Portal:Myanmar

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar and also known as Burma (the official name until 1989), is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (formerly Rangoon).
Myanmar is a member of the East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the Commonwealth of Nations despite once being part of the British Empire. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The country is very rich in natural resources, such as jade, gems, oil, natural gas, teak and other minerals, as well as also endowed with renewable energy, having the highest solar power potential compared to other countries of the Great Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from instability, factional violence, corruption, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of colonial exploitation with little regard to human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (PPP) at US$221.5 billion. The income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the economy is controlled by cronies of the military junta. Myanmar is one of the least developed countries; as of 2020, according to the Human Development Index, it ranks 147 out of 189 countries in terms of human development, the lowest in Southeast Asia. Since 2021, more than 600,000 people were displaced across Myanmar due to the surge in violence post-coup, with more than 3 million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance. (Full article...)
Selected articles -
-
The National League for Democracy (Burmese: အမျိုးသား ဒီမိုကရေစီ အဖွဲ့ချုပ်, IPA: [ʔəmjóðá dìmòkəɹèsì ʔəpʰwḛdʑoʊʔ]; abbr. NLD; Burmese abbr. ဒီချုပ်) is a deregistered liberal democratic political party in Myanmar (Burma). It became the country's ruling party after a landslide victory in the 2015 general election but was overthrown in a military coup d'état in February 2021 following another landslide election victory in 2020.
Founded on 27 September 1988, the NLD has become one of the most influential parties in Myanmar's pro-democracy movement. Aung San Suu Kyi, the former State Counsellor of Myanmar, serves as its leader. The party won a substantial parliamentary majority in the 1990 Myanmar general election. However, the ruling military junta refused to recognise the result. On 6 May 2010, the party was declared illegal and ordered to be disbanded by the junta after refusing to register for the elections slated for November 2010. In November 2011, the NLD announced its intention to register as a political party to contest future elections, and Myanmar's Union Election Commission approved their application for registration on 13 December 2011. (Full article...) -
Hkakaborazi National Park is a national park in northern Myanmar with an area of 1,472 sq mi (3,810 km2). It was established in 1998.
It surrounds Hkakabo Razi, the highest mountain in the country.
It ranges in elevation from 2,950 to 18,730 ft (900 to 5,710 m) comprising evergreen forest and mixed deciduous forests in Nogmung Township, Kachin State. It is managed by the Nature and Wildlife Conservation Division.
It is contiguous with Bumhpa Bum Wildlife Sanctuary and Hukaung Valley Wildlife Sanctuary. These protected areas together with Hponkanrazi Wildlife Sanctuary comprise the largest continuous expanse of natural forest called the Northern Forest Complex stretching over an area of 11,624 sq mi (30,110 km2). Its objective is to conserve the biodiversity of the Ayeyarwady and Chindwin river basins. (Full article...) -
The Irrawaddy River (Burmese: ဧရာဝတီမြစ်, pronounced [ʔèjàwədì mjɪʔ], official romanisation: Ayeyarwady) is the largest river in Myanmar. Originating from the confluence of the N'mai and Mali rivers, it flows from north to south before emptying through the Irrawaddy Delta in the Ayeyarwady Region into the Andaman Sea. Its drainage basin of about 404,000 square kilometres (156,000 sq mi) covers 61% of the land area of Burma, and contains five of its largest cities.
As early as the sixth century, the river was used for trade and transport, and an extensive network of irrigation canals was developed to support agriculture. The river is still of great importance as the largest commercial waterway of Myanmar. It also provides important ecosystem services to different communities and economic sectors, including agriculture, fisheries, and tourism. (Full article...) -

The Thadingyut Festival (Burmese: သီတင်းကျွတ်ပွဲတော်), also known as the Lighting Festival of Myanmar, is held on the full moon day of the Burmese lunar month of Thadingyut. As a custom, it is held at the end of the Buddhist sabbath (Vassa) and is the second most popular festival in Myanmar after Thingyan Festival (New Year Water Festival). Thadingyut festival is the celebration to welcome the Buddha’s descent from the heaven after he preached the Abhidhamma to his mother, Maya, who was reborn in the heaven. (Full article...) -

The Royal Armed Forces (Burmese: တပ်မတော်, [taʔmədɔ̀]) were the armed forces of the Burmese monarchy from the 9th to 19th centuries. It refers to the military forces of the Pagan Kingdom, the Kingdom of Ava, the Hanthawaddy Kingdom, the Toungoo dynasty and the Konbaung dynasty in chronological order. The army was one of the major armed forces of Southeast Asia until it was defeated by the British over a six-decade span in the 19th century.
The army was organised into a small standing army of a few thousand, which defended the capital and the palace, and a much larger conscript-based wartime army. Conscription was based on the ahmudan system, which required local chiefs to supply their predetermined quota of men from their jurisdiction on the basis of population in times of war. The wartime army also consisted of elephantry, cavalry, artillery and naval units. (Full article...) -
The Burma Railway, also known as the Siam–Burma Railway, Thai–Burma Railway and similar names, or as the Death Railway, is a 415 km (258 mi) railway between Ban Pong, Thailand, and Thanbyuzayat, Burma (now called Myanmar). It was built from 1940 to 1943 by South East Asian civilians abducted and forced to work by the Japanese and a smaller group of captured Allied soldiers, to supply troops and weapons in the Burma campaign of World War II. It completed the rail link between Bangkok, Thailand, and Rangoon, Burma. The name used by the Japanese Government was Tai–Men Rensetsu Tetsudō (泰緬連接鉄道), which means Thailand-Burma-Link-Railway.
At least 250,000 Southeast Asian civilians were subjected to forced labour to ensure the construction of the Death Railway and more than 90,000 civilians died building it, as did around 12,000 Allied soldiers. The workers on the Thai side of the railway were Tamils, Malays, and fewer Chinese civilians from Malaya. Possibly over 345,000 died while working, with the death rate per month rivaling that of Auschwitz. (Full article...) -
The Kachin conflict or the Kachin War is one of the multiple conflicts which are collectively referred to as the internal conflict in Myanmar. Kachin insurgents have been fighting against the Tatmadaw (Myanmar Armed Forces) since 1961, with only one major ceasefire being brokered between them, which lasted from 1994 to 2011, a total of 17 years.
Since the resumption of hostilities in 2011, thousands of civilians have been killed, whilst over 100,000 more have been displaced. Widespread use of landmines, child soldiers, systematic rape and torture have been alleged by both sides. (Full article...) -
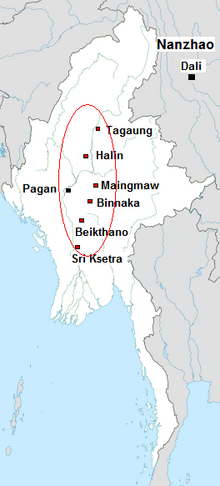
The Early Pagan Kingdom (Burmese: ခေတ်ဦး ပုဂံ ပြည်) was a city-state that existed in the first millennium CE before the emergence of the Pagan Empire in the mid 11th century. The Burmese chronicles state that the "kingdom" was founded in the second century CE. The seat of power of the small kingdom was first located at Arimaddana, Thiri Pyissaya, and Tampawaddy until 849 CE when it was moved to Pagan (Bagan).
Radiocarbon dating shows the earliest human settlement in the Pagan region dates only from the mid-7th century CE. It existed alongside Pyu city-states that dominated Upper Burma. The city-state of Pagan, according to mainstream scholarship, was founded in the mid 9th century by the Mranma of Nanzhao Kingdom. Burmans at Pagan expanded irrigation-based cultivation while borrowing extensively from the Pyus' predominantly Buddhist culture. It was one of many competing city-states in the Pyu realm until the late 10th century when the principality began absorbing its surrounding states. The expansion accelerated in the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, the first ever unification of the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. (Full article...) -
The Battle of the Sittang Bend and the Japanese Breakout across Pegu Yomas were linked Japanese military operations during the Burma Campaign, which took place nearly at the end of World War II. Surviving elements of the Imperial Japanese Army who had been driven into the Pegu Yoma attempted to break out eastwards in order to join other Japanese troops retreating from the British forces. The break-out was the objective of the Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army with support at first from the Thirty-Third Army and later the Fifteenth Army. As a preliminary, the Japanese Thirty-Third Army attacked Allied positions in the Sittang Bend, near the mouth of the river, to distract the Allies. The British had been alerted to the break-out attempt and it ended calamitously for the Japanese, who suffered many losses, with some formations being wiped out.
There were around 14,000 Japanese casualties, with well over half being killed, while British forces suffered only 95 killed and 322 wounded. The break-out attempt and the ensuing battle became the last significant land battle of the Western powers in the Second World War. (Full article...) -
Hkakabo Razi (Burmese: ခါကာဘိုရာဇီ, pronounced [kʰàkàbò ɹàzì]; simplified Chinese: 开加博峰; traditional Chinese: 開加博峯; pinyin: Kāijiābó Fēng) is believed to be Myanmar's highest mountain. The 5,881-meter (19,295 ft)-tall mountain is the highest mountain in Southeast Asia as well. It is located in the northern Myanmar state of Kachin in an outlying subrange of the Greater Himalayan mountain system near the border tripoint with India and China. Its highest status has recently been challenged by 5,870-meter (19,260 ft)-tall Gamlang Razi, located about 6.6 kilometers (4.1 mi) WSW on the Chinese border.
The peak is enclosed within Khakaborazi National Park. The park is entirely mountainous and is characterized by broad-leaved evergreen tropical rain forest at low altitudes, a sub-tropical temperate zone from 8,000 to 9,000 ft (2,400–2,700 m), then broad-leaved, semi-deciduous forest and finally needle-leaved evergreen, snow forest. Above 11,000 ft (3,400 m), the highest forest zone is alpine, different from the forest not only in kind but in history and origin. Still higher, around 15,000 ft (4,600 m), cold, barren, windswept terrain and permanent snow and glaciers dominate. At around 17,500 ft (5,300 m), there is a large ice cap with several outlet glaciers. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that one academic described the introduction of femboys to Myanmar as a tactic to achieve an "ideological revolution"?
- ... that former Burmese actress Honey Nway Oo turned rebel and took up arms against the military junta following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état?
- ... that the mission of the United Nations special envoy on Myanmar has been called a "diplomatic graveyard"?
- ... that Maung O, Prince of Salin, and his sister Nanmadaw Me Nu became de facto rulers of Burma when King Bagyidaw was suffering from depression?
- ... that as part of the coronation of Mindon Min, the square yuzana around the capital was designated a sanctuary?
- ... that the talabaw soup, which consists primarily of bamboo shoots, is the essential dish of Myanmar's Karen people, who use it to supplement rice?
- ... that the Burmese and South Korean first ladies held their first informal conversation 44 years after the establishment of bilateral relations between the two countries?
- ... that Rolling Stone named Mission of Burma's "Academy Fight Song" as one of the 100 greatest debut singles of all time?
Related portals and projects
General images -
-
Political Map of Burma (Myanmar) c. 1450 CE. (from History of Myanmar)
-
The shores of Irrawaddy River at Nyaung-U, Bagan (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
The restored Taungoo or Nyaungyan dynasty c. 1650 CE. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Salween river at Mae Sam Laep on the Thai-Myanmar border (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Former US President Barack Obama poses barefoot on the grounds of Shwedagon Pagoda, one of Myanmar's major Buddhist pilgrimage sites. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Hlei pyaingbwè - a Burmese regatta (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Mount Popa, a dormant volcano in the Central Lowlands (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Myinhkin thabin - equestrian sport (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Boxing match, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Portuguese ruler and soldiers mounting an Elephant. Philips, Jan Caspar (draughtsman and engraver) (from History of Myanmar)
-
19th-century funeral cart and spire, which would form part of the procession from the home to the place of cremation (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Protesters in Yangon carrying signs reading "Free Daw Aung San Suu Kyi" on 8 February 2021. (from History of Myanmar)
-
A group of Buddhist worshipers at Shwedagon Pagoda, an important religious site for Burmese Buddhists (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Aung San Suu Kyi addresses crowds at the NLD headquarters shortly after her release. (from History of Myanmar)
-
A theatrical performance of the Mon dance (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
A wide range of Burmese lacquerware from Bagan (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Two female musicians play the saung at a performance in Mandalay. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
British soldiers remove their shoes at the entrance of Shwedagon Pagoda. To the left, a sign reads "Foot wearing is strictly prohibited" in Burmese, English, Tamil, and Urdu. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Protesters in Yangon with a banner that reads non-violence: national movement in Burmese, in the background is Shwedagon Pagoda. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Pagan Kingdom during Narapatisithu's reign. Burmese chronicles also claim Kengtung and Chiang Mai. Core areas shown in darker yellow. Peripheral areas in light yellow. Pagan incorporated key ports of Lower Burma into its core administration by the 13th century. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Sculpture of Myanmar mythical lion (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Mountains near Pindaya on the Shan Plateau (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Grandfather Island, Dawei (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Recorder's Court on Sule Pagoda Road, with the Sule Pagoda at the far end, Rangoon, 1868. Photographer: J. Jackson. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Saint Mary's Cathedral in Downtown Yangon is the largest Roman Catholic cathedral in Burma. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
The paddle steamer Ramapoora (right) of the British India Steam Navigation Company on the Rangoon river having just arrived from Moulmein. 1895. Photographers: Watts and Skeen (from History of Myanmar)
-
Aerial view of a burned Rohingya village in Rakhine state, Myanmar, September 2017 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Jade Mine in Hpakant (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
A bull fight, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
British soldiers dismantling cannons belonging to King Thibaw's forces, Third Anglo-Burmese War, Ava, 27 November 1885. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Myanmar (Burma) map of Köppen climate classification (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
A wedding procession, with the groom and bride dressed in traditional Burmese wedding clothes, reminiscent of royal attire (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
British soldiers on patrol in the ruins of the Burmese town of Bahe during the advance on Mandalay, January 1945. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Temples at Mrauk U, was the capital of the Mrauk U Kingdom, which ruled over what is now Rakhine State. (from History of Myanmar)
-
A large fracture on the Mingun Pahtodawgyi caused by the 1839 Ava earthquake. (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Vegetable stall on the roadside at the Madras Lancer Lines, Mandalay, January 1886. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
Major topics
Categories
More topics
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portals |

![Image 1 The National League for Democracy (Burmese: အမျိုးသား ဒီမိုကရေစီ အဖွဲ့ချုပ်, IPA: [ʔəmjóðá dìmòkəɹèsì ʔəpʰwḛdʑoʊʔ]; abbr. NLD; Burmese abbr. ဒီချုပ်) is a deregistered liberal democratic political party in Myanmar (Burma). It became the country's ruling party after a landslide victory in the 2015 general election but was overthrown in a military coup d'état in February 2021 following another landslide election victory in 2020. Founded on 27 September 1988, the NLD has become one of the most influential parties in Myanmar's pro-democracy movement. Aung San Suu Kyi, the former State Counsellor of Myanmar, serves as its leader. The party won a substantial parliamentary majority in the 1990 Myanmar general election. However, the ruling military junta refused to recognise the result. On 6 May 2010, the party was declared illegal and ordered to be disbanded by the junta after refusing to register for the elections slated for November 2010. In November 2011, the NLD announced its intention to register as a political party to contest future elections, and Myanmar's Union Election Commission approved their application for registration on 13 December 2011. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)