Mentawai Islands Regency: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.6.2) (Balon Greyjoy) |
||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
The Mentawai Islands lie above the [[Sunda megathrust]], a seismically active zone responsible for many great [[earthquake]]s. This megathrust runs along the southwestern side of [[Sumatra]] island, forming the interface between the [[Eurasian Plate]] and [[Indo-Australian Plate]]. |
The Mentawai Islands lie above the [[Sunda megathrust]], a seismically active zone responsible for many great [[earthquake]]s. This megathrust runs along the southwestern side of [[Sumatra]] island, forming the interface between the [[Eurasian Plate]] and [[Indo-Australian Plate]]. |
||
Earthquake and [[tsunami]] activity has been high since the [[2004 Indian Ocean earthquake]]. In 1833, the region was hit with an [[1833 Sumatra earthquake|earthquake]], possibly similar in size to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.drgeorgepc.com/Tsunami1833Indonesia.html|title=INDONESIA - THE GREAT EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI OF 1833 OFF THE COAST OF CENTRAL SUMATRA - Dr. George Pararas-Carayannis|author=|date=|website=www.DrGeorgePC.com|access-date=May 3, 2017}}</ref> another large earthquake struck in [[1797 Sumatra earthquake|1797]]. On October 25, 2010, an earthquake in southern Sumatra led to a deadly tsunami that devastated villages in [[South Pagai|South]] and [[North Pagai]].<ref Name="politiktimes">{{cite web |
Earthquake and [[tsunami]] activity has been high since the [[2004 Indian Ocean earthquake]]. In 1833, the region was hit with an [[1833 Sumatra earthquake|earthquake]], possibly similar in size to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake;<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.drgeorgepc.com/Tsunami1833Indonesia.html|title=INDONESIA - THE GREAT EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI OF 1833 OFF THE COAST OF CENTRAL SUMATRA - Dr. George Pararas-Carayannis|author=|date=|website=www.DrGeorgePC.com|access-date=May 3, 2017}}</ref> another large earthquake struck in [[1797 Sumatra earthquake|1797]]. On October 25, 2010, an earthquake in southern Sumatra led to a deadly tsunami that devastated villages in [[South Pagai|South]] and [[North Pagai]].<ref Name="politiktimes">{{cite web| last =| first =| authorlink =| coauthors =| title =Indonesia Earthquake and Tsunami Kill 113, Merapi Volcano Eruptions Hours Later| work =News article| publisher =[[politiktimes.com]]| date =October 26, 2010| url =http://politiktimes.com/top-news/3-international-news/473-indonesia-earthquake-and-tsunami-kill-113-merapi-volcano-eruptions-hours-later.html| doi =| access-date =October 26, 2010| deadurl =yes| archiveurl =https://web.archive.org/web/20101105162346/http://www.politiktimes.com/top-news/3-international-news/473-indonesia-earthquake-and-tsunami-kill-113-merapi-volcano-eruptions-hours-later.html| archivedate =November 5, 2010| df =}}</ref> On March 3, 2016, an earthquake of 7.8 magnitude occurred off the Indian Ocean, a few hundred kilometres from Mentawai islands, as a result of strike-slip faulting within the oceanic lithosphere of the Indo-Australia plate.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us10004u1y#general_region|title=M7.8 – Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia|access-date=March 2, 2016}}</ref> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 19:20, 22 January 2018
Mentawai Islands Regency
(Kabupaten Kepulauan Mentawai) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates: 2°11′S 99°39′E / 2.183°S 99.650°E | |
| Country | Indonesia |
| Province | West Sumatra |
| Capital | Tua Pejat |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Yudas Sabaggalet |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,011.35 km2 (2,321.00 sq mi) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 76,421 |
| • Density | 13/km2 (33/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (WIB) |
| Area code | +62 759 |
| Website | www |
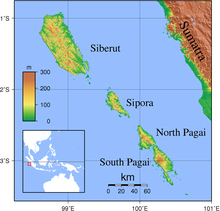
The Mentawai Islands are a chain of about seventy islands and islets approximately 150 kilometres (93 miles) off the western coast of Sumatra in Indonesia. Siberut at 4,030 square kilometres (1,556 square miles) is the largest of the islands. The other major islands are Sipura, North Pagai (Pagai Utara) and South Pagai (Pagai Selatan). The islands lie off the Sumatran coast, across the Mentawai Strait. The indigenous inhabitants of the islands are known as the Mentawai people. The Mentawai Islands have become a noted destination for surfing.[1]
Administration


The Mentawai Islands have been administered as a regency within the West Sumatra (Sumatera Barat) province since 1999. The regency seat is Tua Pejat, on the island of Sipora. Padang, the capital of the province, lies on the Sumatran mainland opposite Siberut. The regency is divided into ten districts (kecamatan), tabulated below from south to north with their 2010 census populations.[2]
- South Pagai (8,782)
- Sikakap (9,531)
- North Pagai (5,212)
- South Sipora (8,460)
- North Sipora (9,097)
- South Siberut (8,446)
- South West Siberut (6,069)
- Middle Siberut (6,069)
- North Siberut (7,774)
- West Siberut (6,733)
Ecology

The islands have been separated from Sumatra since the mid-Pleistocene period, which has allowed at least twenty endemic species to develop amongst its flora and fauna. This includes six endemic primates: the Kloss's gibbon (Hylobates klossii), Mentawai macaque (Macaca pagensis), Siberut macaque (Macaca siberu), Mentawai langur (Presbytis potenziani), Siberut langur (Presbytis siberu), and pig-tailed langur (Simias concolor). They are highly endangered due to logging, unsustainable hunting, and conversion of rainforest to palm oil plantations.[3] Some areas of the Mentawai Islands rainforest ecoregion are protected, such as the Siberut National Park. Red junglefowl, the Asian palm civet and crab-eating macaque are also native.[4]
Seismic activity

The Mentawai Islands lie above the Sunda megathrust, a seismically active zone responsible for many great earthquakes. This megathrust runs along the southwestern side of Sumatra island, forming the interface between the Eurasian Plate and Indo-Australian Plate.
Earthquake and tsunami activity has been high since the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. In 1833, the region was hit with an earthquake, possibly similar in size to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake;[5] another large earthquake struck in 1797. On October 25, 2010, an earthquake in southern Sumatra led to a deadly tsunami that devastated villages in South and North Pagai.[6] On March 3, 2016, an earthquake of 7.8 magnitude occurred off the Indian Ocean, a few hundred kilometres from Mentawai islands, as a result of strike-slip faulting within the oceanic lithosphere of the Indo-Australia plate.[7]
See also
- Mentawai ethnic group
Notes
- ^ "SURFAID". SURFAID. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ Whittaker, D. 2006. A conservation action plan for the Mentawai primates. Primate Conservation 20: 95–105.
- ^ "Mentawai Islands rain forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- ^ "INDONESIA - THE GREAT EARTHQUAKE AND TSUNAMI OF 1833 OFF THE COAST OF CENTRAL SUMATRA - Dr. George Pararas-Carayannis". www.DrGeorgePC.com. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ "Indonesia Earthquake and Tsunami Kill 113, Merapi Volcano Eruptions Hours Later". News article. politiktimes.com. October 26, 2010. Archived from the original on November 5, 2010. Retrieved October 26, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "M7.8 – Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia". Retrieved March 2, 2016.


