Next Portuguese legislative election
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
230 seats in the Assembly of the Republic 116 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Next Portuguese legislative election will take place on or before 8 October 2028 to elect members of the Assembly of the Republic to the 17th Legislature of Portugal. All 230 seats to the Assembly of the Republic will be at stake.
Due to the unstable situation of the minority government led by Luís Montenegro, the risk of a snap election well before the end of the current Parliament, in 2028, is very strong.[1]
Background
The Democratic Alliance (AD), composed by Social Democratic Party (PSD), CDS – People's Party (CDS–PP) and the People's Monarchist Party (PPM), led by PSD leader Luís Montenegro, won by a very narrow margin the 2024 legislative election with almost 29 percent of the votes and 80 seats in the 230 seat Assembly of the Republic. The Socialist Party (PS), in power between 2015 and 2024 and led by Pedro Nuno Santos, in the aftermath of the resignation of then Prime Minister António Costa due to an investigation around alleged corruption involving the award of contracts for lithium and hydrogen businesses,[2] suffered a big decrease in support winning 28 percent of the votes and 78 seats. The populist/far-right party Chega (CH) surged in the elections, gathering 18 percent of the votes and 50 seats in Parliament, the best result for third party in decades and becoming kingmaker.[3] The Liberal Initiative (IL) was able to hold on to their eight seats and gather five percent of the votes. The left-wing/far-left parties, the Portuguese Communist Party (PCP) and the Left Bloc (BE), achieved, again, disappointing results with BE holding on to their five seats and four percent of the votes, while the Communists' alliance got their worst result ever with just three percent of the votes and four seats. LIVRE nearly surpassed PCP by gathering also three precent of the votes and four seats. People Animals Nature (PAN) was able to win just one seat.[4]
Eleven days after election day, on 21 March 2024, Luis Montenegro was asked by President of the Republic Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa to form a government, a minority one in this case.[5] The new government was sworn into office on 2 April 2024.[5]
Politics of Portugal
The President of Portugal has the power to dissolve the Assembly of the Republic by his/her own will. Unlike in other countries, the President can refuse to dissolve the parliament at the request of the Prime Minister or the Assembly of the Republic and all the parties represented in Parliament. If the Prime Minister resigns, the President can appoint a new Prime Minister after listening to all the parties represented in Parliament and then the government programme must be subject to discussion by the Assembly of the Republic, whose members of parliament may present a motion to reject the upcoming government, or dissolve Parliament and call new elections.
Date
According to the Portuguese Constitution, an election must be called between 14 September and 14 October of the year that the legislature ends. The election is called by the President of Portugal but is not called at the request of the Prime Minister; however, the President must listen to all of the parties represented in Parliament and the election day must be announced at least 60 days before the election.[6] If an election is called during an ongoing legislature (dissolution of parliament) it must be held at least after 55 days. Election day is the same in all multi-seats constituencies, and should fall on a Sunday or national holiday. The next legislative election must, therefore, take place no later than 8 October 2028.[7]
Leadership changes and challenges
Liberal Initiative
On 8 April 2024, former 2021 Presidential candidate Tiago Mayan Gonçalves, announced a manifesto called "United by liberalism" and said he will be a candidate for the party's leadership when a ballot arrives, thus challenging incumbent leader Rui Rocha.[8] The party's next leadership convention is schedule for 5, 6 and 7 July 2024 in Santa Maria da Feira.[9]
Electoral system
The Assembly of the Republic has 230 members elected to four-year terms. Governments do not require absolute majority support of the Assembly to hold office, as even if the number of opposers of government is larger than that of the supporters, the number of opposers still needs to be equal or greater than 116 (absolute majority) for both the Government's Programme to be rejected or for a motion of no confidence to be approved.[10]
The number of seats assigned to each district depends on the district magnitude.[11] The use of the d'Hondt method makes for a higher effective threshold than certain other allocation methods such as the Hare quota or Sainte-Laguë method, which are more generous to small parties.[12]
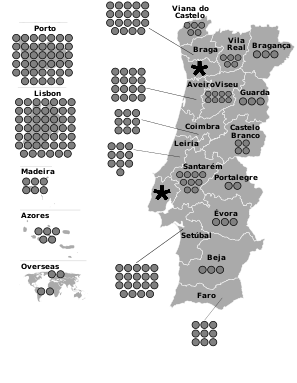
The distribution of MPs by electoral district for the 2024 legislative election was the following:[13]
| District | Number of MPs | Map |
|---|---|---|
| Lisbon | 48 | 
|
| Porto | 40 | |
| Braga and Setúbal | 19 | |
| Aveiro | 16 | |
| Leiria | 10 | |
| Coimbra, Faro and Santarém | 9 | |
| Viseu | 8 | |
| Madeira | 6 | |
| Azores, Viana do Castelo and Vila Real | 5 | |
| Castelo Branco | 4 | |
| Beja, Bragança, Évora and Guarda | 3 | |
| Portalegre, Europe and Outside Europe | 2 |
Parties
The table below lists parties currently represented in the Assembly of the Republic.
Opinion polling
See also
Notes
- ^ As leader of the Social Democratic Party (PSD).
- ^ a b The Social Democratic Party (PPD/PSD), the CDS - People's Party (CDS-PP) and the People's Monarchist Party (PPM) contested the 2024 election in a coalition called Democratic Alliance (AD) and won a combined 28.8% of the vote and elected 80 MPs to parliament. 78 of the MPs elected in 2024 are from PPD/PSD, while CDS-PP elected 2. PPM elected zero.
- ^ a b The Portuguese Communist Party (PCP) and the Ecologist Party "The Greens" (PEV) contested the 2024 election in a coalition called Unitary Democratic Coalition (CDU) and won a combined 3.2% of the vote and elected 4 MPs to parliament. The 4 MPs elected in 2024 are all from PCP. PEV elected zero.
- ^ LIVRE has no formal single leader; the party has a 15-member leadership committee of which Rui Tavares and Teresa Mota serve as spokespersons.
- ^ Some sources state that People Animals Nature (PAN) is neither on the left nor the right.[14]
References
- ^ "Tomadas de posse, eleições e risco de dissolução marcam o calendário político de Montenegro". ECO (in Portuguese). 22 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2023.
- ^ "António Costa demite-se: "Obviamente"". CNN Portugal (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 12 November 2023. Retrieved 7 November 2023.
- ^ "Chega é um dos grandes vencedores destas eleições". RTP. 11 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Diário da República, 1.ª série, n.º 59-A/2024". diariodarepublica.pt. Retrieved 23 March 2024.
- ^ a b "Portugal's centre-right leader Luis Montenegro appointed prime minister". France 24. 21 March 2024. Archived from the original on 21 March 2024. Retrieved 21 March 2024.
- ^ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). web.archive.org. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "Electoral law to the Assembly of the Republic" (PDF).
- ^ "Tiago Mayan pronto para encabeçar candidatura à liderança da IL quer refundar partido". ECO (in Portuguese). 8 April 2024. Retrieved 16 December 2023.
- ^ "Convenção Nacional da Iniciativa Liberal agendada para 5, 6 e 7 de julho". Expresso (in Portuguese). 8 April 2024. Retrieved 8 April 2024.
- ^ "Constitution of the Portuguese Republic" (PDF).
- ^ "Effective threshold in electoral systems". Trinity College, Dublin. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ Gallagher, Michael (1992). "Comparing Proportional Representation Electoral Systems: Quotas, Thresholds, Paradoxes and Majorities" (PDF).
- ^ "Mapa Oficial n.º 1-A/2024" (PDF). CNE – Comissão Nacional de Eleições. 16 January 2024. Retrieved 16 January 2024.
- ^ Martins, Paula (25 January 2022). "The politics of Portugal – who are the parties?". Reuters. Archived from the original on 18 November 2022. Retrieved 7 February 2022.