschrift für Germanistische Linguistik. 26, 1998, S. 309. The number of native speakers is unknown, estimated at 1 million by SIL Ethnologue. Low German at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Westphalian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ The question whether Low German should be considered as subsumed under "German" as the official language of Germany has a complicated legal history. In the wake of the ratification of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (1998), Schleswig-Holstein has explicitly recognized Low German as a regional language with official status (§ 82b LVwG).
- ^ a b Luxembourgish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Macedonian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ German dialect, Main-Franconian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Maltese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Manx at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Whitehead, Sarah (2 April 2015). "How the Manx language came back from the dead". theguardian.com. Retrieved 4 April 2015.
- ^ Mari at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Megleno-Romanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Mirandese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Moksha at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Montenegro". Ethnologue. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ^ Neapolitan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ In 2008, law was passed by the Region of Campania, stating that the Neapolitan language was to be legally protected. "Tutela del dialetto, primo via libera al Ddl campano". Il Denaro (in Italian). 15 October 2008. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2013.
- ^ total 22,000 native speakers (2010 Russian census) out of an ethnic population of 44,000. Most of these are in Siberia, with about 8,000 ethnic Nenets in European Russia (2010 census, mostly in Nenets Autonomous Okrug)
- ^ Jèrriais at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Norwegian". Ethnologue. Retrieved 6 August 2018.
- ^ Occitan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required). Includes Auvergnat, Gascon, Languedocien, Limousin, Provençal, Vivaro-Alpine. Most native speakers are in France; their number is unknown, as varieties of Occitan are treated as French dialects with no official status.
- ^ Total 570,000, of which 450,000 in the Russian Federation. Ossetian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ German dialect, Palatinate German at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Picard at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Piedmontese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Piedmontese was recognised as Piedmont's regional language by the regional parliament in 1999. Motion 1118 in the Piedmontese Regional Parliament, Approvazione da parte del Senato del Disegno di Legge che tutela le minoranze linguistiche sul territorio nazionale – Approfondimenti, approved unanimously on 15 December 1999, Text of motion 1118 in the Piedmontese Regional Parliament, Consiglio Regionale del Piemonte, Ordine del Giorno 1118.
- ^ Polish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Portuguese at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Includes Friulian, Romansh, Ladin. Friulian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Ladin at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romansch at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Statuto Speciale Per Il Trentino-Alto Adige Archived 26 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine (1972), Art. 102.
- ^ German dialect, Kölsch at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Romani, Balkan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romani, Baltic at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romani, Carpathian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romani, Finnish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romani, Sinte at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romani, Vlax at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Romani, Welsh at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Constitution of Kosovo, p. 8 Archived 11 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Romanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ "Româna". unilat.org (in Romanian). Latin Union. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- ^ a b L1: 119 million in the Russian Federation (of which c. 83 million in European Russia), 14.3 million in Ukraine, 6.67 million in Belarus, 0.67 million in Latvia, 0.38 million in Estonia, 0.38 million in Moldova. L1+L2: c. 100 million in European Russia, 39 million in Ukraine, 7 million in Belarus, 7 million in Poland, 2 million in Latvia, c. 2 million in the European portion of Kazakhstan, 1.8 million in Moldova, 1.1 million in Estonia. Russian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required).
- ^ mostly Northern Sami (sma), ca. 20,000 speakers; smaller communities of Lule Sami (smj, c. 2,000 speakers) and other variants. Northern Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Lule Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) Southern Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Kildin Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Skolt Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Inari Sami at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required).
- ^ AA. VV. Calendario Atlante De Agostini 2017, Novara, Istituto Geografico De Agostini, 2016, p. 230
- ^ Scots at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Gaelic, Scottish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Serbian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Sicilian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Silesian at Ethnologue (19th ed., 2016)

- ^ German dialect, Lower Silesian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Slovak at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Slovene at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Sorbian, Upper at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ GVG § 184 Satz 2; VwVfGBbg § 23 Abs. 5; SächsSorbG § 9, right to use Sorbian in communication with the authorities guaranteed for the "Sorbian settlement area" (Sorbisches Siedlungsgebiet, Lusatia).
- ^ Spanish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ German dialect, Swabian German at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ a b Swedish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ German dialect, Swiss German at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Tabassaran at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Tat at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Judeo-Tat at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) 2,000 speakers in the Russian Federation according to the 2010 census (including Judeo-Tat). About 28,000 speakers in Azerbaijan; most speakers live along or just north of the Caucasus ridge (and are thus technically in Europe), with some also settling just south of the Caucasus ridge, in the South Caucasus.
- ^ Tatar at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ c. 12 million in European Turkey, 0.6 million in Bulgaria, 0.6 million in Cyprus and Northern Cyprus; and 2,679,765 L1 speakers in other countries in Europe according to a Eurobarometer survey in 2012: https://languageknowledge.eu/languages/turkish
- ^ Udmurt at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Ukrainian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ German dialect, Upper Saxon German at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Russian Census 2010. Veps at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Venetian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ A motion to recognise Venetian as an official regional language has been approved by the Regional Council of Veneto in 2007. "Consiglio Regionale Veneto – Leggi Regionali". Consiglioveneto.it. Archived from the original on 24 July 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- ^ Võro at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Walloon at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Highest Alemannic dialects, Walser German at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Welsh at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Moribund German dialect spoken in Wilamowice, Poland. 70 speakers recorded in 2006. Wymysorys at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Yenish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Total population estimated at 1.5 million as of 1991, of which c. 40% in the Ukraine. Yiddish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Eastern Yiddish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required), Western Yiddish at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Abkhazia is a de facto state recognized by Russia and a handful of other states, but considered by Georgia to be ruling over a Georgian region
- ^ Abkhazian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Lewis, M. Paul, ed. (2009). "Ethnologue report for Turkey (Asia)". Ethnologue: Languages of the World. SIL International. Archived from the original on 7 July 2010. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ "Armenian 2011 census data, chapter 5" (PDF).
- ^ Note: de facto independent republic, Azerbaijan claims sovereignty over it.
- ^ "Ethno-Caucasus – Население Кавказа – Республика Абхазия – Население Абхазии".
- ^ Council of Europe (16 January 2014). "European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. Fourth periodical presented to the Secretary General of the Council of Europe in accordance with Article 15 of the Charter. CYPRUS" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Azeri community in Dagestan excluded
- ^ "UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in danger". www.unesco.org. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ^ a b "2014 Georgian census" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2017.
- ^ Censuses of Republic of Azerbaijan 1979, 1989, 1999, 2009Archived 30 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Cyprus" (PDF). Euromosaic III. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
- ^ "Ethnologue: Azerbaijan". Tedsnet.de. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ SIL Ethnologue gives estimates, broken down by dialect group, totalling 31 million, but with the caveat of "Very provisional figures for Northern Kurdish speaker population". Ethnologue estimates for dialect groups: Northern: 20.2M (undated; 15M in Turkey for 2009), Central: 6.75M (2009), Southern: 3M (2000), Laki: 1M (2000). The Swedish Nationalencyklopedin listed Kurdish in its "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), citing an estimate of 20.6 million native speakers.
- ^ http://armstat.am/file/article/sv_03_13a_520.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ^ a b "Laz". Ethnologue.
- ^ Thede Kahl (2006): The islamisation of the Meglen Vlachs (Megleno-Romanians): The village of Nânti (Nótia) and the "Nântinets" in present-day Turkey, Nationalities Papers, 34:01, p80-81: "Assuming that nearly the total population of Nânti emigrated, then the number of emigrants must have been around 4,000. If the reported number of people living there today is added, the whole Meglen Vlachs population is c. 5,000. Although that number is only a rough estimate and may be exaggerated by the individual interviewees, it might correspond to reality."
- ^ "Endangered Languages Project: Mingrelian".
- ^ Özkan, Hakan (2013). "The Pontic Greek spoken by Muslims in the villages of Beşköy in the province of present-day Trabzon". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies. 37 (1): 130–150. doi:10.1179/0307013112z.00000000023.
- ^ "2011 Armenian Census" (PDF).
- ^ a b c Падение статуса русского языка на постсоветском пространстве. Demoscope.ru. Archived from the original on 25 October 2016. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
- ^ a b c Русскоязычие распространено не только там, где живут русские. demoscope.ru. Archived from the original on 23 October 2016.
- ^ Στατιστική Υπηρεσία – Πληθυσμός και Κοινωνικές Συνθήκες – Απογραφή Πληθυσμού – Ανακοινώσεις – Αποτελέσματα Απογραφής Πληθυσμού, 2011 (in Greek). Demoscope.ru. Archived from the original on 7 May 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ^ "Endangered Languages Project: Svan".
- ^ John M. Clifton, Gabriela Deckinga, Laura Lucht, Calvin Tiessen, "Sociolinguistic Situation of the Tat and Mountain Jews in Azerbaijan," In Clifton, ed., Studies in Languages of Azerbaijan, vol. 2 (Azerbaijan & St Petersburg, Russia: Academy of Sciences of Azerbaijan & SIL International 2005). Page 3.
- ^ "Population enumerated by age, sex, language spoken and district (1.10.2011) (sheet D1A)". Population – Country of Birth, Citizenship Category, Country of Citizenship, Language, 2011. CYstat. June 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Census.XLS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ Cole, Jeffrey (2011), Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, p. 367, ISBN 978-1-59884-302-6
- ^ France: 4,000,000, Germany: 500k (2015), Spain: 200k UK: 159k (2011 census)
- ^ Arab diaspora, mostly in France, Italy, Spain, Germany, UK, Sweden, Belgium, Netherlands, Denmark, current size unknown due to the European migrant crisis of 2015–present.
- ^ Germany: 1,510k, France: 444k, Netherlands: 388k, Austria: 197k, Russia: 146k, UK: 99k, Switzerland: 44k, Sweden: 44.
- ^ See Turks in Europe: only counting recent (post-Ottoman era) immigration: Germany: 4,000,000, France: 1,000,000, UK: 500,000, Netherlands: 500,000, Austria: 400,000, Switzerland, Sweden and Russia: 200,000 each.
- ^ 830k in Russia (2010 census), 100k in Ukraine (SIL Ethnologue 2015).
- ^ 2,000,000 Armenians in Russia. France 750k, Ukraine 100k, Germany 100k, Greece 60-80k, Spain 40k, Belgium 30k, Czechia 12k, Sweden 12k, Bulgaria 10-22k, Belarus 8k, Austria 6k, Poland 3-50k, Hungary 3-30k, Netherlands 3-9k, Switzerland 3-5k, Cyprus 3k, Moldova 1-3k, UK 1-2k.
- ^ Germany: 541k
- ^ Kurdish population: mostly Kurds in Germany, Kurds in France, Kurds in Sweden.
- ^ Sylheti: 300k in the UK, Bengali: 221k in the UK.
- ^ see British Indian, Bangladeshi diaspora, Bengali diaspora.
- ^ 515k in Russia (2010 census)
- ^ [[Azerbaijani diaspora ]]: Russia 600k, Ukraine 45k, not counting 400,000 in Azerbajian's Quba-Khachmaz Region (Shabran District, Khachmaz District, Quba District, Qusar District, Siyazan District) technically in Europe (being north of the Caucasus watershed).
- ^ France: 500k
- ^ Kabyle people in France: 1,000,000.
- ^ Germany 120k, Russia: 70k, UK 66k, Spain 20k.
- ^ Overseas Chinese: France 700,000, UK: 500,000, Russia: 300,000, Italy: 300,000, Germany: 200,000, Spain: 100,000.
- ^ UK: 269k (2011 census).
- ^ Pakistani diaspora, the majority Pakistanis in the UK.
- ^ Russia: 274k (2010 census)
- ^ see Uzbeks in Russia.
- ^ UK: 76k, Sweden: 74k, Germany: 72k, France 40k.
- ^ Iranian diaspora: Germany: 100k, Sweden: 100k, UK: 50k, Russia: 50k, Netherlands: 35k, Denmark: 20k.
- ^ UK: 280k
- ^ see British Punjabis
- ^ UK: 213k
- ^ see Gujarati diaspora
- ^ UK: 101k, Germany: 35k, Switzerland: 22k.
- ^ Tamil diaspora: UK 300k, France 100k, Germany 50k, Switzerland 40k, Netherlands, 20k, Norway 10k.
- ^ UK: 86k, Sweden: 53k, Italy: 50k
- ^ Somali diaspora: UK: 114k, Sweden: 64k, Norway: 42k, Netherlands: 39k, Germany: 34k, Denmark: 21k, Finland: 19k.
External links
- Everson, Michael (2001). "The Alphabets of Europe". evertype.com. Retrieved 19 March 2010.
- Haarmann, Harald (2011). "Europe's Mosaic of Languages". Institute of European History. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- Reissmann, Stefan; Argador, Urion (2006). "Luingoi in Europa" (in Esperanto, English, and German). Reissmann & Argador. Archived from the original on 22 June 2009. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
- Map of Minorities & Regional and Minority Languages of Europe, Language Diversity (2017)
- Zikin, Mutur (2007). "Europako Mapa linguistikoa" (in Basque). muturzikin.com. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
