Tabuaeran
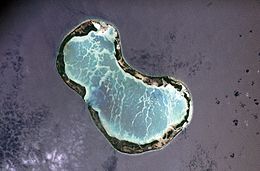 NASA image of Tabuaeran in 2006, with the man-made 'English Channel' cut at left | |
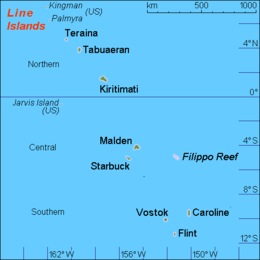 Map of the Line Islands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | North Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 3°51′36″N 159°21′52″W / 3.86000°N 159.36444°W |
| Archipelago | Line Islands |
| Area | 33.7 km2 (13.0 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 3 m (10 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Island council | Tabuaeran |
| Largest settlement | Tereitaki |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 1,990 (2020 census) |
| Pop. density | 68.7/km2 (177.9/sq mi) |
| Languages | Gilbertese |
| Ethnic groups | I-Kiribati |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |

Tabuaeran, also known as Fanning Island,[1] is an atoll that is part of the Line Islands of the central Pacific Ocean and part of the island nation of Kiribati. The land area is 33.73 square kilometres (13.02 square miles), and the population in 2015 was 2,315.[2] The maximum elevation is about 3 m (10 ft) above high tide.
The lagoon has an area of 110 square kilometres (42 square miles). The deepest water in the lagoon is about 15 metres (49 feet), but most of it is very shallow.[2]
History
Tabuaeran was first inhabited by Polynesian people. Archaeological evidence points to a single large village being maintained for several hundred years on the west side of the atoll with other scattered production and agricultural sites across the atoll.[3] Radiometric dates range from 1100 AD to 1425 AD (Cal. 810 ±50 BP and 620 ± 60 BP at 2 sigma). Continuous habitation is likely as stratigraphic cultural layers are uninterrupted and quite deep.[4] Some archaeologists have argued that Tabuaeran and Kiritimati were one community living across a matched set of islands as despite their relative proximity, their climates and resources differ wildly covering what would otherwise be resource shortages. While this hypothesis is still being tested, the period of human habitation on these two islands does match up.[4] Geochemical analysis of stone tools provides a clear window into trade networks that existed throughout Polynesia and in the case of Tabuaeran, a positive match was made with a quarry located in Eiao, Marquesas.[5]
The first white man to sight Tabuaeran was American captain Edmund Fanning of the American ship Betsy on June 11, 1798; it was named for him.[6] At the time, the atoll was uninhabited and, like all of the Line Islands, had no truly native population. After Fanning, it was visited by whalers of several nationalities. The whaler Harriet had wrecked there in late 1831 or early 1832.
By 1854, Captain Henry English[7] and 150 labourers from Manihiki settled, and began producing coconut oil for export. He put the island under British protection when Captain W. H. Morshead arrived on HMS Dido on 16 October 1855.[8]
In about 1857 a whaling ship put ashore William Greig who carried out planting of coconut trees to expand the production of copra, and who also began planting coconut trees on Washington Island.[9] Eventually the sons of Greig owned the plantation with Father Emmanuel Rougier until he sold his interest to the Fanning Island Limited, and started a coconut plantation on Christmas Island.[9]
Captain William Wiseman of HMS Caroline formally annexed Fanning to Great Britain on 15 March 1888.
A deep opening, thereafter called the English Channel, was blasted on the west side of the atoll. Tabuaeran hosted a station on the Canada-to-Australia section of the All Red Line telegraph cable system, beginning in 1902. Fanning Island Post Office opened on 29 November 1902.[10] During World War I, the cable station was visited in September 1914 by the Imperial German Navy light cruiser SMS Nürnberg and was severely damaged when a landing force went ashore to put the station out of action.[11][12] In 1939 the atoll was incorporated into the British colony of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands. In 1979, it gained independence, becoming part of the Republic of Kiribati.
An airfield was constructed on Napari (Napali) islet when the University of Hawaii operated a tide monitoring station on the atoll. The station and the airfield closed in 1981. The airfield reopened in 2016, with regular domestic flights to Kiritimati.[2]
Present
The administrative centre of the atoll is Paelau, on the west side.
Tabuaeran had a population of 1,960 at the 2010 census,[2] principally Gilbertese settlers brought from the main Kiribati archipelago by Fanning Island Plantations, Ltd., to work in the copra industry.
The population declined from 2,539 at the 2005 census following the closure of the secondary school (since reopened), cessation of visits by Norwegian Cruise Line (NCL), and reduced operations by Atoll Seaweed Company.[2]
Eight villages are listed in the 2015 census:
| No. | Village | Population (2005 Census) |
Population (2010 Census) |
Population (2015 Census) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Napari (Napali) | 194 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Tereitaki | 438 | 346 | 505 |
| 3 | Betania | 260 | 175 | 203 |
| 4 | Paelau (Napia, English Harbour) | 250 | 200 | 257 |
| 5 | Aontenaa (Aontena) | 177 | 190 | 259 |
| 6 | Terine (Tenenebo) | 461 | 453 | 406 |
| 7 | Tereitannano (Tereitaki) | 249 | 168 | 241 |
| 8 | Aramari | 358 | 244 | 274 |
| 9 | Mwanuku (Manuku or Eten) | 152 | 184 | 170 |
| Tabuaeran | 2,539 | 1,960 | 2,315 |
The main diet is imported rice and tinned meats, supplemented by local foods: reef fish and shellfish, babai (Cyrtosperma merkusii), coconut, pigs, chickens, and seaweed (limu).[2]
Major exports are copra and hand crafts (including cowrie shell, shark tooth knives, and Kiribati stamps). An Australian supply ship calls two or three times a year. The sailing vessel Kwai also stops on the island.[13]
The main health centre is located at Paelau in the west, with additional clinics on Napari (Napali) islet in the north and Kimarimari in the south.[2] Helpful organizations with concerns for the local schools, churches and healthcare needs are Pacific CARE Missions and Pacific Island Aid.
Ecology
Overfishing and pollution have impacted on the ocean surrounding the island. In the ocean surrounding uninhabited islands of the Northern Line Islands, sharks comprised 74% of the top predator biomass (329 g m-2) at Kingman Reef and 57% at Palmyra Atoll (97 g m-2), whereas low shark numbers have been observed at Tabuaeran and Kiritimati.[14]
Cruising
Since 2010, the Holland America cruise ships Rotterdam, Westerdam, Eurodam, and Volendam have scheduled visits to Tabuaeran. Seaborne Cruiseline has scheduled visits since 2012. The visits help the island regain income lost since Norwegian Cruise Line ceased weekly visits in 2007.
Until 2007, NCL ships based in Honolulu visited Tabuaeran weekly, partly to avoid U.S. port charges for foreign-flagged ships (see Passenger Vessel Services Act of 1886). NCL ceased visits after introducing US-flagged ships, changing cruise schedules, and eliminating Tabuaeran as a port of call.[15]
Education
The island has three primary schools, one junior secondary school, and one senior secondary school, Meleangi Tabai High School.[2] The government has previously sought to re-open the high school campus on Kiritimati.[16]
Culture
Tabuaeran features in John Updike's short story "The Blessed Man of Boston, My Grandmother's Thimble, and Fanning Island." It is collected in his books Pigeon Feathers and Other Stories and The Early Stories.
See also
References
- ^ Both Gilbertese and English names are recognised by the Constitution of Kiribati
- ^ a b c d e f g h "21. Tabuaeran" (PDF). Office of Te Beretitent - Republic of Kiribati Island Report Series. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 28 April 2015.
- ^ Emory, P.K. (1934). "Archaeology of the Pacific Equatorial Islands". Bernice P. Bishop Museum Bulletin. 123.
- ^ a b Di Piazzi, Anne (June 2001). "An Island for Gardens, and Island for Birds and Voyaging: A Settlement Pattern for Kiritimati and Tabuaeran , Two "Mystery Islands" in the Northern Lines, Republic of Kiribati". The Journal of the Polynesian Society. 110 (2): 149–170. JSTOR 20706989.
- ^ Di Piazza, Anne (October 2001). "Voyaging and Basalt Exchange in the Phoenix and Line Archipelagoes: The Viewpoint from Three Mystery Islands". Archaeology in Oceania. 36 (3): 146–152. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4453.2001.tb00488.x. JSTOR 40387203.
- ^ Bryan, E.H. American Polynesia and the Hawaiian Chain. Honolulu, Hawaii: Tongg Publishing Company, 1941 pages 141-144.
- ^ Harvest, of Nantucket, April 22, 1854, Nantucket Historical Association #345.
- ^ Kenneth J. Panton (2015). Historical Dictionary of the British Empire. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 181.
- ^ a b "Islands for Sale – Romantic History of Fanning and Washington". V(12) Pacific Islands Monthly. 23 July 1935. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ Premier Postal History. "Post Office List". Premier Postal Auctions. Retrieved 5 July 2013.
- ^ Barty-King, Girdle Around the World
- ^ R Bruce Scott: Gentlemen on Imperial Service
- ^ SAILING SHIP KWAI
- ^ Stuart A. Sandin; et al. (27 February 2008). "Baselines and Degradation of Coral Reefs in the Northern Line Islands". PLOS ONE. 3 (2). 3 (2) PLoS ONE: e1548. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.1548S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001548. PMC 2244711. PMID 18301734.
- ^ NCL Announces Jade, Jewel And Gem For Largest Ever European Deployment
- ^ "VSA Assignment Description Assignment title English Language Trainer (of Trainers/ Teachers) Country Kiribati Archived 2018-07-06 at the Wayback Machine." Volunteer Service Abroad (Te Tūao Tāwāhi). Retrieved on 6 July 2018. p. 7.